AP U.S Government & Politics
Unit 1
1.2 & 1.3
Anti-Federalists
Opposed the Constitution
George Mason & Samuel Adams
Brutus Papers
Small farmers, shopkeepers, laborers
Weak national government
Direct election of officials
Shorter terms
Rule by the common man
Strengthened protections for individual liberties
They are the reason why we have the Bill of Rights in the Constitution
Federalists
Supported the Constitution
Didn’t need a Bill of Rights
James Madison, Alexander Hamilton, and John Jay
Federalist Papers
Large landowners, wealthy merchants, professionals
Weaker state governments
Strong national government
Indirect election of officials
Longer terms
Government by the elite
Expected a few violations of individual liberties
Essential Vocabulary
Participatory Democracy: Emphasizes broad participation in politics and civil society
Pluralist Democracy: Recognizes group-based activism by nongovernmental interests striving for impact on political decision-making
Elite Democracy: which emphasizes limited participation in politics and civil society
1.7 & 1.8
Essential Vocabulary
10th Amendment: “Powers not delegated to the United States by the Constitution, nor prohibited by it to the states, are reserved to the States respectively, or to the people.”
Federalism: A government in which authority is divided between two sovereign levels of government: aka the federal and state governments.
Government Powers Under U.S. Federalism:
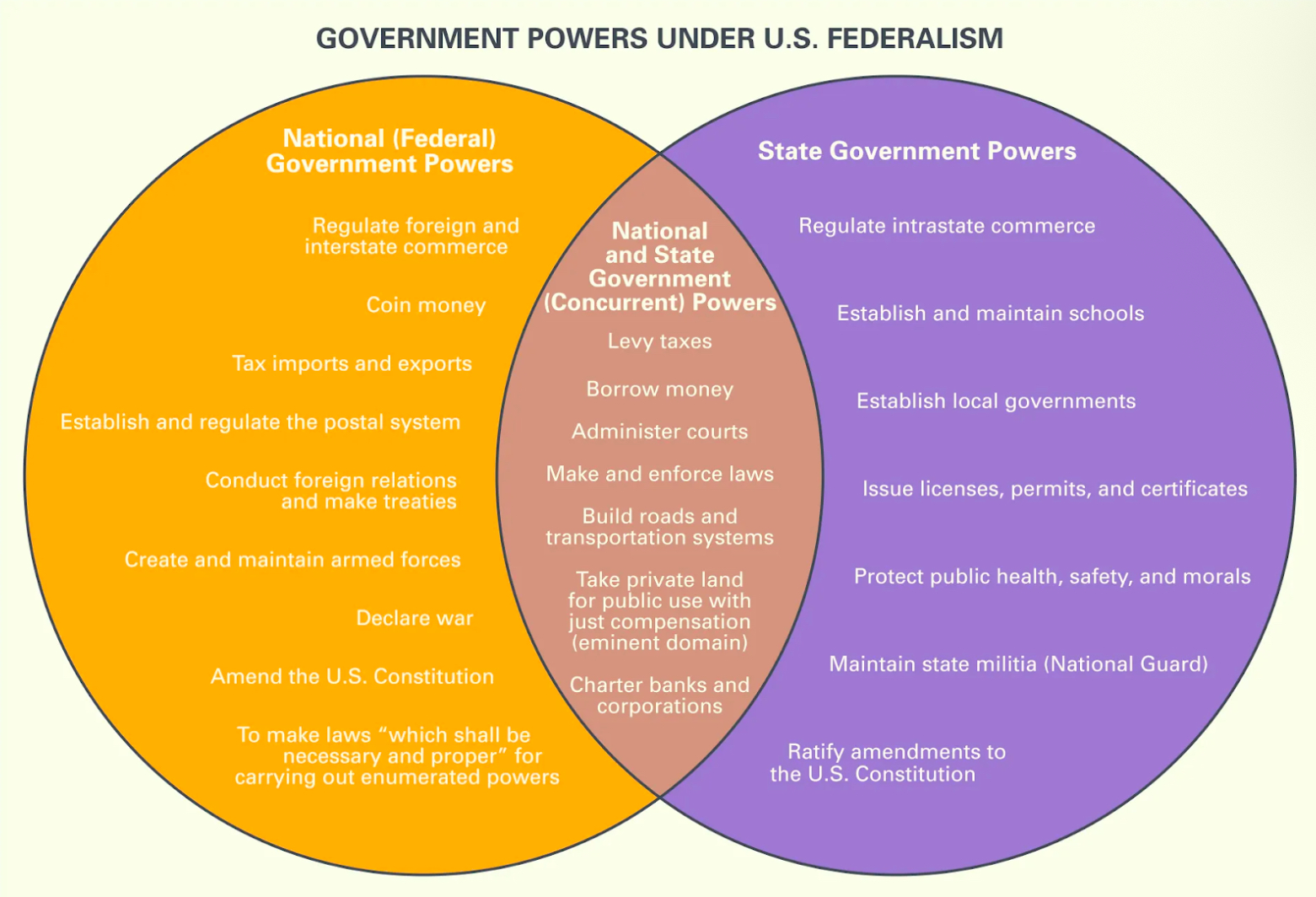
Constitutional Clauses
Necessary and Proper Clause (Elastic Clause) [Article I]:
Allows Congress to pass laws to carry out its “implied” powers, but Supreme Court interpretations can influence the extent of these powers.
Commerce Clause [Article I]:
Allows the national government to regulate interstate commerce, but Supreme Court interpretations can influence the extent of this power.
Supremacy Clause [Article VI]:
Laws of the United States shall be the supreme law of the land, but Supreme Court interpretations may affect when specific actions exceed this constitutional power.
Due Process & Equal Protection Clauses [14th Amendment]:
The national government has the power to enforce protections for any person against the states, but Supreme Court interpretations can influence the extent of those protections.
Supreme Court Cases
McCulloh v. Maryland(1819):
Federal Bank was on state property and not registered with the state
This bank was then taxed by the state, disrupting the federal government's operations.
The Supreme Court ruled that the state government cannot disrupt the operations of the federal government by taxing them in such a manner.
It was ruled that federal decisions and actions are supreme over state decisions.
Federal laws override state laws.
U.S. v. Lopez(1995):
The student decides to carry a gun to school. He is arrested. State charges dropped, federal charges gained because federal law against guns in schools was broken.
Federal law is questioned because gun rights are states’ rights
The federal government brought up the commerce clause to defend the Gun Free Schools Act
Federal Government Arguments:
A state with guns in schools can cause gun violence, which can direct people away from that state, which negatively affects trade.
Arguments of the federal government:
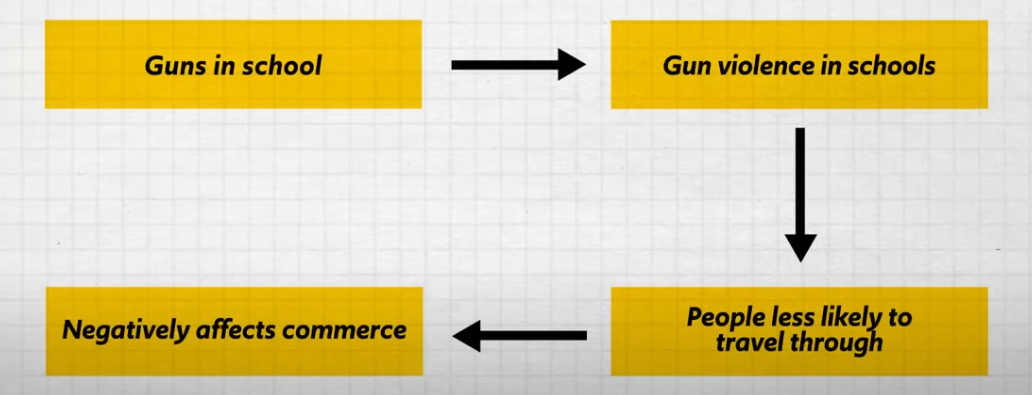
Lopez's Arguments:
Gun regulation on school property is a power specifically reserved for the states.
The connection between the commerce clause and gun violence is weak at best, tyrannical federal overreach at worst.
Supreme Court sides with Lopez
Unit 2
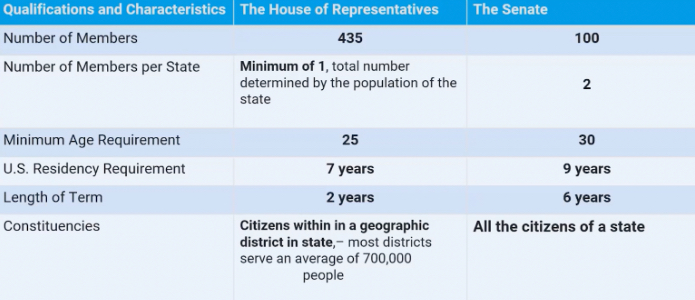
Formality in the House of Representatives
Debate must be limited
Each member can speak for only one hour that time can be shortened
Members can only offer amendments to a bill if it is germane(specifically related to the bill)
Speaker of the House (or someone the Speaker appoints) controls who speaks
Rules committee can speed up, slow down, or even “kill” a bill before it gets to the floor
Rules committee assigns every bill to the appropriate standing committee, schedules bills for debate and determines when voting on a bill will take place
Senate Formalities
Less centralized than the House
Does not have strict hierarchy like the House
Senators can speak as long as they want
Filibuster = a senator can speak long enough for the deadline to pass or get the opposition to give in
Coalitions
Caucus/conference = members of each house who belong to the same party
Independent members can shoose which conference they want to associate with
Sub groups will also form
Bipartisan = groups that are made of members of both parties
Member states with similar interest work together
Farming, fishing, oil production, etc.
Members from different states may work together for a common cause
List of enumerated (delegated) powers
Taxation
Creation of a military
Ability to declare war
Establish a court system
Establish a postal system
Create money
Regulated commerce
Regulate immigration/naturalization
Powers of impeachment
House brings on charges
Senate tries the case
Power of the Purse (delegated power)
Congress may raise money and spend money on behalf of the people
Congress must pass a budget for the government
Implied powers of Congress
Necessary and proper clause!
Examples:
National Bank
Draft
IRS
National Minimum Wage
National Medicare Care
2.3
Ideology: Beliefs
Gridlock: When politics get so divided, it is hard to pass laws
Gerrymandering: Redistricting to give a political party an advantage
Racial Gerrymandering: Redistricting based on race
Delegate Model
Believes he or she must vote with the will of the people
Believes he or she is there to represent the people’s beliefs and desires, not their own
Trustee Model
Politico Model
2.4 + 2.5
Formal Powers of the President
Commander in Chief of the Army & Navy
Grant pardons (except in cases of impeachment)
Make treaties
Appointment of ambassadors, judges, etc.
Must be approved by the Senate
May fill vacancies in the Senate during recess if needed
Veto legislation from Congress
Pocket veto
Informal (Implied) Powers of the President
Foreign policy
President has the ability to influence relationships with other countries
Bargaining & persuasion
Social media use?
Executive orders
Can use these to bypass Congress and make laws by himself
Executive agreements
Agreements w/ other countries even though Congress does not approve
Signing statements
President’s way of expressing his concerns over a passed law
Executive privilege
Do not have to tell everything to the public
Can’t hide criminal information
Checks and Balances in Congress
Senate = power of advice and consent
Presidential appointments must be approved by the Senate
Presidential appointments
Ambassadors to other nations
Approved by Senate
White House Staff
Presidential Cabinet
Approved by Senate
Judges to Federal Courts
This is hotly contested
Provides a long lasting influence for the President
2.7
Bully Pulpit: President uses his position to shape public opinion and promote their political platform.
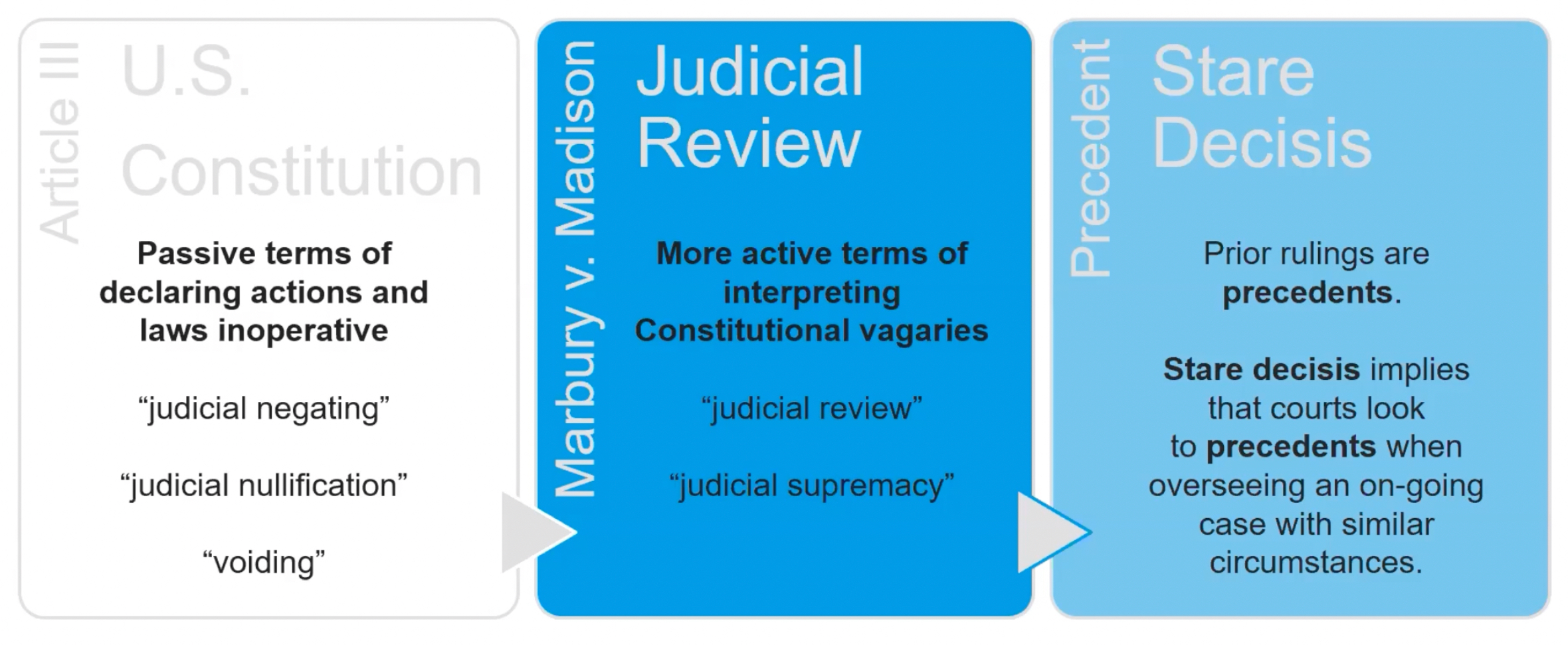
US Constitution
Judicial Negating:
Judicial Nullification:
Voiding:
Judicial Review
The Supreme Court’s power to declare laws unconstitutional. This was established in the Marbury v. Madison case.
Stare Decisis
The legal principle that courts should respect precedent set by previous judicial decisions, ensuring consistency and stability in the law.
Courts should rule similarily to previous court rulings
Setting a precedent means that a court establishes a way you interpret a law and future cases should follow that interpretation of the law.
Courts look at precedents when overseeing an on-going case with similar circumstances.
2.12 + 2.13
The bureaucracy and rulemaking
What does the Bureaucracy look like?
Cabinet Department’s (15 of them)
Appointed by President and confirmed by the Senate
Secretary of Education, Secretary of Defense
Independent Executive Agencies
Have a narrow focus
Appointed by President and confirmed by the Senate
NASA, IRS,
Independent Regulatory Commissions
Protect the public interest by enforcing rules over federal regulations
Usually headed by Boards - can be removed
Food and Drug Administration (FDA), Federal Communications Commission (FCC)
Government Corporations
A government organization that provides a service
United States Postal Service (USPS)
Bereaucracy implements federal policy
Quasi-legislative (interact with Congress)
Rule-making (writes and enforces legislation)
Testify in Congressional oversight meetings
Quasi-judicial
Administrative discretion
Administrative adjudication
**Congress or the President gives a mandate and the Bureaucracy will work to make that a reality
Bureaucracy Rule Implementation Examples
Department of Homeland Security
Set rules and regulations for naturalization
Department of Transportation
Set standards for airline safety
Investigate airline issues and non-compliance
Department of Veteran Affairs
Set requirements for disability benefits
Securities Exchange Commission
Define insider trading violations
Prosecute non-compliant businesses

Iron Triangle
How people get shit done in the government —- Antosz
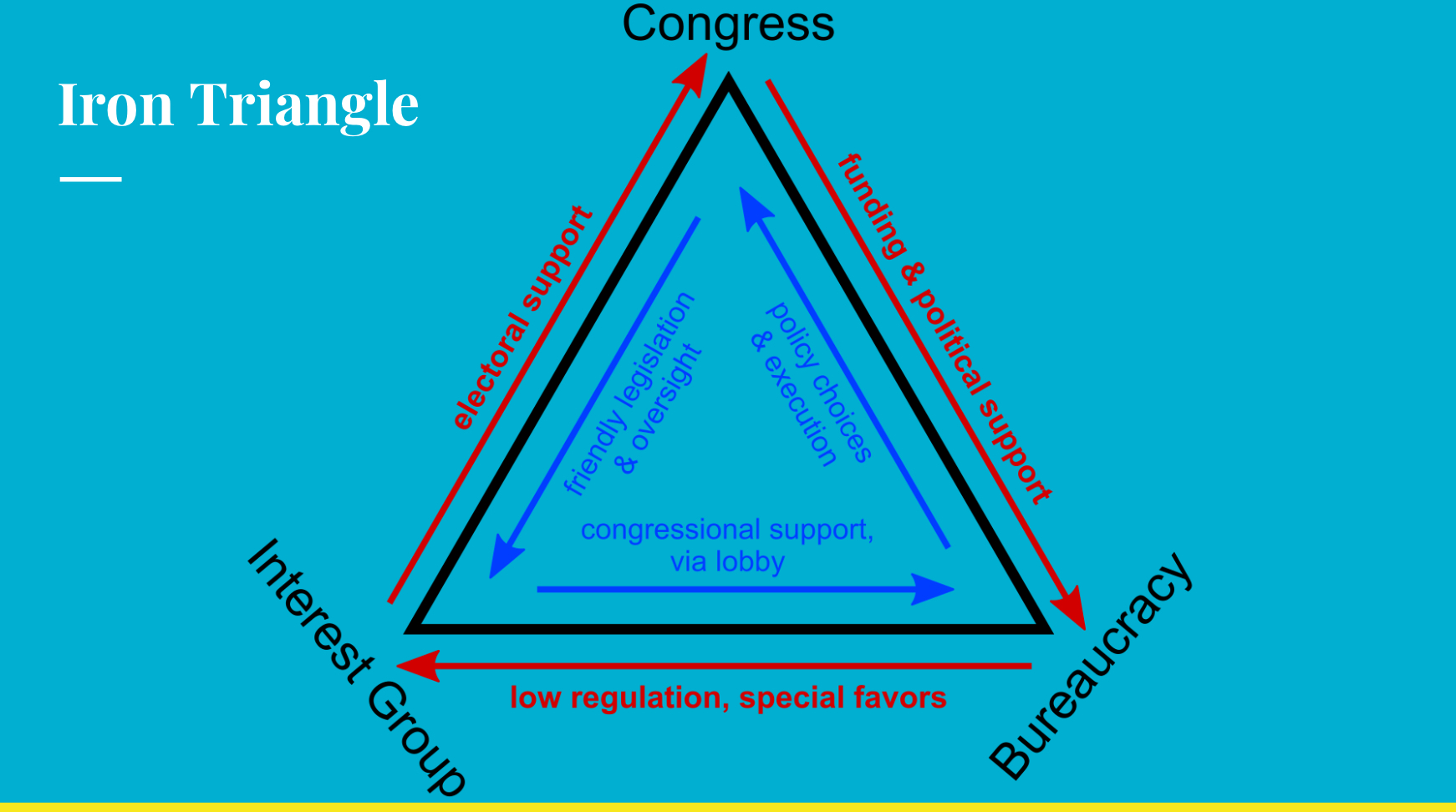
Unit 3
3.7
Selective Incorporation
Definition: The process by which the Bill of Rights is applied to the states.
(AKA: incorporating the Bill of Rights to the states)
14th Amendment
“No state shall make or enforce any law which shall abridge the privileges or immunities of citizens of the United States”
Due Process Clause: “nor shall any state deprive any person of life, liberty, or property without due process of law”
Gitlow v. New York
Establishes selective incorporation
Ruling extends the 1st Amendment’s free speech and press to the state
3.10 + 3.11
Social Movements
Social Movements
Civil Rights Act of 1964
Enacted to outlaw discrimination based on race, color, religion, sex, or national origin.
Title 2: Prohibits discrimination in public accommodations (e.g., hotels, restaurants, theaters).
Title 7: Prohibits discrimination by employers on the basis of race, color, religion, sex, gender, gender identity, pregnancy, and national origin. It established the Equal Employment Opportunity Commission (EEOC) to enforce this provision.
Title 7 motivated social movements to ensure safe work environments. If people are discriminated, it encouraged people to speak up.
Voting Rights Act of 1965
This was a law to enforce the 15th Amendment. It outlawed literacy tests and provided appointment for federal examiners. It applied a national prohibition of the denial or abridgement of the right to vote on account of race or color. With the 24th Amendment, passed a year before, the Voting Rights Act made sure there was no discrimination in voting. Poll taxes, literacy tests, etc, led to this law being passed since it was used to discriminate against Black People. The 24th Amendment which abolished poll taxes was passed alongside this law.
Title 9
It prevents people from being discriminated based on sex in education programs or activities receiving federal financial assistance. It was the result of the women’s rights movement.
Civil Rights vs. Civil Liberties
Civil Rights | Civil Liberties |
Ensures that every American regardless of sex, religion, or race has access to these civil liberties | Rights guaranteed to every American citizen by the Constitution |
14th Amendment
Protects citizens from discrimination based on:
Race
Religion
National Origin
Sex
Key Phrases:
Privileges and Immunities
Up to the states
Due Process Clause
Process oriented protection of natural law
Equal Protection Clause
Bridges the 5th and 14th amendments
How social movemens look for change:
Constitutional Amendments
Acts of Congress
Executive Directives (Orders)
Judicial Review & Stare Decisis
Civil Rights Movements (required to know)
1950s/1960s: African American Civil Rights Movements
Martin Luther King Jr.
Malcolm X
Civil Rights Act 1964
Voting Rights Act 1965
1960s/1970s: Women’s Rights Movement
19th Amendment (1920)
NOW Organization
The Feminine Mystique
A book by Betty Friedan that questioned the societal roles for women (taking care of children, being a stay at home mom)
Title IX (filled the gap in the Civil Rights Act of 1964)
1970s/1980s: LGBTQ+ Movements
“Don’t Ask Don’t Tell” Policy
You can’t be openly gay in the military: We don’t ask you if you’re gay, you don’t tell us if you’re gay.
1970s: Right to Life Movement
Response to Roe v. Wade
3.13
Affirmative Action: Describes policies enacted that favor groups that have been historically discriminated against
Affirmative Action has been interpreted as diversity in the workforce, meaning, seeking different minority groups (for hiring, for colleges, etc.)
Controversy
Is it constitutional to have minority quotas(minimum amounts of minorities) in various institutions?
Is the constitution color-blind?
Supreme Court Rulings
De Jure Segregation: Racial discrimination by law
De Facto Segregation: Racial segregation by personal choice
Supreme Court ruled against DE JURE segregation.
Supreme Court ruled against minority quotas in colleges.
Supreme Court ruled that firefighters can take a test and be determined whether they can be hired, even if black people score less becasue the test was an accurate representation of the job.
Unit 4
5 Values Shared by All Americans
Individualism
Self-reliance & independence
Equality of Opportunity
Free Enterprise
Laissez faire economics
Rule of Law
Every citizen is equal under the law - no special privileges
Limited Government
Government is limited defined, and established through checks and balances
Political Socialization (aka: How do you figure out your political beliefs?)
Family
Schools
Peers
Media
Civic/Religious Organizations
Globalization
How Does Ideology Change?
Generational Effects
A person’s voting behavior and ideology is influenced by the generation they are born into
Silent Generation (born before 1945)
High belief in church attendance and religious beliefs
Rigid gender roles to men and women
Tough on crime & pro troops
Baby boomers (WWII - 1960s)
More liberal than silent generation (grew up in the 1960s)
Still voted conservative (for the most part)
Generation X (Mid 1960s - 1980)
Grew up with divorce
First to use the internet
More diversity
More liberal
Millennials (1981-1996)
Even more ethnically diverse
More likely to think about racial discrimination in society
More favorable to immigrants
How do Political Events Affect Socialization?
Silent Generation
Great Depression
Baby Boomers
Vietnam War
Millenials
9/11
4.1
Polls
If a poll is created with scientific rigor, then it is the best tool for measuring public opinion.
The process includes:
Writing questions that are as free from bias as possible
Presenting questions to a small, randomized group of people
Generalizing those results to a larger population
4 types of polls
Opinion Poll
What people think on certain things
Helps get a feel for the public’s opinion on a certain topic of dicerning people’s feeling on certain candidates or polocies.
Benchmark Poll
How favored is the candidate among the people
Taken at the beginning of a candidate’s run and gives the campaign a benchmark against which they can compare future polls to see how the candidate is faring.
Tracking Poll
How opinion shifts over time
Conducted over time, usually with the same group of people, gives information on how the group feels about a given issue.
Entrance/Exit Poll
Who people voted for
Conducted at voting sites and asks people how they voted
Sample = A small group of people to represent a bigger group of people
Samping Methodology
A sample needs to be representative
Sampling Error
Neutral Questions
Two Major Types of Polls
Focus Group
Mass Survey
4.6
Public opinion affects election outcomes and policy debates
On primary debates, the most favorable person on opinion polls gets put at the center of the debate stage.
Politicians generally vote for policies that are favored by the people
The relationship between public opinion polls and elections and policy debates can be affected by how people view…
Social Desirability Bias
When people filling out surveys give out socially desirable answer, even if they don’t follow through with it. (when people don’t want others to know who they voted for on a poll and give a false answer)
Non-Response Bias
Certain groups are more likely to respond to public opinion polls than others. (More Hillary supporters can respond to a survey, showing a Hillary victory, but Trump can win because more people who don’t respond to surveys may vote for Trump)
Polls can be funded by partisan groups and are not reliable
4.9 + 4.10
Fiscal Policy: Decisions government makes about spending & taxation
16th amendment established the federal income tax
Congress created the Internal Revenue Service (IRS)
Monetary Policy: Decisions government makes about how much money is in the economy
Federal Reserve buys and sells bonds, sets reserve requirements, and sets interest rates
Congress passes an annual budget every year
Congress is considered to have the “power of the purse”
Liberal Economic Perspective
Government spending is good
Push for government spending
Keynesian economics
FDR during the Great Depression
Conservative Economic Perspective
Free Markets, no taxes
Allows the free market to regulate itself
Invisible Hand
Laissez faire
The economy should not be affected by the government
Supply side economics
AKA Trickle down economics
Rich people spend money on the middle class, the middle class spends it on the lower class (the money trickles down)
Support businesses!
Libertarian Economic Perspective (leans conservative in this topic)
Least amount of government regulations possible
No regulation on business and no government programs.
Liberal Social Ideology
Don’t want the government to be involved in social issues
Marijuana legalization
Abortion
Same-sex marriage
Support social welfare programs
Conservative Social Ideology
Want the government to be involved in:
Marijuanna
Abortion
Same-sex marriage
Wary of increased spending on social welfare
Libertarian Social Ideology (leans more liberal in this topic)
No government involvement
Government should protect private property and uphold individual freedoms
Unit 5
5.1
Voting Rights and Protections in the Constitution
Legal protections are found in the following amendments:
15: Granted African American men the right to vote
17: Direct election for senators
19: Granted women the right to vote
24: Eliminated poll taxes (a barrier to voting)
26: Lowered the voting age to 18
Voting Models
Rational choice voting: Person votes based on self-interest; carefully studies the issues/platforms (I want this so I’ll vote for this)
Retrospective voting: Person votes based on the recent track record of the candidates (This guy seems to do well, I’ll vote for him again)
Prospective voting: Person votes based on predictions of how a party or candidate will perform in the future (I think this guy will do good in the future, I’ll vote for him)
Party-line voting: Person votes for all the candidates of the voter’s party