CHAPTER 1: HISTORY, THEORIES, & METHODS
what is child development?
periods of development
conceptions and prenatal
infancy
early childhood
middle childhood
adolescence
dimensions of development
biological
cognitive
social
emotional
behavioral
defining development
qualitative changes
changes in type or kind
development
quantitative changes
changes in amount
growth
child development: field of study that tries to understand the processes that govern the appearance and growth of children’s
biological structures
psychological traits
behavior
understanding
ways of adapting to demands of life
why do researchers study child development?
to gain insight into:
human nature
origins of adult behavior
origins of sex differences and gender roles
effects of culture on development
origins, prevention, and treatment of developmental problems
optimize conditions of development
what views of children do we find throughout history?
ancient times and middles ages
children viewed as innately evil
age 7 is the “age of reason”
children were treated as miniature adults
John Locke
child came into world as tabula rasa or “blank slates”
focus on role of environment and experience
Jean-Jacques Rousseau
children are inherently good
industrial revolution
childhood is recognized as a special time period of life
children still labored in factories from dawn to dusk
20th century
laws to protect child rights in labor, education, neglect
juvenile courts
pioneers in the study of child development
Charles Darwin (1809-1882)
theory of evolution
use of baby biography
G. Stanley Hall (1844-1924)
child development as an academic discipline
questionnaire methodology with children
Alfred Binet (1857-1911)
First standardized intelligence test
theories of child development
John B. Watson
behaviorism- learning
nurture
Arnold Gesell
biological maturation
nature
theories of development help us:
describe
explain
predict
influence events being studied
formulation of relationships underlying observed events
include descriptive terms and concepts
based on assumptions about behavior
allows explanation and predictions
wide range of applicability
enable the influence of events
the psychoanalytic perspective
view children (and adults) involved in conflict
internal basic drives conflict with external limits
internalize ‘external’ demands and rules
conflict then occurs between these opposing inner forces
Freud’s theory of psychosexual development
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development
stage theories
distinct periods of development
Freud’s theory of psychosexual development
Sigmund Freud (1856-1939)
level of awareness
conscious and unconscious
parts of personality
id
ego
superego
quantity of gratification at each stage
fixated at that stage
stages
oral stage
sucking
early weaning or breast-fed too long
fixation: nail-biting, smoking, “biting wit”
anal stage
control and elimination of waste
excessively strict or permissive toilet training
fixation: anal-retentive (neatness); anal-explusion (sloppiness)
phallic stage
parent-child conflict over masturbation
view same-sex parent as rival
latency stage
sexual feelings remain unconscious
genital stage
begins at adolescence
desire sexual gratification through intercourse with member of other sex
interest in any other sexual gratification indicates fixation at an earlier stage in development
evaluation
contributions
comprehensive theory of childhood
influenced parents, child-care workers, and educators
criticisms
based on patients (women) who were emotionally troubled
little empirical data
placed too much emphasis on instincts and unconscious motives (Erik Erikson, Karen Horney)
Erikson’s theory of psychosocial development
Erik Erikson (1902-1994)
modified and expanded Freud’s theory
successful resolution of life crises bolsters sense of identity
differences from psychosexual development
focuses on development of self-identity
includes conscious and purposeful acts in development
extends stages to eight; through adulthood
stages
trust vs. mistrust
autonomy vs. shame and doubt
initiative vs. guilt
industry vs. inferiority
identity vs. role diffusion
intimacy vs. isolation
generativity vs. stagnation
ego integrity vs. despair
evaluation
highly appealing
emphasizes choice and minimizes urges
portrays people as prosocial and helpful
some empirical support
learning perspectives
behaviorism
observable behaviors only
classical conditioning
operant conditioning
social cognitive theory
observational learning
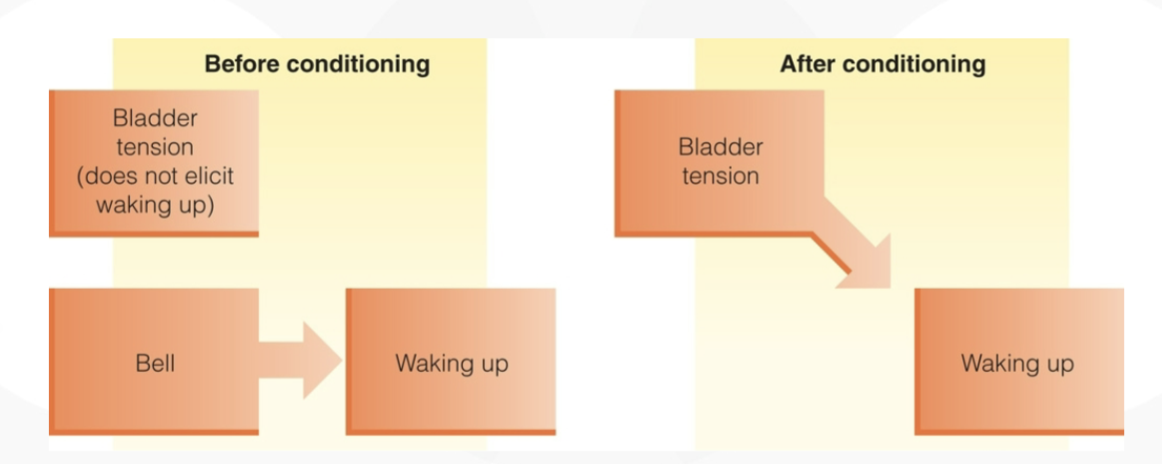
classical conditioning
simple learning
neutral stimulus repeatedly paired with the second stimulus
elicits the response usually brought by the second stimulus
example: bell and pad method to eliminate bed-wetting
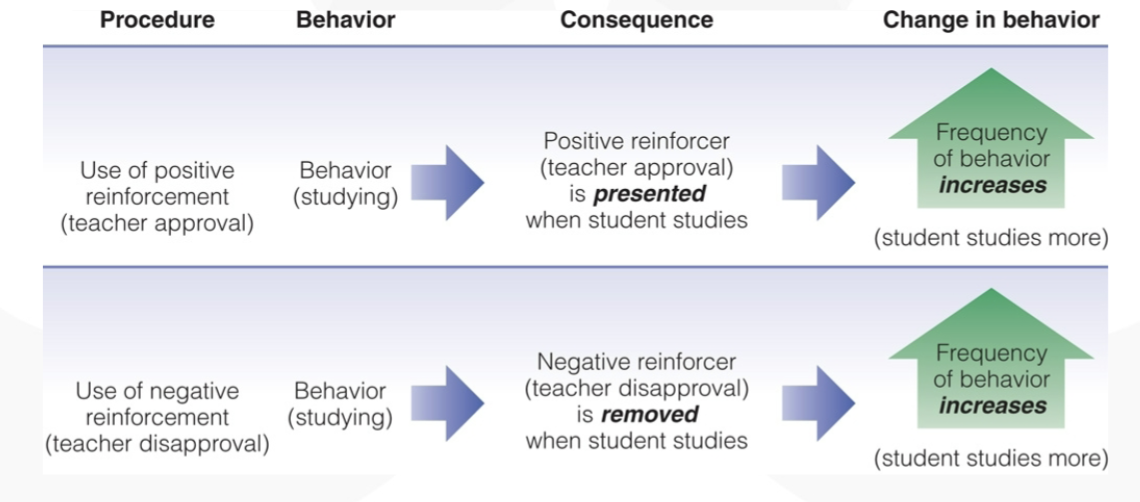
operant conditioning
learn to do something because of its effects
B.F. Skinner
reinforcement
any stimulus that increases the frequency of the behavior they follow
principles
positive reinforcers
something applied that increases the frequency of the behavior
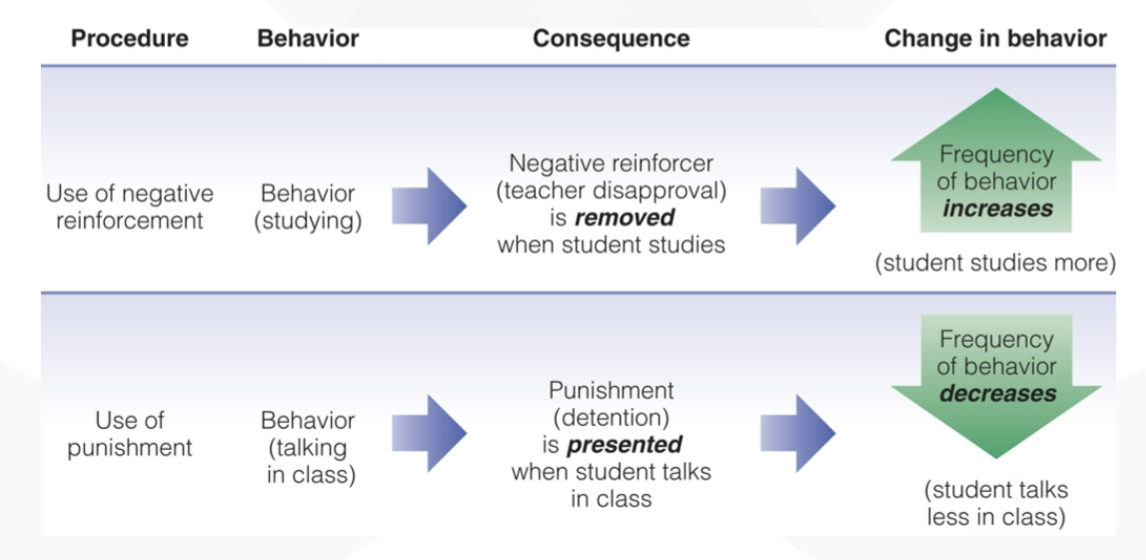
negative reinforcers
something removed that increases the frequency of the behavior
punishments
aversive events that decrease the behavior they follow
effective in emergencies, but less preferable in general
offers no alternative, acceptable form of behavior
tends to suppress undesirable behavior only under certain conditions
may cause withdrawal from the situation
can create anger and hostility
may be imitated as a way of coping with stress
instead, reward children for desirable behavior
application
shaping
teaching complex behaviors
reinforcing small steps toward the behavioral goal
socialization of children
parent and child
child and child
teacher and child
time out
social cognitive theory
Albert Bandura
acquire basic “know-how” through observational learning
skills may lie latent
child is an active learner
intentionally seek out or create environments where reinforcers are available
evaluation of learning theories
contributions
meets the goals of describing, explaining, predicting, and influencing aspects of children’s behavior
principles are abundant in education and clinical application
criticisms
unclear if learning is only mechanical
underestimates role of biological maturation factors
the cognitive perspective
focuses on children’s mental processes
how children perceive and mentally represent the world
Jean Piaget (1896-1980)
cognitive-developmental theory
information-processing theory
Piaget’s cognitive-developmental theory
working with Binet on IQ tests for children, Piaget became interested in children’s wrong answers
Piaget’s work was not widely read until mid 1950s
difficult to understand
reflected on biological-cognitive perspective until behaviorism and psychoanalysis were popular
he viewed children as budding scientists
basic concepts
scheme
pattern of action involved in acquiring or organizing knowledge
adaptation
interaction between child and environment
assimilation
responding to new object or event according to existing schemes
accomodation
adjusting scheme to a new object or event
equilibration
process of restoring equilibrium after a period of accomodation
stages
4 major stages
sensorimotor
preoperational
concrete operational
formal operational
sequence is universal
development is based on children’s interactions with their environments
influential in many educational settings
evaluation
criticisms
Piaget may have underestimated children’s abilities by age
cognitive growth may be more gradual than Piaget’s distinctive stages
contributions
different view of children from psychoanalytic and behaviorist
foundation for research
information-processing theory
influenced by the concepts of computer science
process of encoding information (input)
storage of information (long-term memory)
retrieval of information (short-term memory)
manipulation of information to solve problems (output)
software (mental processes)
hardware (brain)
consider cognitive development
size of short-term memory
number of programs that can run simultaneously
applications in education
the biological perspective
physical development
gains in height and weight
brain development
developments connected with hormones, reproduction, and heredity
ethology
study of behaviors that are specific to a species
ethology and evolution
concerned with instinctive behavior patterns
influenced by Charles Darwin, Konrad Lorenz, and Niko Tinbergen
pre-wired- instinctive behavior patterns
fixed action patterns (FAPs)
influence of prenatal hormones
Lorenz’s work on attachment during the first year
imprinting
evaluation
assume instinctive behaviors can be modified through learning
suggestion that instincts play a role in human behavior
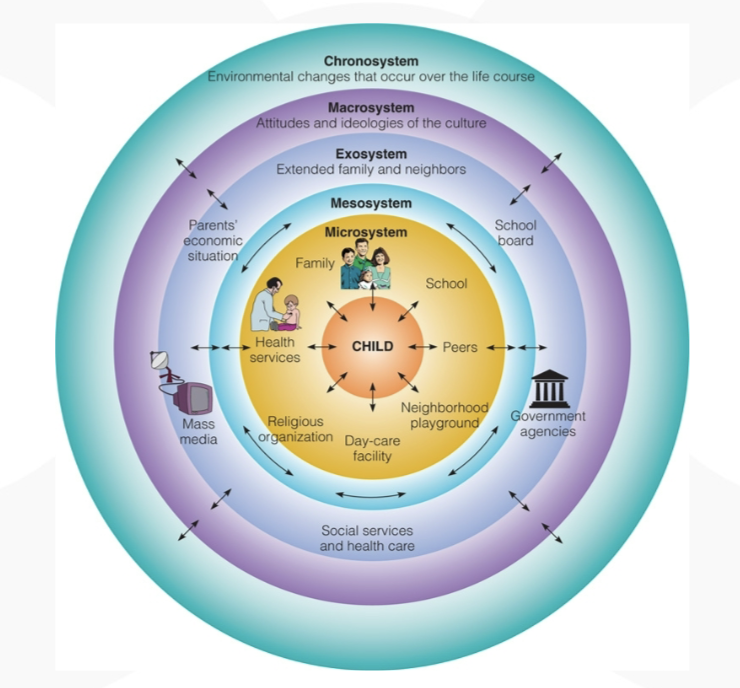
ecological system theory
explains development through interactions between children and the settings in which they live
Urie Bronfenbrenner (1917-2005)
focus on two way interactions between parent and child, not just maturational or child-rearing approaches
view the contexts of human development as a series of systems
5 embedded systems
microsystem
mesosystem
exosystem
macrosystem
chronosystem
evaluation of theory
helps focus attention on changing systems
sociocultural perspective
views children as social beings who are influenced by the cultures in which they live
Lev Semenovich Vygotsky’s (1896-1934) sociocultural theory
impact of human diversity on children
zone of proximal development (ZPD)
range of tasks child can perform with help of someone more skilled
use of conversations, external and internal, to guide the learning
scaffolding
adult provides problem-solving methods until child can perform independently
may also be used by children with peers
evaluation
research support for:
scaffolding
private speech
teachers often discourage private speech due to distraction
sociocultural perspective & human diversity
awareness of diversity among children
ethnic groups
understanding of children’s family values and cultural expectations
gender
understanding of gender-role expression
socio-economic status
associated with opportunity
nature-nurture controversy
to what extent is human behavior the result of
nature- heredity
nurture- environmental issues
orientation toward nature
cognitve-development theory
biological theorists
orientation toward nurture
learning theories
contemporary view- both nature and nurture
continuity- discontinuity controversy
do developmental changes occur:
continuously (gradually)?
discontinuously (qualitative leaps)?
orientation toward continuity
maturational theories
orientation toward discontinuity
stage theories (Freud, Piaget)
active- passive controversy
for learning to occur, do educators need to:
motivate passive learners, or
encourage active learners to explore?
perspectives of children as both active and passive
Bronfenbrenner’s bidirectional influence
Bandura’s two way influences between children and the environment
what is the scientific method?
forming a research question
developing a hypothesis
testing the hypothesis
drawing conclusions
publishing findings
naturalistic observation
field studies
observation done in natural settings (real life)
control for interference
examples of naturalistic observation studies:
activity levels of 3 to 5 year olds in preschools
motor behavior of Native American Hopi children strapped to cradleboards
language development in various countries
socialization patterns in diverse cultures
case study
account of behavior of an individual
diaries
direct observations
questionnaires
standardized tests
interviews
other sources of records
examples of case studies:
Piaget’s observation of children’s behavior
Freud’s studies of his patients
survey
assist in studying behavior and mental processes that cannot be observed
questionnaires or interviews
used to study attitudes
may question parents or teachers about children
may also use records to obtain information
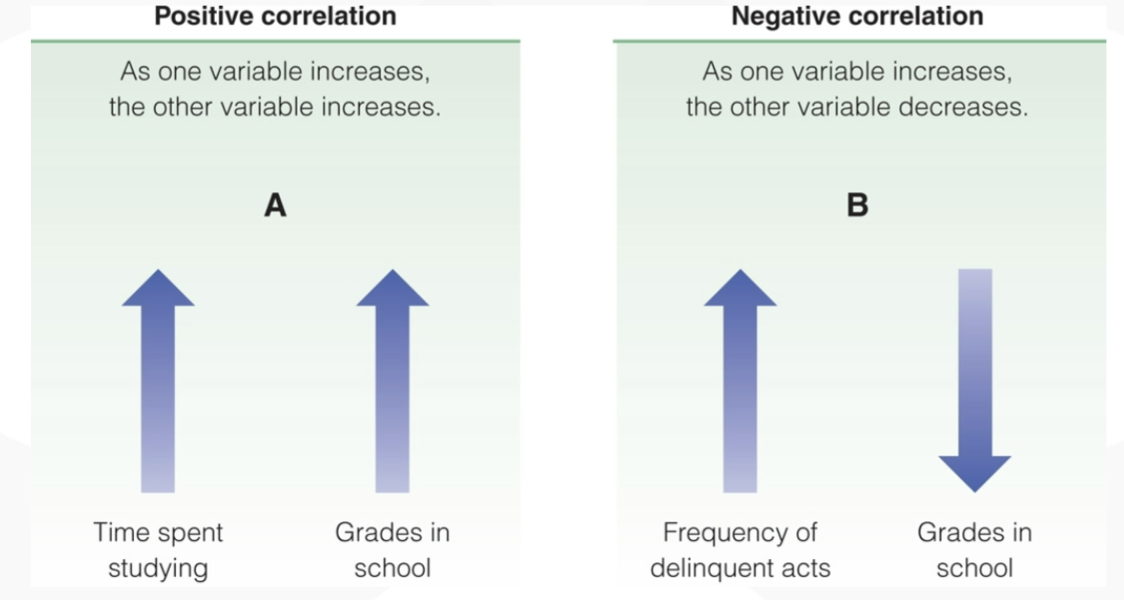
correlation
mathematical calculation to determine relationships between behaviors and/or traits (variables)
correlation coefficient
mathematical number between +1.00 and -1.00
positive correlation
negative correlation
limitation: shows relationships, not cause and effects
what is an experiment?
used to determine cause and effect
research method in which one group receives treatment and another does not
independent and dependent variables
independent variable- manipulated by experimenter
dependent variable- measured results- depends on independent variable
experimental and control groups
experimental group- receive the treatment
control group- do not receive the treatment
random assignment
ethical and practical
considerations
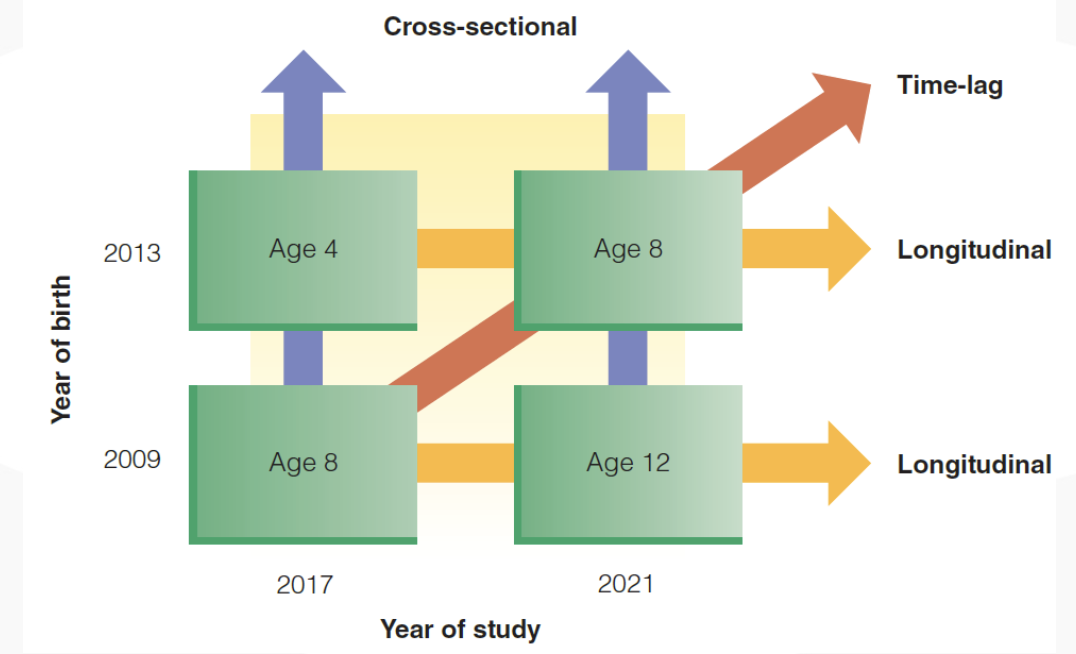
how do researchers study development over time?
longitudinal research
same children are observed repeatedly over time
most stand months or a few years, not decades
drawbacks to longitudinal research
may lose participants over time
difficult to enlist volunteers for long-term participcation
researchers must be patient
older researcher may need to rely on younger researchers to continue to research
cross-sectional studies
children of different ages are observed and compared
cohort effect
cross-sequential research
combines longitudinal (time period) and cross-sectional (cohorts) methods
breaks time span into convenient segments
time-lag comparisons
ethical considerations
professional groups propose guidelines for research with children
APA
Society for Research in Child Development
Government review boards
risk of physical or psychological harm
voluntary informed consent
right to withdraw from study
debriefing
confidentiality
prior approval of research by review committee