
BIOLOGY MID-TERM REVIEW
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is how your body sends messages quickly between your brain and other body parts. It helps you move, feel, think, and respond to things around you.
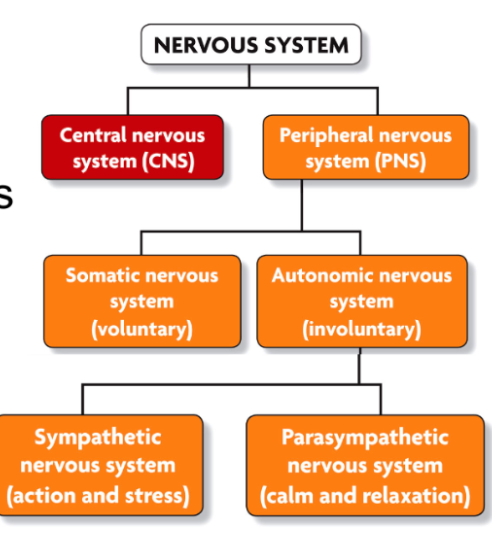
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Organs: The brain and spinal cord.
Job: The brain controls thoughts and decisions, while the spinal cord sends messages between the brain and body.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Organs: Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Job: It connects the rest of your body to the CNS and helps you move and feel.
What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is a group of glands that release hormones into your blood. Hormones help control things like growth, energy use, and mood.
Organs: Glands like the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, and reproductive organs (ovaries/testes).
Job: Controls long-term body processes like growth and metabolism through hormones.
What is a Stimulus?
A stimulus causes your body to react, like touching something hot, hearing a loud noise, or seeing a bright light. It triggers a response, like moving your hand or blinking.
——————————————————————————————————————————
What is a Neuron?
A neuron is a specialized cell in the nervous system that transmits electrical and chemical signals. It is the basic building block of the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system, allowing communication throughout the body.
What are the 3 Parts of a Neuron?
Cell body: Contains the nucleus and organelles. It processes information and maintains the cell’s function.
Dendrites: Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons and send them to the cell body.
Axon: A long, thread-like part of the neuron that carries signals away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.
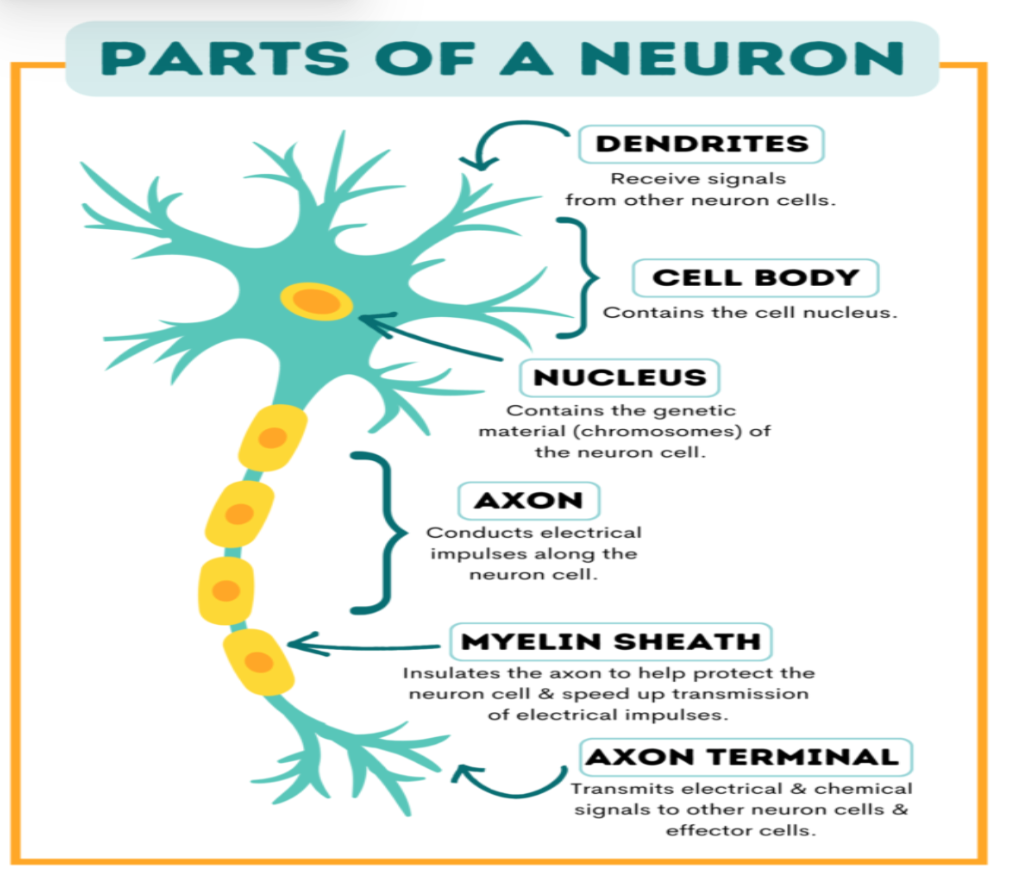
What are the 3 Types of Neurons?
Sensory neurons: Carry information from sensory organs (like skin, eyes, and ears) to the central nervous system (CNS).
Motor neurons: Send signals from the CNS to muscles and glands to cause movement or action.
Interneurons: Connect sensory and motor neurons, mostly found in the brain and spinal cord. They process information and help with reflexes and higher functions.
How Does a Neuron Stay at Rest?
Resting potential means no signal is being transmitted.
-There is more Na+ outside of the cell
-There is more K+ inside of the cell
What is a Resting Potential?
Resting potential is when 3 sodium leaves and 2 potassium enter the cell is called a resting potential. When sodium rushes inside(through sodium channels), it creates an impulse or action potential.
What are the Two Types of Ions that Cause Resting Potential?
Sodium ions (Na+): More concentrated outside the neuron.
Potassium ions (K+): More concentrated inside the neuron.
Sodium/Potassium Channel
The sodium/potassium pump is a protein in the neuron’s membrane that uses energy to actively move 3 sodium ions out of the neuron and 2 potassium ions in, maintaining the resting potential and keeping the inside of the neuron negatively charged.
What is an Action Potential?
An action potential is a brief electrical charge that travels along the axon. It occurs when a neuron is stimulated, causing sodium ions to rush in and potassium ions to rush out, reversing the resting potential and generating a signal.
How is the Signal Transmitted Between Neurons?
Signals are transmitted between neurons at a synapse. When the action potential reaches the end of an axon (axon terminal), it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters cross the gap (synaptic cleft) between neurons and bind to receptors on the next neuron, starting a new action potential in the receiving neuron.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/15fn8V9vafaRPwv6gVuEpl1LZ6tE06_DO/view
——————————————————————————————————————————
Scenes gather stimuli and send them to the nervous system.
The nervous system responds to stimuli
- Pupils shrink when too much light enters the eyes
- Goosebumps when cold air touches the skin
5 types of sensory receptors to help the human body:
Photoreceptors = Sense light
Mechanoreceptors = pressure, movement and tension
Thermoreceptors = monitor temperature
Chemoreceptors = detects chemicals
Pain receptors = heat, cold, pressure and chemicals from damaged tissue
The pathway of the light through the human eye:
Cornea → Iris → Pupil → Lens → Retina → Optic nerve → Brain
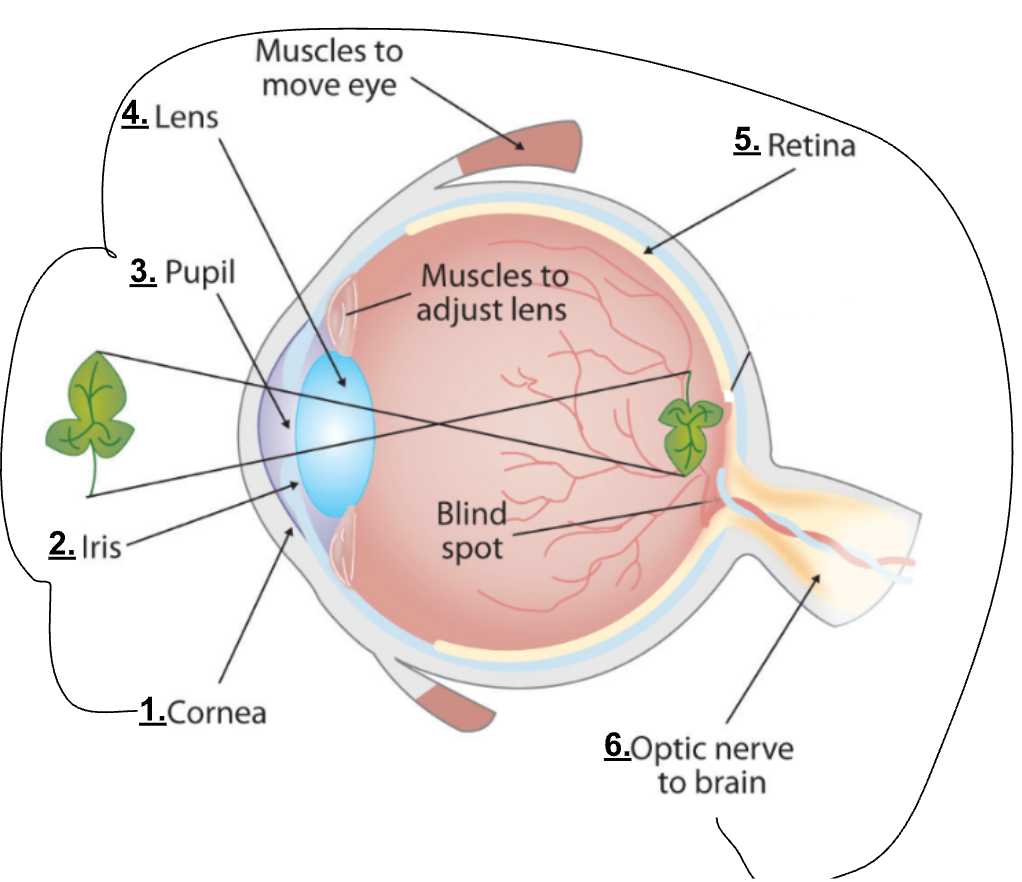
The senses detect physical and chemical stimuli
The eye contributes to the vision
- Photorecoptrs sense light
Two photoreceptors work together. Rod Cells and cone cells
Rod cells detect only black and white
Cone cells only detect colors
HAVE TO WATCH THIS VIDEO FOR THE EAR
https://drive.google.com/file/d/14ev_5ErowYCylM7klpbXcLDBk0l_q2TN/view
———————————————————————————————————————
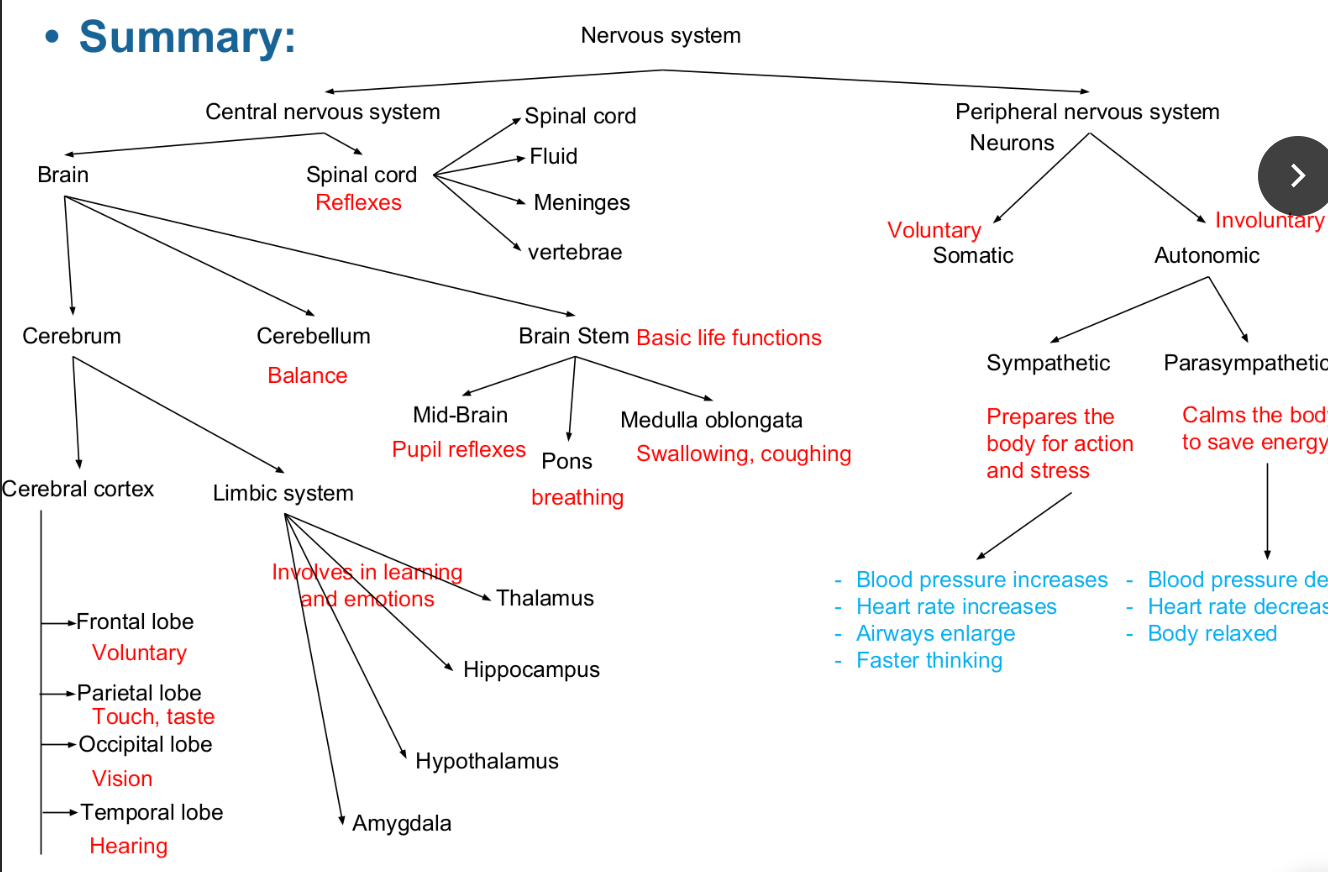
The nervous system’s two parts work together.
The CNS includes the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord.
-Composed of interneurons
-Receive information then interprets it and sends signals to PNS
The PNS includes the peripheral nerves.
- Connects the CNS to all organs
- Sensory Neurons sense the signal
- Influence voluntary and involuntary responses
White and gray matter
• In the brain, the gray matter is outside and the white matter is inside.
• In the spinal cord, the white matter is outside and the gray matter is inside.
How CNS and PNS pass signals between one another.
Sensory receptor generates impulse → PNS passes impulse to CNS → CNS interprets impulse. → CNS then passes NEW impulse to PNS → PNS stimulates a response.
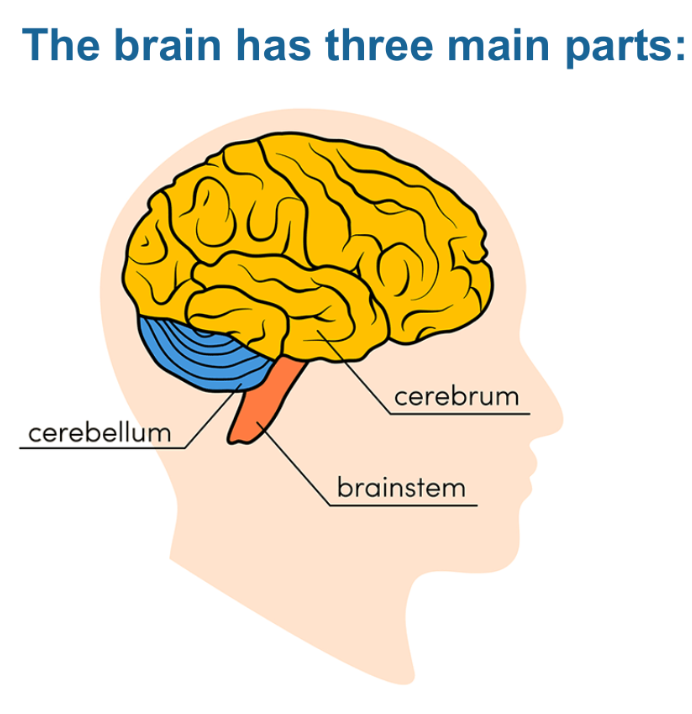
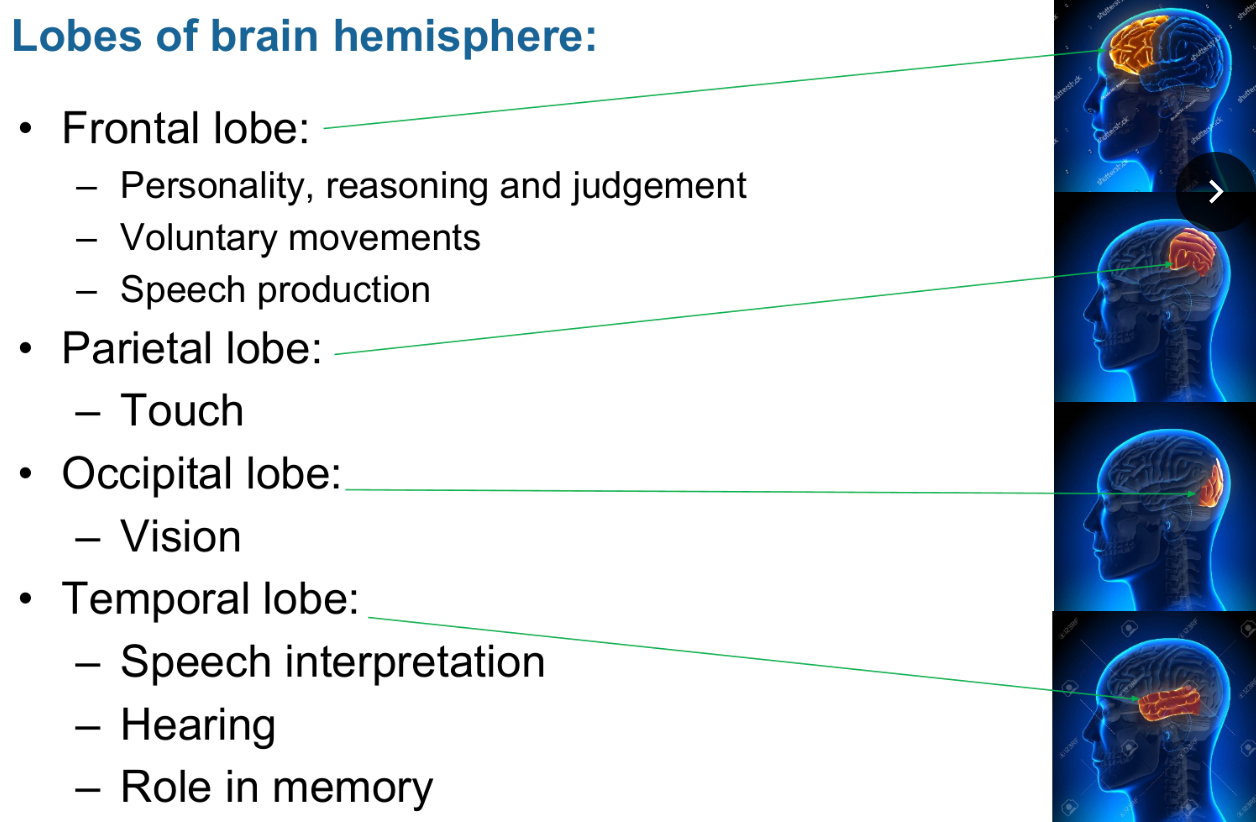
The three main parts of the brain:
1. Cerebrum
• Intelligence, learning, judgment
• Speech and memory
• Sense of hearing, vision, taste, and smell
• Skeletal muscle movements
2. Cerebellum
• Balance and coordination
• Posture
3. Brain Stem (Medulla Oblongata)
• Changes in heart rate
• Breathing, blood pressure, vomiting, swallowing
• Digestion
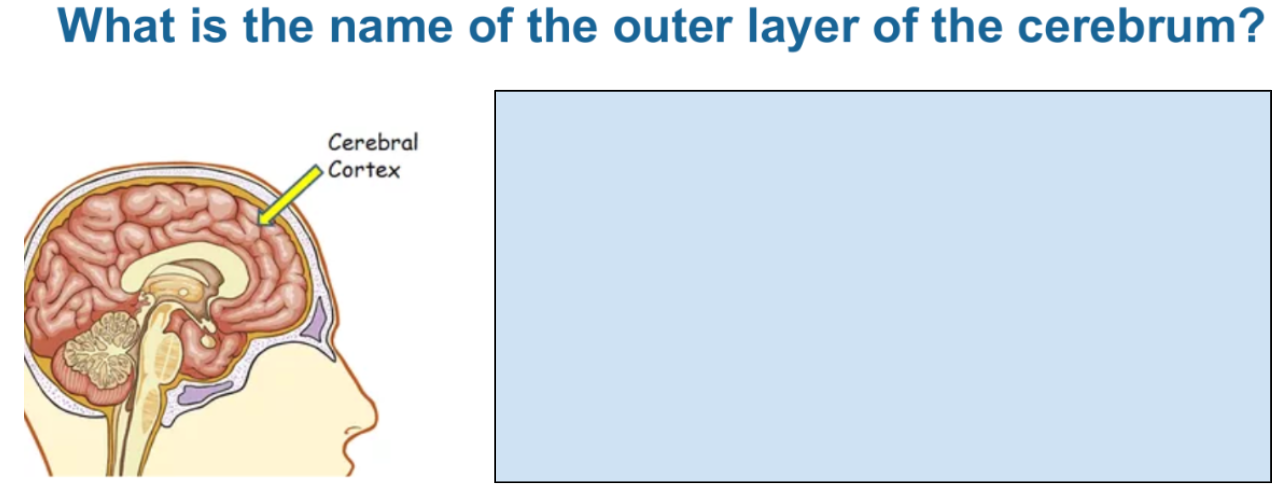
Cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum
Interprets information and generates responses.
Neurons are arranged in groups to perform specific tasks.
Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal.
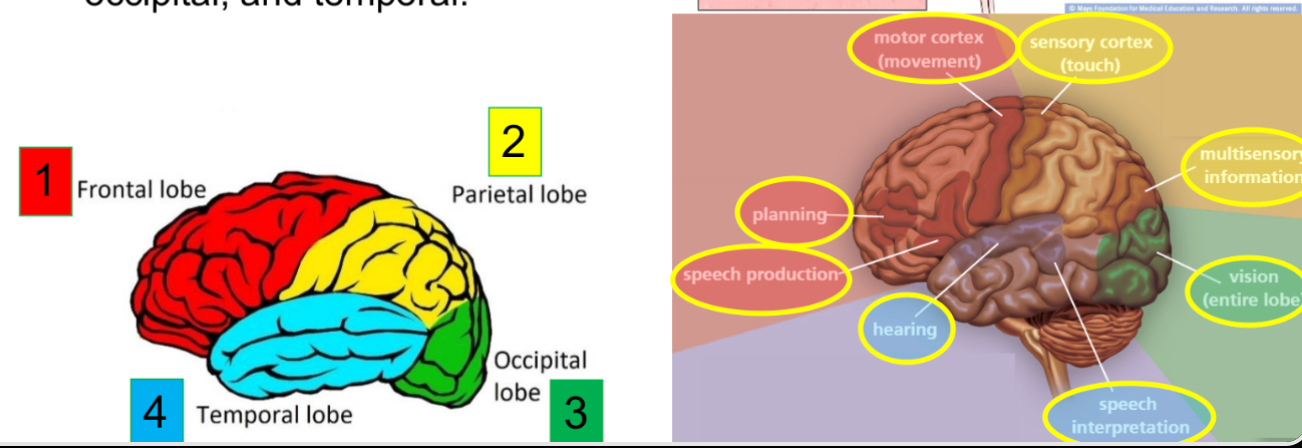
Underneath the cerebral cortex
Involved in learning and emotions
Hippocampus (learning and memory)
Amygdala (regulates emotion, encodes memories)
Thalamus (sorts information)
Hypothalamus (gathers information about temperature, hunger, and thirst)
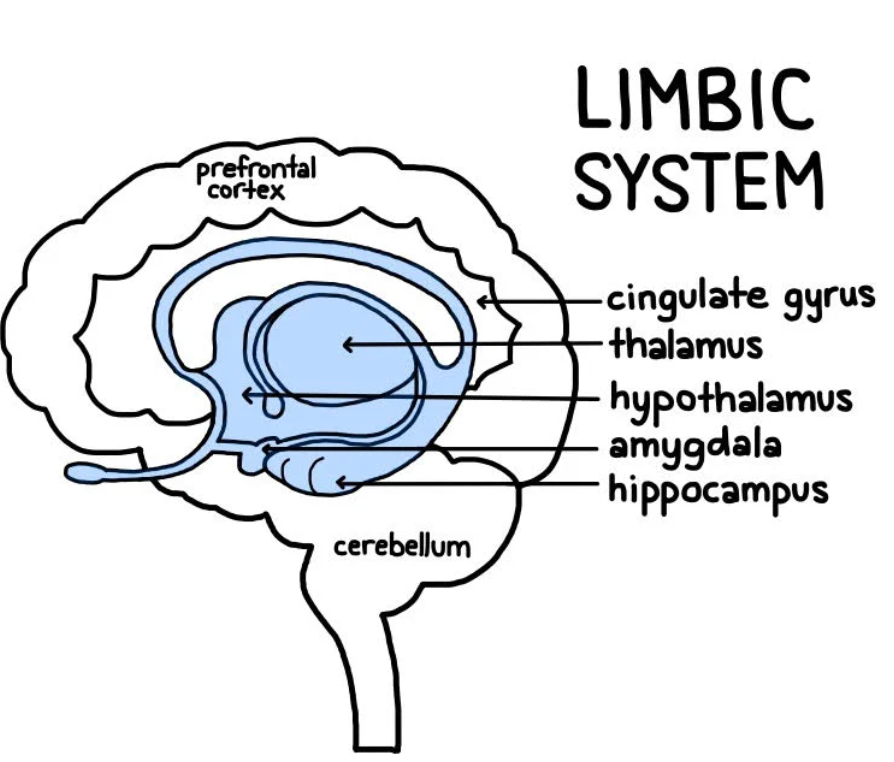
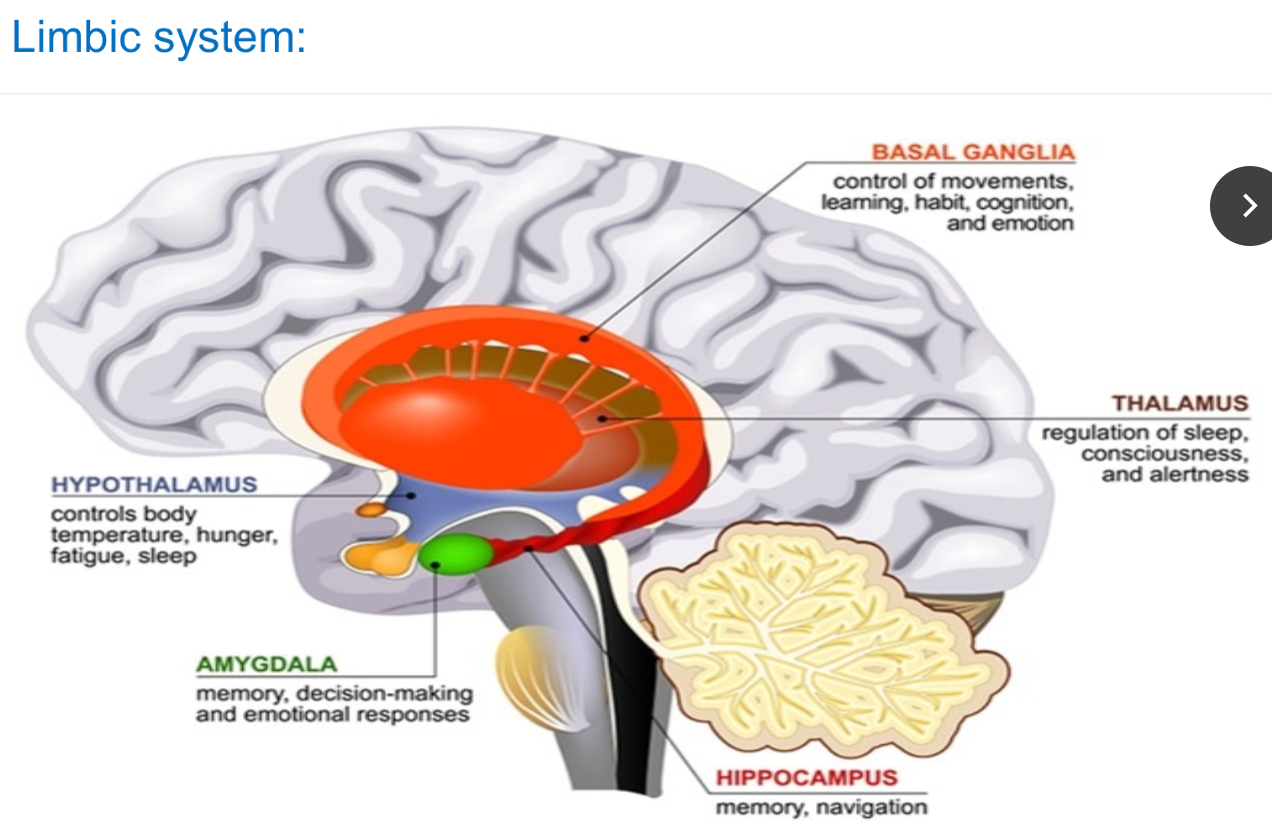
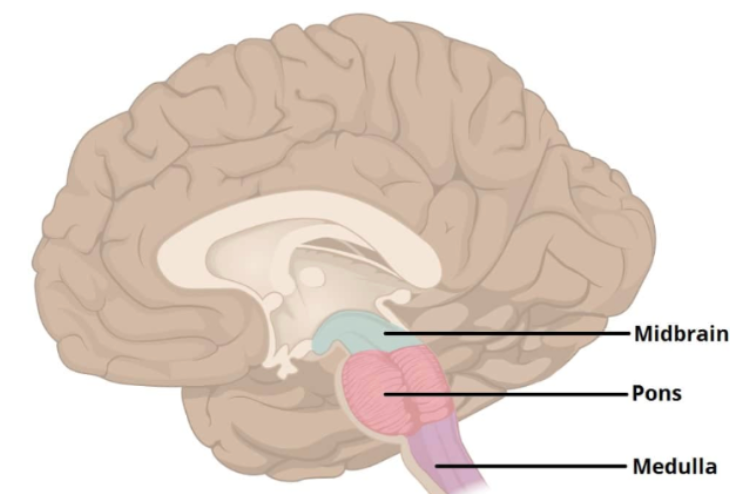
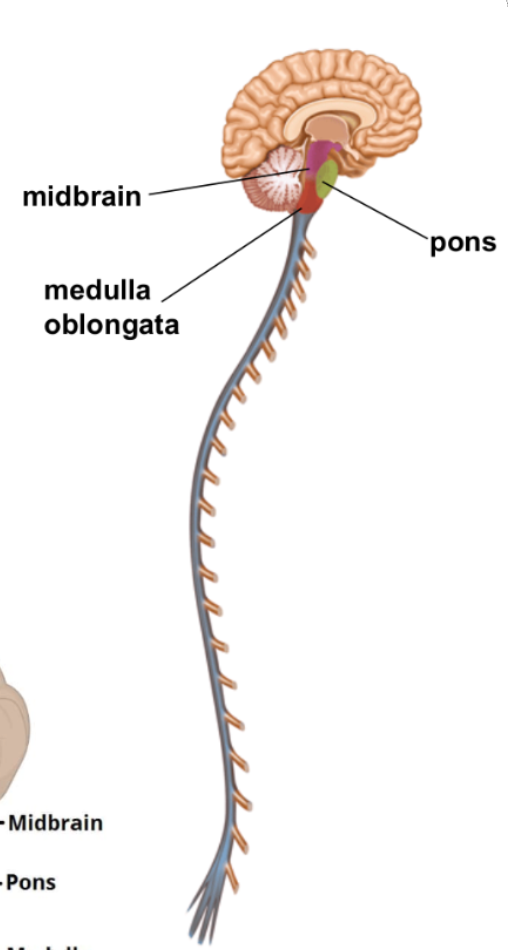
The brain stem has three parts:
Midbrain controls some reflexes (pupil size)
Pons regulates breathing
Medulla oblongata controls heart function, swallowing, and coughing
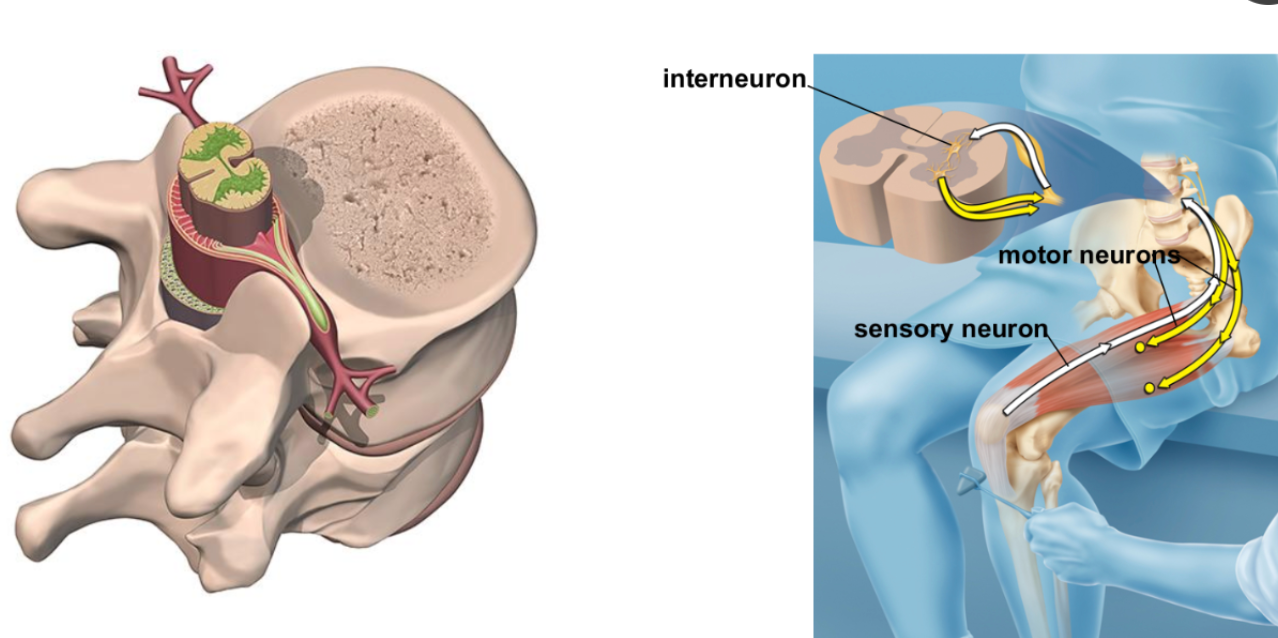
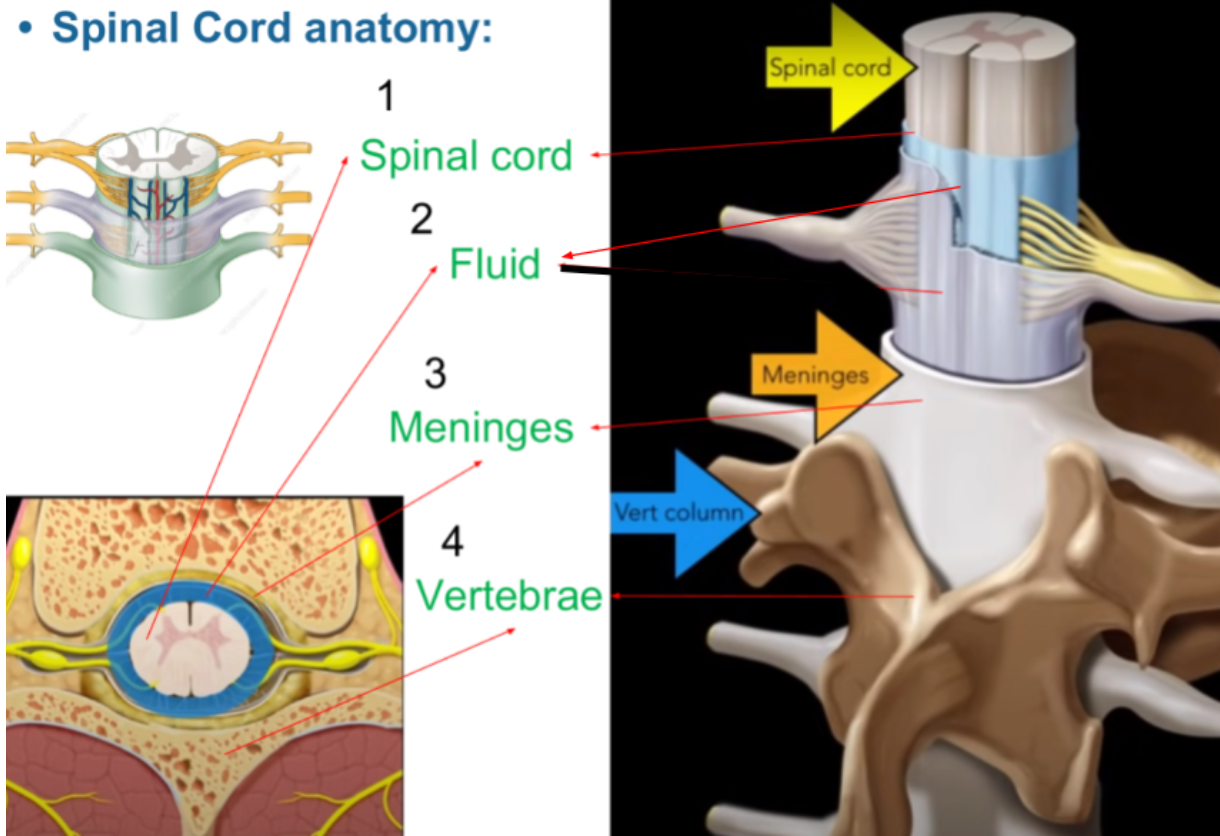
The spinal cord controls reflexes and body movements.
sensory neuron sends impulses to spinal cord
spinal cord directs impulse to motor neuron
does not involve the brain
The somatic nervous system regulates voluntary movements.
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions:
sympathetic nervous system: “fight vs. flight”
parasympathetic nervous system: calms the body, conserves energy
Three Modern Techniques Used to Image the Brain:
fMRI: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves.
CT Scan: Uses X-rays.
PET Scan: Uses radioactive tracers.
Which Technique is Better for Studying Brain Activity?
fMRI is better for studying brain activity.
Main Use of CT Scan and MRI:
CT Scan: Diagnoses brain injuries and tumors.
MRI: Provides detailed images of soft tissues and neurological disorders.
Two Main Differences Between CT Scan and MRI:
Technology: CT uses X-rays; MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves.
Image Detail: MRI provides better detail for soft tissues than CT.
Stimulant: Increases neurotransmitter activity, enhancing alertness and energy.
Inhibitor: Decreases neurotransmitter activity, helping regulate mood and relieve depression.
Stimulants or Inhibitors:
Dopamine: Stimulant
GABA: Inhibitor
Serotonin: Inhibitor (can have stimulant-like effects sometimes)
Schizophrenia: Dopamine levels increase.
Parkinson's Disease: Dopamine levels drop.
Endocrine System: A network of glands that release hormones to regulate body functions.
Gland: An organ that produces and secretes hormones.
Hormone: A chemical messenger that travels through the bloodstream to target organs.
Receptor: A protein that binds to a specific hormone, initiating a response in the target cell.
Target Cell: A cell that has receptors for a particular hormone and responds to its signals.
BIOLOGY MID-TERM REVIEW
What is the Nervous System?
The nervous system is how your body sends messages quickly between your brain and other body parts. It helps you move, feel, think, and respond to things around you.
Central Nervous System (CNS)
Organs: The brain and spinal cord.
Job: The brain controls thoughts and decisions, while the spinal cord sends messages between the brain and body.
Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)
Organs: Nerves outside the brain and spinal cord.
Job: It connects the rest of your body to the CNS and helps you move and feel.
What is the Endocrine System?
The endocrine system is a group of glands that release hormones into your blood. Hormones help control things like growth, energy use, and mood.
Organs: Glands like the thyroid, adrenal glands, pancreas, and reproductive organs (ovaries/testes).
Job: Controls long-term body processes like growth and metabolism through hormones.
What is a Stimulus?
A stimulus causes your body to react, like touching something hot, hearing a loud noise, or seeing a bright light. It triggers a response, like moving your hand or blinking.
——————————————————————————————————————————
What is a Neuron?
A neuron is a specialized cell in the nervous system that transmits electrical and chemical signals. It is the basic building block of the brain, spinal cord, and nervous system, allowing communication throughout the body.
What are the 3 Parts of a Neuron?
Cell body: Contains the nucleus and organelles. It processes information and maintains the cell’s function.
Dendrites: Branch-like structures that receive signals from other neurons and send them to the cell body.
Axon: A long, thread-like part of the neuron that carries signals away from the cell body to other neurons, muscles, or glands.

What are the 3 Types of Neurons?
Sensory neurons: Carry information from sensory organs (like skin, eyes, and ears) to the central nervous system (CNS).
Motor neurons: Send signals from the CNS to muscles and glands to cause movement or action.
Interneurons: Connect sensory and motor neurons, mostly found in the brain and spinal cord. They process information and help with reflexes and higher functions.
How Does a Neuron Stay at Rest?
Resting potential means no signal is being transmitted.
-There is more Na+ outside of the cell
-There is more K+ inside of the cell
What is a Resting Potential?
Resting potential is when 3 sodium leaves and 2 potassium enter the cell is called a resting potential. When sodium rushes inside(through sodium channels), it creates an impulse or action potential.
What are the Two Types of Ions that Cause Resting Potential?
Sodium ions (Na+): More concentrated outside the neuron.
Potassium ions (K+): More concentrated inside the neuron.
Sodium/Potassium Channel
The sodium/potassium pump is a protein in the neuron’s membrane that uses energy to actively move 3 sodium ions out of the neuron and 2 potassium ions in, maintaining the resting potential and keeping the inside of the neuron negatively charged.
What is an Action Potential?
An action potential is a brief electrical charge that travels along the axon. It occurs when a neuron is stimulated, causing sodium ions to rush in and potassium ions to rush out, reversing the resting potential and generating a signal.
How is the Signal Transmitted Between Neurons?
Signals are transmitted between neurons at a synapse. When the action potential reaches the end of an axon (axon terminal), it triggers the release of chemicals called neurotransmitters. These neurotransmitters cross the gap (synaptic cleft) between neurons and bind to receptors on the next neuron, starting a new action potential in the receiving neuron.
https://drive.google.com/file/d/15fn8V9vafaRPwv6gVuEpl1LZ6tE06_DO/view
——————————————————————————————————————————
Scenes gather stimuli and send them to the nervous system.
The nervous system responds to stimuli
- Pupils shrink when too much light enters the eyes
- Goosebumps when cold air touches the skin
5 types of sensory receptors to help the human body:
Photoreceptors = Sense light
Mechanoreceptors = pressure, movement and tension
Thermoreceptors = monitor temperature
Chemoreceptors = detects chemicals
Pain receptors = heat, cold, pressure and chemicals from damaged tissue
The pathway of the light through the human eye:
Cornea → Iris → Pupil → Lens → Retina → Optic nerve → Brain

The senses detect physical and chemical stimuli
The eye contributes to the vision
- Photorecoptrs sense light
Two photoreceptors work together. Rod Cells and cone cells
Rod cells detect only black and white
Cone cells only detect colors

HAVE TO WATCH THIS VIDEO FOR THE EAR
https://drive.google.com/file/d/14ev_5ErowYCylM7klpbXcLDBk0l_q2TN/view
———————————————————————————————————————
The nervous system’s two parts work together.
The CNS includes the brain, brain stem, and spinal cord.
-Composed of interneurons
-Receive information then interprets it and sends signals to PNS
The PNS includes the peripheral nerves.
- Connects the CNS to all organs
- Sensory Neurons sense the signal
- Influence voluntary and involuntary responses
White and gray matter
• In the brain, the gray matter is outside and the white matter is inside.
• In the spinal cord, the white matter is outside and the gray matter is inside.
How CNS and PNS pass signals between one another.
Sensory receptor generates impulse → PNS passes impulse to CNS → CNS interprets impulse. → CNS then passes NEW impulse to PNS → PNS stimulates a response.

The three main parts of the brain:
1. Cerebrum
• Intelligence, learning, judgment
• Speech and memory
• Sense of hearing, vision, taste, and smell
• Skeletal muscle movements
2. Cerebellum
• Balance and coordination
• Posture
3. Brain Stem (Medulla Oblongata)
• Changes in heart rate
• Breathing, blood pressure, vomiting, swallowing
• Digestion
Cerebral cortex is the outer layer of the cerebrum
Interprets information and generates responses.
Neurons are arranged in groups to perform specific tasks.
Each hemisphere is divided into four lobes: frontal, parietal, occipital, and temporal.



Underneath the cerebral cortex
Involved in learning and emotions
Hippocampus (learning and memory)
Amygdala (regulates emotion, encodes memories)
Thalamus (sorts information)
Hypothalamus (gathers information about temperature, hunger, and thirst)


The brain stem has three parts:
Midbrain controls some reflexes (pupil size)
Pons regulates breathing
Medulla oblongata controls heart function, swallowing, and coughing


The spinal cord controls reflexes and body movements.
sensory neuron sends impulses to spinal cord
spinal cord directs impulse to motor neuron
does not involve the brain

The somatic nervous system regulates voluntary movements.
The autonomic nervous system controls involuntary functions:
sympathetic nervous system: “fight vs. flight”
parasympathetic nervous system: calms the body, conserves energy



Three Modern Techniques Used to Image the Brain:
fMRI: Uses magnetic fields and radio waves.
CT Scan: Uses X-rays.
PET Scan: Uses radioactive tracers.
Which Technique is Better for Studying Brain Activity?
fMRI is better for studying brain activity.
Main Use of CT Scan and MRI:
CT Scan: Diagnoses brain injuries and tumors.
MRI: Provides detailed images of soft tissues and neurological disorders.
Two Main Differences Between CT Scan and MRI:
Technology: CT uses X-rays; MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves.
Image Detail: MRI provides better detail for soft tissues than CT.
Stimulant: Increases neurotransmitter activity, enhancing alertness and energy.
Inhibitor: Decreases neurotransmitter activity, helping regulate mood and relieve depression.
Stimulants or Inhibitors:
Dopamine: Stimulant
GABA: Inhibitor
Serotonin: Inhibitor (can have stimulant-like effects sometimes)
Schizophrenia: Dopamine levels increase.
Parkinson's Disease: Dopamine levels drop.
Endocrine System: A network of glands that release hormones to regulate body functions.
Gland: An organ that produces and secretes hormones.
Hormone: A chemical messenger that travels through the bloodstream to target organs.
Receptor: A protein that binds to a specific hormone, initiating a response in the target cell.
Target Cell: A cell that has receptors for a particular hormone and responds to its signals.
 Knowt
Knowt
