ICT - Emerging Technologies
Extended reality (XR) - refers to real and virtual combined environments, and is a ‘catch all’ term for all immersive technologies.
Virtual Reality - An artificial environment created by software that has the ability to take the user out of real-world environment into a digital environment. users must use a VR headset or HMD (head mounted device) which allows 360 degree view of virtual word. sometimes use data goggles, sensor suits, data gloves or helmet
Input and Output of Vr - Input: Data gloves, VR Headset, microphones, cameras.
Output - speakers/headphones, monitor/projector, HMD,
Applications of VR - 1. education (for example, looking inside an ancient building as part of a history lesson)
2. engineering (for example, seeing how new designs like bridges will look in an existing environment)
3. sport (for example, a golfer trying to improve his swing can use this technology and get feedback to improve his game)
xi. scientific visualisation (for example, part of a molecular structure in chemistry, or a cell in biology).
Risks of VR - users get addicted, training in VR environment isn’t real, high cost, causes eye strain and fatigue, people not aware of physical surroundings leads to accidents
Augmented Reality - interactive experience where objects that reside in real world are enhanced by computer generated information such as images, text and animation. combination of real and virtual worlds
AR vs VR - 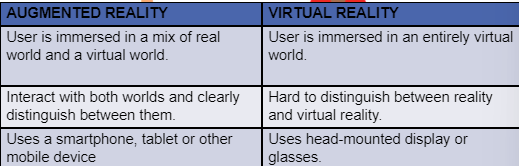
Effects of AR on society - 1. safety and rescue operations: (for example, it is possible to provide 3D images of an area where a rescue mission is to take place)
2. entertainment - (for example, AR takes users into a virtual environment where it is possible to interact with the characters)
3. shopping and retail (for example, using your smartphone camera you can try out make-up and see how it looks on you before buying it, or you can see how a piece of furniture will look and fit your space)
d. healthcare - (doctors can make use of AR to have a better understanding of a patient’s body