Sensations & Perception chp 5
Sensation v Perception
Intentional blindness - not noticing something very visible b/c the person was paying attention to something else
change blindness
change deafness
selective attention - can only pay attention to one thing at a time
cocktail party effect - in a loud space we are tuned for certain stimulants (ex our name)
stroop effect - if you have two similar stimuli takes you longer to process
diff. between sensation and perception?
sensation - the sensory stimulus
perception - how sensory input is organized, interpreted & consciously experienced
bottom up processing - works to make a whole, building meaning out of the qualities (ex given limited ingredients then having to make a recipe)
top down processing - taking all info we know to apply it to the next situation (ex someone slammed the door, they must be mad)
absolute threshold - minimum amount of stimulus energy that must be present for the stimulus to be detected 50% of the time
difference threshold - depends on the stimulus intensity
Weber’s Law - the difference threshold is a constant % of the original stimulus
sensory adaptation - diminished sensitivity (neurons stop firing) as a result of constant stimulus
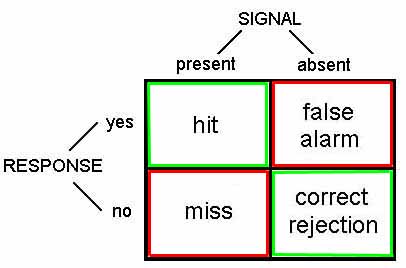
signal detection theory - the intensity of the stimuli + the psychological & physical state of the person contribute to whether or not the person is able to detect the stimuli
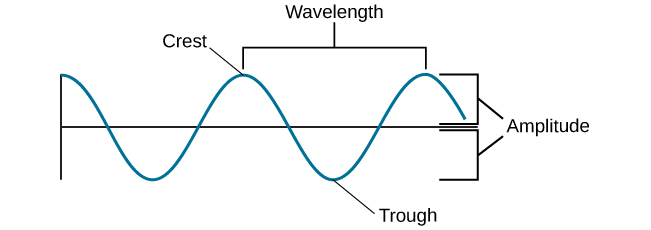
Waves & Wavelengths
saccades - our eyes always vibrate a little bit
wavelength - distance from the center line to the top point of the crest or the bottom point of the trough. hue
amplitude - the length of a wave from one peak to the next. brightness/intensity of color
High-frequency sound waves are perceived as high-pitched sounds
low-frequency sound waves are perceived as low-pitched sounds
Vision
Rods | Cones |
peripheral | central |
black/white | color |
lots of them | one cone/one bipolar cell |
not a lot of detail | lots of detail |
low light | lots of light |
optic chiasm - the spot where the optic nerve from each eye merges just below the brain
trichromatic theory - hypothesizes we have three types of cones (red, blue & green) & all the three colors work together to make all the colors on the spectrum
opponent-process theory - if the receptor is drained from red will fire green (same w/ blue/yellow, white/black)
explains after images because if you stare at the color red & look away you will see a green after image
afterimages - (opponent process result) continuation of a visual sensation after removal of the stimulus (ex when you look at the sun, look away & still see its glow)
Auditory
monocular cues - cue that only requires one eye
perceptual constancy - perceiving objects as constant even as illumination & retinal images changes
perceptual set - overarching framework which we interpret stuff
perceptual adaptation - Perceptual systems adapt to their inputs (ex dark theater, then visions adjusts) ONLY SEEING & HEARING
temporal theory - can’t account for the entire range, based theory that hair in ear vibrates to make the noise signal
frequency theory - different portions of the ear sensitive to different frequencies (so diff parts determine what sounds you hear)
cochlear implant - composed of mic, speech processor & electrode array. receives sound → stimulates auditory nerve —> sends to brain
amplitude - height of wave; determines loudness of the sound
frequency - length of the wave; determines pitch
Misc. Senses
gustation - taste
sweet | energy |
salty | necessary for processes (ex living) |
umami | protein/growth |
sour | potentially toxic |
bitter | potentially poison |
spice is not a taste, spice is pain from your tongue being signaled to the brain
olfaction - smell
smell & taste work together you can’t taste something if you can’t smell it
Gustation & Olfaction are chemical senses because they respond to chemicals instead of energy (sound waves, & light waves)
nociceptor - pain cells
vestibular sac - bubble of air that determines vestibular sense
vestibular sense - balance relative to the ground, where you are in space
kinesthetic sense - perception of body’s movement through space
proprioception - perception of the body’s position
Gestalt - literal meaning: form/pattern. the brain creates a perception that is more than simply the sum of available sensory inputs, and it does so in predictable ways
Energy Senses | vision, hearing, touch |
Chemical Senses | gustation, olfaction |
Body Position Senses | vestibular sense, kinesthetic sense |