BUSINESS SECTION 5
Production-The process of using raw materials (input) and transforming them in some way to produce goods or services(output)
Productivity- a measure of how much output can be produced from a given level of input.
HOW TO CALCULATE - Quantity of output/quantity of input
FACTORS OF PRODUCTION
Land
This refers to all natural resources on the earth including those in the sea and atmosphere around us
Labour
Refers to all physical and mental contributions of an employee
Can be divided into :
skilled(engineers etc)
semi skilled (driver etc)
unskilled(vendor etc.)
Capital
Refers to all the man made items that go into producing other things
Enterprise
refers to bringing together all other factors tgether to produce goods to make a profit while taking risks.
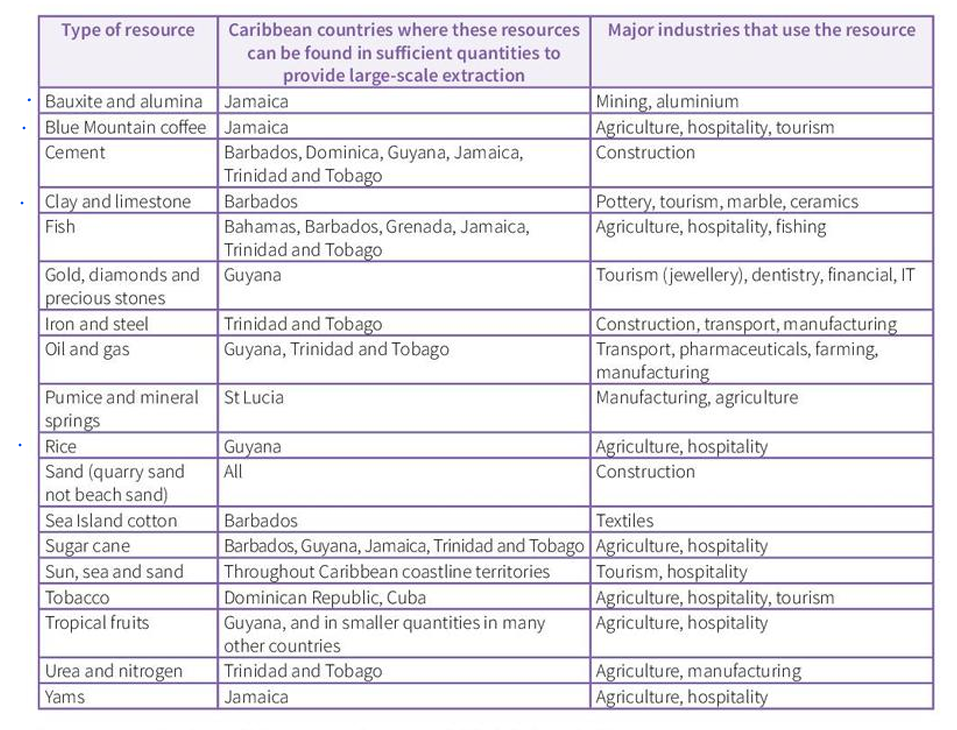
RESOURCES IN THE CARIBBEAN
IMPORTANCE OF PRODUCTIVITY
IMPROVING THE LABOUR SUPPLY
This invloves several strategies and considerations
Wage incentives: higher wages can motivate people to work longer hours
Labour Productivity: its not only about the number of hours worked but also the intensity and efficiency of warranty higher productivity can result from:
Working longer: increased production levels but may not impact productivity
Working harder: raises both production levels and productivity to some extent working smart here
Working smarter: enhances both significantly by using time and resources more efficiently
HUMAN RESOURCE DEVELOPMENT
Involves enhancing the effectivveness and motivation of employees. This includes creating systems like appraisals to identify and support personal development, and providing learning and development opportunities.
IMPORTANCE OF POSITIVE WORK ETHIC
USE OF CAPITAL TO INCREASE PRODUCTIVITY
LAND USE AND DECLINING PRODUCTIVITY IN THE REGION
ROLE OF CAPITAL IN PRODUCTION
Capital provides the necessary resources to facilitate the transformation of inputs into outputs. It enhances efficiency increased output per worker and drives economic growth by enabling businesses to produce goods and services more effectively and competitively.
TYPES OF CAPITAL
FIXED
Refers to durable capital equipment that can be used repeatedly in the production process example tractors.
WORKING
Reference to capital needed to pay for the day-to-day operations of the business example inventories.
VENTURE
Refers to money that is provided by investors to start up businesses.
METHODS OF PRODUCTION
JOB PRODUCTION
Involves a one off job, these are more expensive to plan prepare and implement than mass production methods typically they involve one or just a few customers and 1 or just a few manufacturers one of jobs take longer than most of forms of production example hairdressers.
BATCH PRODUCTION
Several identical or similar items will be produced in asset or badge the items do not need to be for any specific customer but are made at regular intervals in specific quantities.
FLOW PRODUCTION
Involves products or services that are created in a series of stages on an assembly line, example car assembly plant.
LEAN PRODUCTION
A systematic approach that aims to minimize WASTE while maximizing efficiency productivity and quality.
TYPES OF PRODUCTION
EXTRACTIVE
The process of obtaining raw Materials or resources from natural sources such as mines. Involves extracting, harvesting, or gathering natural resources for prossessing, refinement and use in various industries.
CONSTRUCTION
refers to the process of creating physical structures such as houses and roads and bridges.
MANUFACTURING
Refers to the process of creating goods through various physical and chemical transformation methods. It involves converting raw materials components or parts into finished products.
SERVICE
A service industry provides a direct service to people example taxi services. A commercial service provides a service to a business organization rather than an individual example business insurance.
PRIMARY→ Extracts natural resources → extractive industries
SECONDARY → Makes products often used in raw materials from primary industries →manufacturing and construction
TERTIARY → Provides services → Services to business or individuals
LEVELS OF PRODUCTION
SUBSISTENCE
This level is only sufficient to meet the basic needs of the local population
DOMESTIC CONSUMPTION
provide sufficient goods to meet the needs of people within a given territory or country
SURPLUS
As industries become more efficient, surpluses of product start to develop, and some members of society are able to organize production into small factories and plantation agriculture. Entrepreneurs start to look for ways benefiting from the surpluses by extending the scope of the market in which they operate this inevitably leads to the next level: export
EXPORT
With better organization and production and more intensive use of capital it becomes possible to export goods and services.
ECONOMIES OF SCALE
Economics of scale are the advantages that a larger business has over a smaller one in Terms of being able to produce a larger output at a lower unit cost.
KEY ASPECT: it enables her business to produce a larger output at a lower unit cost
ADVANTAGES
TECHNICAL
Effective techniques are used to produce goods such as the use of automated machinery for mass production purposes imated
COMMERCIAL
Refer to the advantages in the buying and selling of goods, raw materials parts and other purchases.
FINANCIAL
Large firms are able to raise finance more cheaply than smaller firms
MARKETING
Marketing cost are more lower when you produce on a large scale.
INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
Large firms are able to use information technology at a lower unit cost of sale than in small firm.
MANAGEMENT
A larger firm is able to employ a greater number of specialist managers.
RISK-SPREADING
Whereas a small firm will produce or sell in narrow range of products, a large firm is likely to produce and sell a far wider range.
DISECONOMIES OF SCALE
Diseconomies of scale results in increasing output or sales but only at the expense of higher unit costs.
REASONS FOR DISECONOMIES OF SCALE
A firm has become too large to manage effectively
The scale of production is greater than the demand for goods.
Problems that arise from these economies of scale include ineffective communication, staff inertia, losing touch with customers, etc.
CHARACTERISTICS OF COTTAGE INDUSTRY
A cottage industry is one that takes place in people's homes the key distinguishing features of this type of industry include the following:
HOME BASED
People can work from home rather than in a factory
MAINLY MANUAL
Typical people will work with their hands
SMALL-SCALE
The scale of production will be small in contrast the factory production
USES LOCAL RAW MATERIALS
materials will often be sore to locally so that they can be transported easily to family homes
SMALL BUSINESSES
Small businesses play an important role in nation building and serving the needs of people in Caribbean countries, as well as the needs of people across the globe.
MSME
A macro enterprise has between one and five employees
A small enterprise has between 6 and 15 employees
Enterprise has between 16 and 50 employees
FUNCTIONS OF SMALL BUSINESSES
CREATING EMPLOYMENT
MSME provide employment for a large number of people in urban and rural areas. Small firms provide work in many industry, example: retailing, the hotel and catering industry.
PROVIDING SERVICES
MSMEs provide services for larger firms as well as providing services that large firms do not want to provide themselves.
CATERING FOR NICHE MARKETS
Demand may be relatively small and specialized in a niche market, therefore a large firm may find that demand and potential sales are too low for it to target the market.
ADVANTAGES
GENERATE EMPLOYMENT AND INCOMES
small businesses offer individuals the chance to earn income to support themselves and their family.
Necessity entrepreneur: people who become entrepreneurs because they need a national income to get by.
INCREASE COMPETITION FOR LARGER FIRMS
Small businesses provide essential components and supplies for larger businesses The existence of Msme sector means that customers have alternatives to large enterprises where prices may be higher.
Small businesses can supply a local market
Small businesses provide essential components and supplies for a larger businesses
INTRODUCE NEW PRODUCTS AND IDEAS
Being entrepreneurial often involves coming up with new ideas
DISADVANTAGES
The business lacks expertise in certain areas
Owners found it difficult to source finance
Ability to service customers
No benefit from cost advantages
Access to research and development facilities
Less well known
GROWTH
TYPES OF GROWTH
Internal- by investing in new products or selling more of the existing products
External- Involves the takeover of another business, a merger with another business or the creation of a joint venture
TYPES OF INTERNAL GROWTH
OPENING OTHER OUTLETS
Most well known restaurants and hotel chains start from a single premises.
The idea is then introduced to multiple outlets under a single ownership
EMPLOYING MORE WORKERS
If a company wants to grow, it will often take on more staff to deal withh the increased level of business.
INCREASING CAPITAL
A key aspect of growth will be the aquisition of more financial capital in order to invest in better resources and equipment
ESTABLISHING E-COMMERCE
Creating an online trading platform such as a website enables small businnesses to expand organically to a potentional worldwide market without having to open up outlets around the globe
FRANCHISING AND OUTSOURCING
Outsourcing is when a business contracts out some of its work to an outside supplier, who will then make goods or provide a service on behalf of the business.
This makes it possible for a business to grow quickly at a low cost because managing tasks are done by people external to the business.
Franchising allows others to use its business idea, format, logo and products for a share of the profits.
TYPES OF EXTERNAL GROWTH
JOINT VENTURES
A joint business is set up between the two companies .
A business arrangement in which 2 or more priorities agree to pull their resources to accomplish a specific task or a goal.
MERGERS
Went to businesses combined to form a single company.
The shareholders of both businesses retain a shared interest in the new businesses.
TAKEOVERS/AQUISITIONS
An accusation occurs when one business gains control of part of another business. Our business may be prepared to sell off one of its divisions that it no longer wishes to keep nearly
To take over another company, one business will buy up a majority or all the shares in the business it wants to take over. It may offer the shareholders in the company being acquired shares in the new business.
EFFECTS OF GROWTH
when our business grows these will inevitably impact many different parts of the business the main effects are:
LABOUR
More workers will be employed due to more activities and responsibilities
For Micro and small businesses, including those in Cottage Industries, it will be possible to switch from the employment of part-time or casual labor to employing people full-time.
CAPITAL
More fixed and working capital will be acquired and the business may have to seek other sources of financing.
USE OF TECHNOLOGY
More technology will be required to speed up production and lower total costs.
POTENTIAL FOR EXPORT
As sales increased the business can change from the domestic level of production to surplus and export .
LINKAGE INDUSTRY
Industries in an economy are very important in determining how effective that economy is. Some sectors of the economy provide more opportunities to create linkage industries than others.
A linkage industry is one that is connected to another industry because it provides supplies for it, or is a market for its finished product.
an industry will have backward links to other industries as well as forward links.
BACKWARD LINKAGE
When an industry depends on the output from an industry which is at an earlier stage of production.
FORWARD LINKAGE
When one industry or firm supplies another industry or firm further up the supply chain.
the term key sectors of the economy refers to industries that have both strung forward and backward linkages.