Potential physiology exam questions
70% marks, 2 hour exam
SAQ paper, examining all 4 organ systems
Each section will have a weight of 25% each
Section A
—
1. Describe, with the aid of a labelled sketch, the structure and function of the trachea.
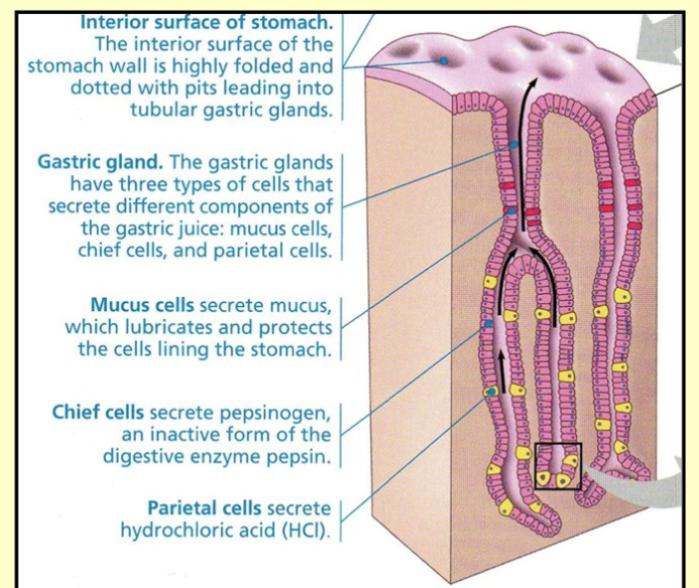
2. Describe how the (i) stomach and (ii) pancreas contribute to the digestion of food in the gastrointestinal tract
Section B
—
3. Describe cardiac pacemaker activity and function.
4. Which factors stimulate the production of aldosterone and explain the effect of increased plasma aldosterone on sodium excretion?
GIT
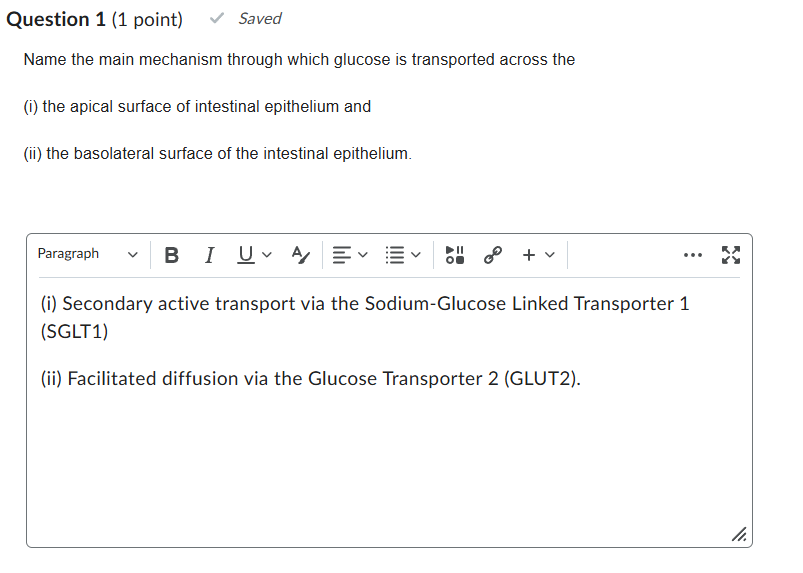
(i) secondary active transport coupled to the sodium gradient (via the sodium/glucose (SGLT1) symporter)
(ii) facilitated diffusion (via glucose (GLUT) transporter)
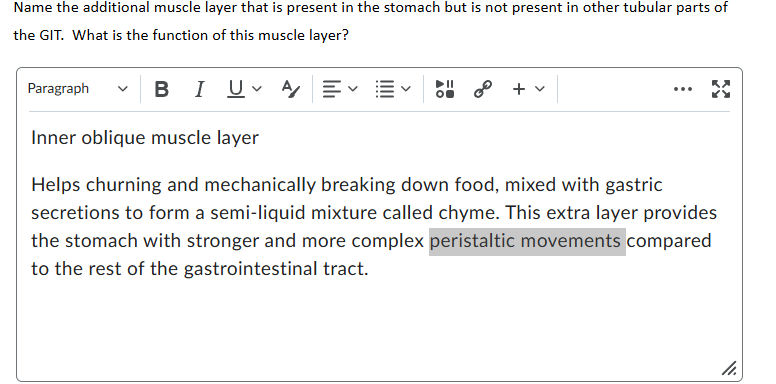
Oblique muscle layer is present in the stomach to facilate churning of chyme
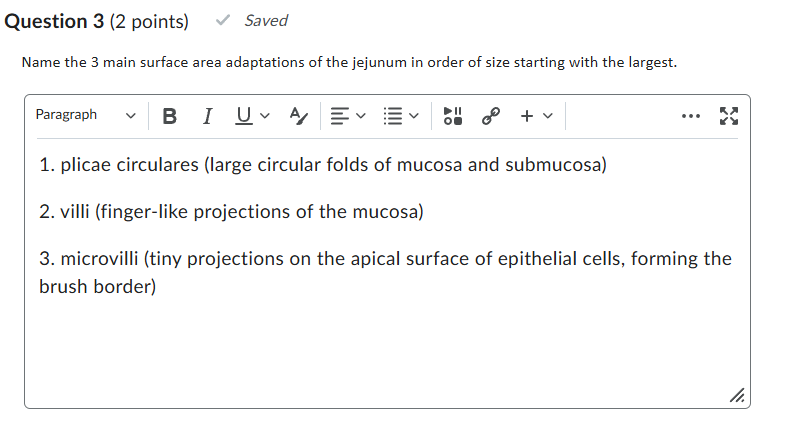
1. Plicae circulares
2. Villi
3. Microvilli
PULMONARY

Ciliated cells help waft mucus out of the lungs
Goblet cells produce mucus and secretion that helps moisten the epithelial surface and trap particulate matter.
Overall the epithelium helps warm, humidify and clean the air.

Higher temp, such as in exercising muscle, reduce the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen. This helps unload oxygen in areas of high metabolic activtiy
Conversely, in areas of slightly lower temp, such as in the lungs, the affinity of haemoglobin for oxygen increases. This helps with the uptake of oxygen and release of CO2

A small amount of oxygen is transported in solution → simply dissolved in the blood
majority of oxygen is transported by binding to haemoglobin in red blood cells
CARDIOVASCULAR
The tricuspid valve functions as a one-way valve that closes during ventricular systole to prevent regurgitation of blood from the right ventricle back into the right atrium. It opens during ventricular diastole, allowing blood to flow from the right atrium into the right ventricle.

Outcomes include decreased cardiac oxygen consumption, reduced pulse pressure, maintenance of large positive pressure in the arterial system throughout the cardiac cycle, maintenance of blood flow through the arterial system during diastole.
The vasa vasorum is a microvascular network that provides blood supply and nourishment for tunica adventitia and outer parts of tunica media of large vessels.
RENAL
1. Presence of second set of arterioles after glomerular capillaries i.e. efferent arterioles which offer resistance to the blood flow.
2. Extensive branching of glomerular capillaries, the increased cross-sectional area results in only minor drop in pressure in glomerular capillaries.
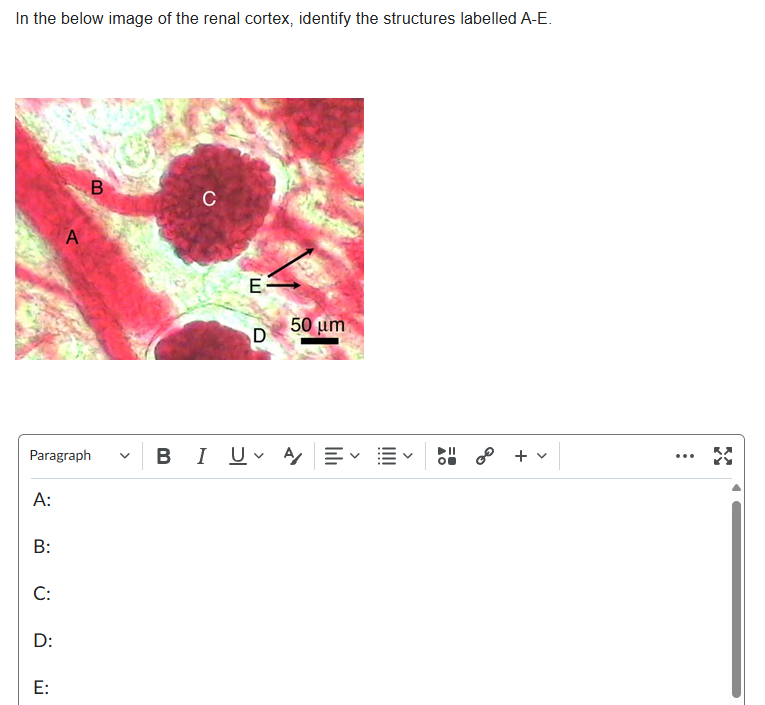
A: Interlobular artery
B: Afferent arteriole
C: Glomerulus
D: Bowman's space
E: Peritubular capillaries


The proximal tubule reabsorbs approximately two-thirds (66%) of the filtered load of sodium (i.e. in this case 10mmol/min of Na+) suggesting that 5mmol/min of Na+ would remain in the tubule at the end of the proximal tubule.