Visual Acuity Study Guide
Ophthalmology → Study of the eye and diseases affecting the eye
Optomologist
Medical school, residency, surgery
Optometrist → OD/Vision correction
Does not go to medical school, but has education on the eye (not medical doctor or perform surgery)
Diagnose and treat refractive disorders (treatment: glasses or contact lenses)
Optician → Certified/glasses
The one who gives you the glasses
Diseases and Refraction Disorders
Conjunctivitis
Pink eye → Contagious inflammation of the conjunctiva (outer covering)
Symptoms → Redness, swelling, pain, draining, pus
Treatment → Antibiotic drops or ointment
Extremely contagious → Prevent by washing hands
Glaucoma
Increased pressure in the eye
Leading cause of blindness
Symptoms → Lose peripheral (side) vision and bad headache
Poor night vision
Aching
Treatment → Medication or surgery
Cataracts
Lens becomes cloudy → Occurs gradually
Symptoms → Blurred vision, halos around lights, vision loss
Treatment → Surgical removal of lens and implant a new lens, glasses, contacts
Diabetic retinopathy
Too much glucose (sugar) and poor circulation to eye → Eye grows new vessels
Treatment → Laser surgery to stop the new vessels
Amblyopia
Lazy eye → Early childhood
Poor vision in one eye
Treatment includes covering the dominant eye and exercises to strengthen the eye → Needs to be treated before 8 or 8 years of age
Myopia
Nearsightedness → Trouble seeing far
Lights rays focus in front of the retina
Hyperopia
Farsightedness → Trouble seeing close
Light rays focus beyond retina
Presbyopia
Loss of the ability to focus on near things
Caused by aging
Astigmatism
Abnormal shape or curve of cornea
Treatment → glasses or contact lenses
Light rays focus on multiple areas of the retina
Parts of the eye
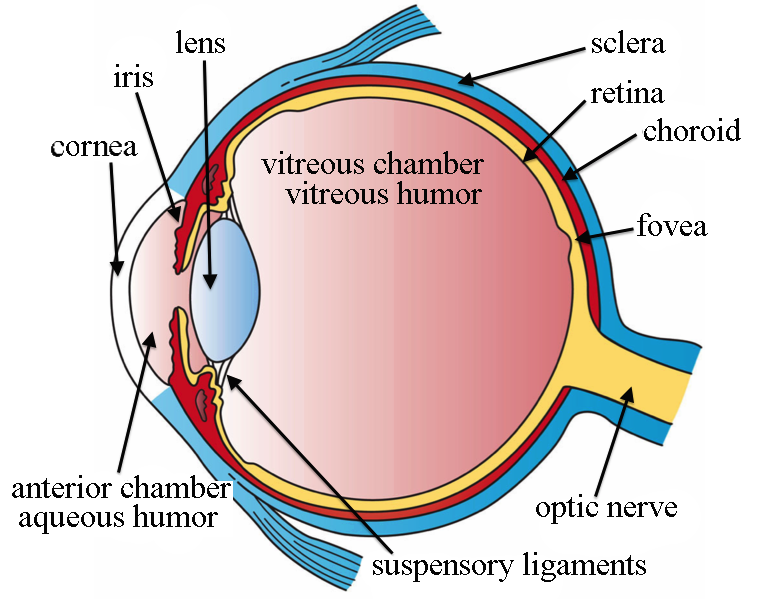
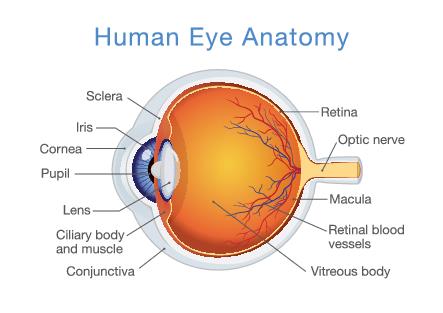
Retina: Back wall of the eye → holds millions of light sensitive cells
Cones: color detecting nerve cells → when damaged, can lead to color blindness
Rods: black and white detecting nerve cells, sense shape and form → when damaged, can lead to poor night vision
Cornea: dome of clear tissue that focuses light
Iris: Colorful part of the eye
Pupil: Opening in the iris that allows light into the eye
Lens: Focuses the light onto the back of the eye → Lens change shape in order to focus on certain objects
Thinner for far away, thicker for close up
Smaller in bright light
Ciliary muscles: muscles that change the shape of the lens
Optic nerve: carries messages to the brain
Brain: Translates the nerve messages into pictures
Sclera: tough white material that covers most of the eye
Tear glands: produces tears
What parts of the eye protect it?
Eyelashes: keep dirt and other unwanted stuff out of the eyes
Eyebrows
Eyelids
Blinking: keeps the eye clean and moist
Depth perception: the ability to judge how near or far objects are
Administering the distance acuity test
Questions to ask students.
Name
Date of birth
Do you wear glasses or contact lenses?
If yes, do you have it with you? If not, can you bring it over?
What eye do you test first
Right (OD)
How many can they miss per line and pass?
One
How many do they miss and have to be retested?
More than one
What do you use to retest?
Goodlite