AP PSYCH UNIT 0
PSYCHOLOGICAL PERSPECTIVES
Behaviorism-
Classical Conditioning: 2 associated stimuli lead to a response (Ivan Pavlov, John B. Watson)
Operant Conditioning: Behaviors shaped/guided by consequences (BF Skinner)
Observational Learning: Model leads to mimic (Albert Bandura)
Psychodynamic-
How behavior springs from unconscious drives and conflicts from childhood (Sigmund Freud, alfred alder)
Socio/Cross Cultural-
How behavior and thinking vary across situations and cultures (Phillip Zimbardo, walter mischel)
Evolutionary-
How natural selection promotes perpetuation of genes (Konrad Lorenz; mating, animals following who they first see (imprint))
Brain is prewired for survival
Biological/Neuroscience-
How body and brain enable emotions, memories, sensory experiences
structures, neurons, hormones, neurotransmitters (Sperry and Gazzaniga)
Humanism-
Individual growth and self development vs. the collective (Carl Rogers, Maslow)
self actualization= potential
love is the number one need for human beings
Cognitive-
THINKING
encoding, processing, storing/retrieving, perception, memory, attention, problem solving
Irrational/illogical > Rational/logical
CBT; changing thinking approach (Albert Ellis, Aaron Beck)
TYPES OF BIAS
Hindsight Bias-
The tendency to after hearing about findings think/say they knew it all along
Experimenter Bias-
Unconscious tendency where researches treat subjects of experimental and control groups differently to increase chance of proving hypothesis correct
Not conscious, if experimenter purposely changes data, it is fraud
Social Desirability Bias-
people responding how they presume the researcher wants them to
Self-Report Bias-
people reporting their own behavior inaccurately
researchers pair surveys with other means to measure behavior bc of this
Small changes in words can also affect bias
Sampling Bias
when not everyone has the same chance to be chosen
should be representative of the population
Experimental Method
Starts with a theory that explains behaviors or events by offering ideas that summarizes and simplifies observations.
Leads to hypothesis, a testable prediction which specifies which results would support/disconfirm it.
Must be given with operational definitions, carefully worded statement of exact procedures so ANYONE can replicate study.
Non-experimental Methods
* Can draw conclusions from these but not causation
Case Study-
examines individuals/groups to reveal things as a whole
may be misleading because of personal stories, may not apply to everyone
ex.: brain damage, animal intelligence, children’s minds
Naturalistic Observation-
Observing and recording naturally occurring behavior w/out manipulation
easy to use w/social media and smart devices
DESCRIBES behavior, not explain
Survey-
self reported attitudes/behaviors by questioning a random sample of the group
people share answers to be socially acceptable, * be aware of bias
Random Sampling-
choosing a sample where the entire populations has an equal chance of being in the sample
Larger=better but only if representative, cannot compensate w/more people
Number names or RNG, don’t send out not everyone answers
Correlation
non experimental research that describes relationship between 2(+) variables
measure of the extent to which 2 factors vary together, how well they predict each other
Correlation Coefficient
Helps us know how well each other predict the other one
from -1 to 1, least strong is closest to 0
Scatterplots
used to show how variables relate
Strong positive: one increases and so does other
Strong negative: one increases other decreases
* Correlational research has directionality problem; cannot tell what causes or effects, could be reversed; may also have 3rd variable
Illusory Correlations
belief that there is actually a relationship between something
uncontrollable evens are fed by regression toward the mean; result will move towards average result next time
Experimentation
used to establish cause and effect by manipulating factors using random assignment
uses experimental group where they receive treatment
control group where they don’t
randomly assigning people to equalize groups and if they differ they can see effect
Placebo
Participants uninformed- single blind
participants and administrators uninformed- double bind
thinking you are getting treatment will relieve symptoms (placebo)
Cofounding variables- other factors that can influence the study
Accounted for with random assignment
Validity- extent to which a test measures what its supposed to
Ethical Guidelines
APA Guidelines-
obtain participants informed consent
protect participants from greater than usual harm
keep info confidential
fully debrief (explain research)
must be voluntary
no coercion
Animal Guidelines
humane care and housing
least suffering possible
animal acquired humanly and legally
Descriptive Statistics
- Numerical Data used to measure and describe characteristics, measures of tendency and variation
Mode- most frequently occuring
mean- arithmetic average
median- middle number of ranked numbers
%tile- % of scores below given score
Range- difference btwn highest and lowest number
SD- computed measure on how much scores deviate from mean
Positively skewed- one high (more positive) outlier
Negatively skewed- one low (more negative) outlier
Bell Curve
most scores fall near mean, fewer at extremes
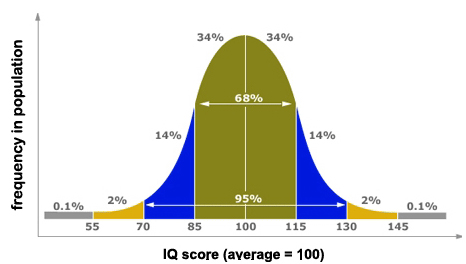
Inferential Statistics
Meta Analysis- statistic procedure for analyzing multiple studies to reach overall conclusion
Statistical Significance- how likely our results from a study occured by chance, strive for .05 chance
P-value- probability of no differences in between the hypotheses
Effect size- strength of relationship btwn 2 variables, larger effect size more one variable can be explained