AP Physics Summer Work
Scalars: A quantity (magnitude) w/out direction.
Ex) Distance: The total length traveled by an object, independent of the direction.
Just add to find the total distance
Speed: How fast/slow an object is moving; the total distance traveled in a certain time.
Vectors: A quantity that has both magnitude and direction.
Ex) Displacement: change in the position of an object (path does not matter).
Displacement is relative to an axis: ‘x’ is horizontal displ. and ‘y’ is vertical displ.
Displacement = Final - Initial; Δx = xf - xi or Δy = yf - yi
Directions are either positive or negative, or in angles.
To add, you have to use vector rules. (Use Pythagorean theorem)
Velocity: How fast the position of an object changes; the rate of change of displacement; describes the speed of an object with its direction.
Negative velocity indicates direction, not speed.
The direction of velocity and displacement always match.
Force: The interaction between two objects; either a push or pull.
A net force is what causes all accelerations.
Net Force: The sum of all forces acting upon an object.
A net force of 0 means that there is no change in motion, or no acceleration; this means that all forces acting on an object are balanced.
If the net force is greater than 0, it means that the forces are unbalanced; there is a change in velocity, or the object is accelerating.
Acceleration: change in velocity; the rate at which an object’s velocity changes.
NOT AN INDICATION OF SPEED.
Only measures changes in velocity (speeding up or slowing down), or direction.
Equation (only holds for constant acceleration):
Constant velocity means that the acceleration is 0; meaning there is no change in the current motion of the object.
Constant acceleration means that the rate at which the velocity of an object changes is constant over a duration.
The velocity and displacement of an object will always be in the same direction.
If the direction of the velocity and acceleration are the same, then the object is speeding up in that direction; if they are not the same, then the object is slowing down in the direction of the velocity.
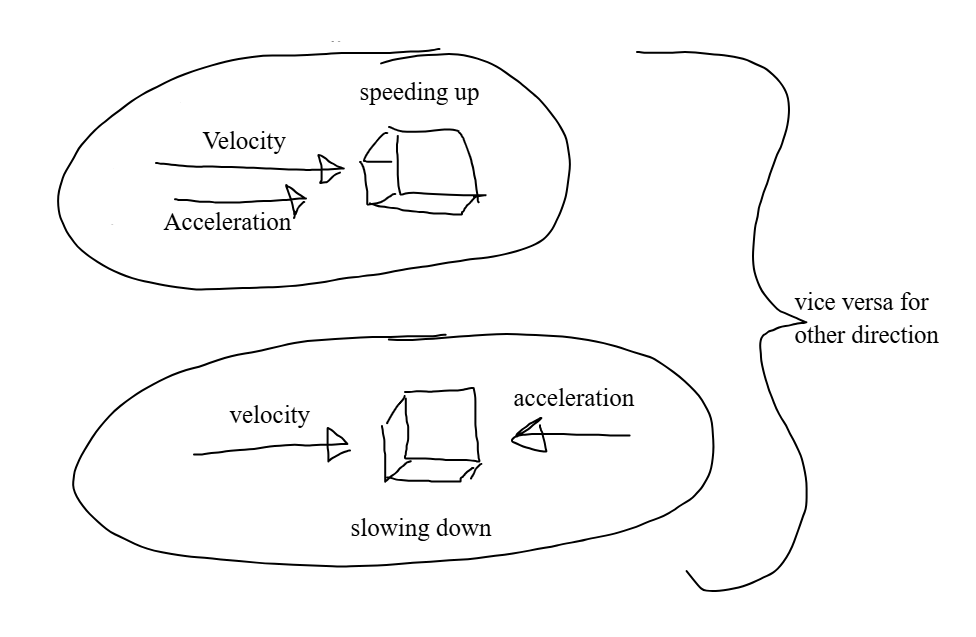
BE SPECIFIC WHEN DESCRIBING THE ACCELERATION OF AN OBJECT.
Formula: “speeding up/slowing down in the positive/negative direction.”