
Muscles Study Guide (copy)
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________. Different fascicle arrangements include:
- ______________________________(e.g., sartorius): Muscles have fascicles running parallel to the long axis, providing extensive range of motion but less power.
- ______________________________(e.g., rectus femoris): Fascicles attach obliquely to a central tendon. This structure allows for greater power but limits range of motion.
- ______________________________(e.g., pectoralis major): Fascicles converge from a broad area to a single tendon, offering versatility in muscle movement.
- ______________________________(e.g., orbicularis oris): Fascicles are arranged in concentric rings, useful for closing openings like the mouth or eyes.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________: The primary muscle responsible for generating a specific movement (e.g., biceps brachii for elbow flexion).
- Antagonist: The muscle that ______________________________the movement of the ______________________________(e.g., triceps brachii for elbow extension).
- Synergist: ______________________________the agonist by providing ______________________________force or ______________________________ unwanted movement (e.g., brachialis assisting the biceps brachii).
- ______________________________: Stabilizes the origin of the agonist, enabling it to function more effectively (e.g., muscles of the shoulder girdle stabilizing the scapula).
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
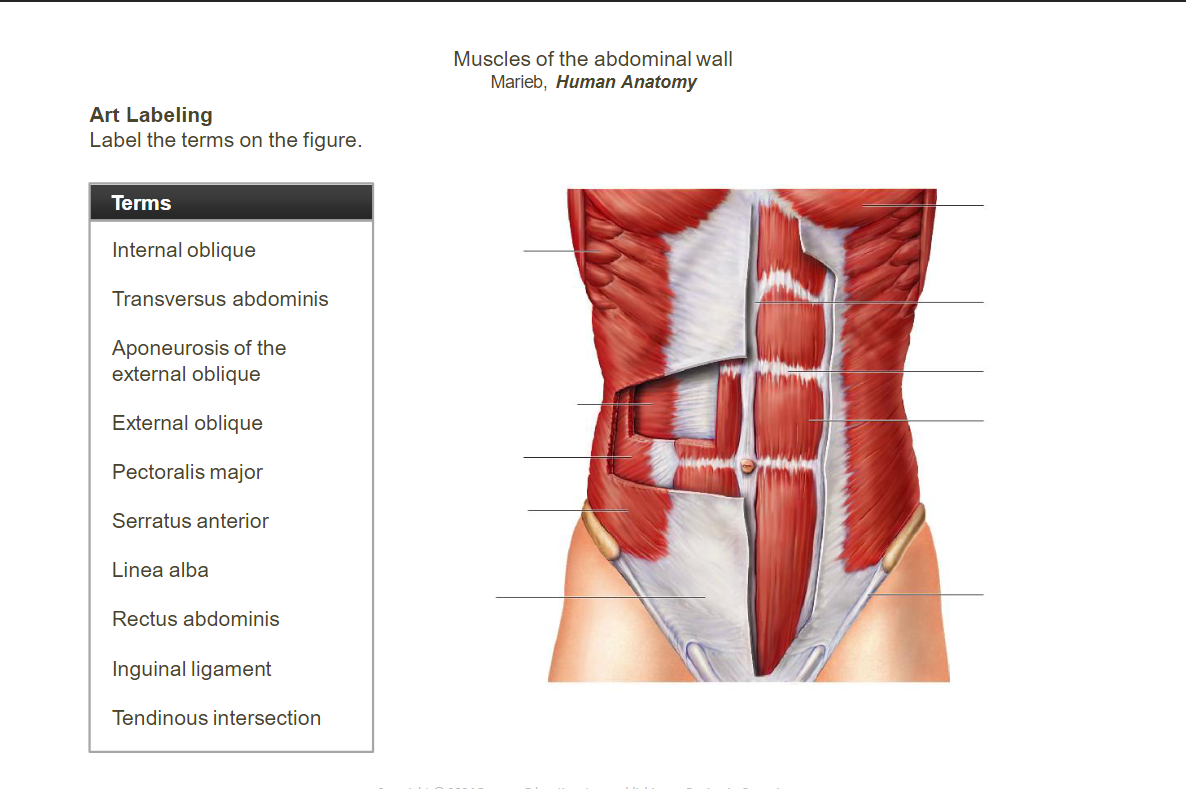
The axial muscles include those located on the __________________________________________________________________________________________, while appendicular muscles are associated with the ______________________________. Use models and diagrams to study the location of these muscles.
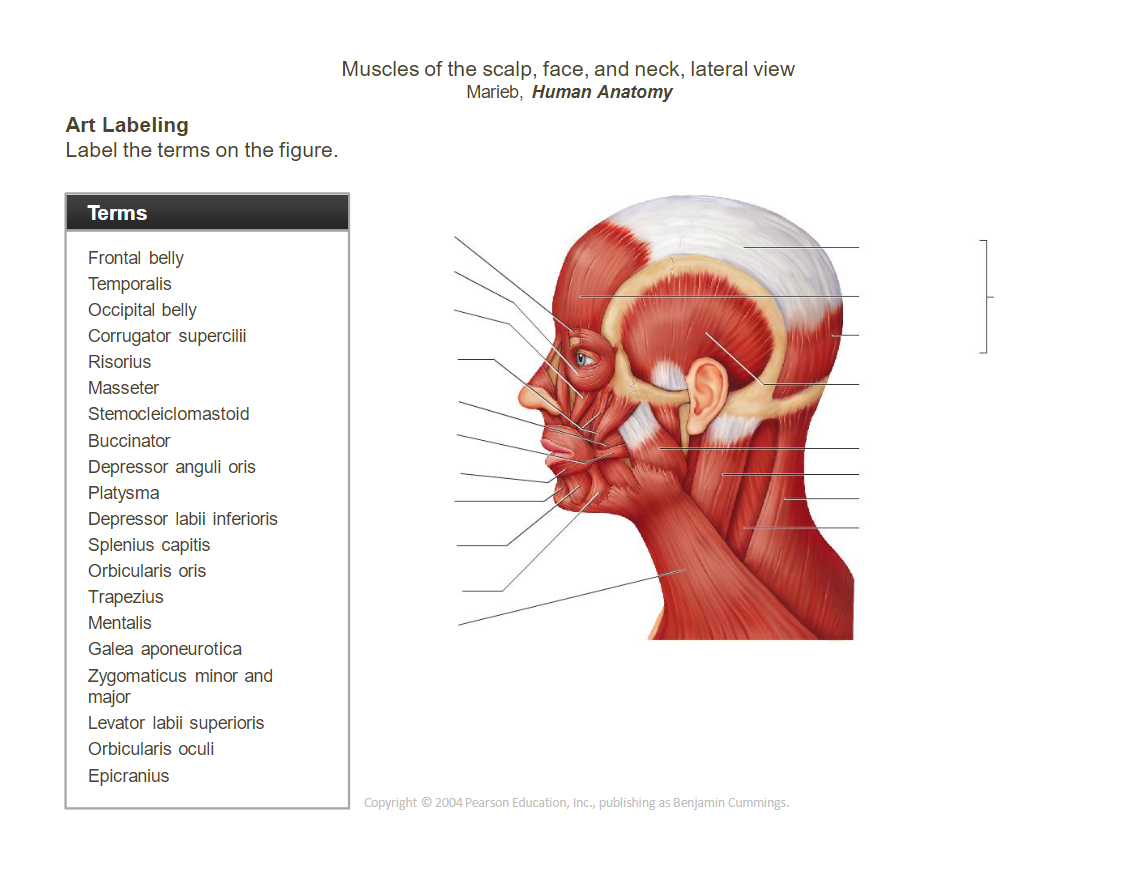
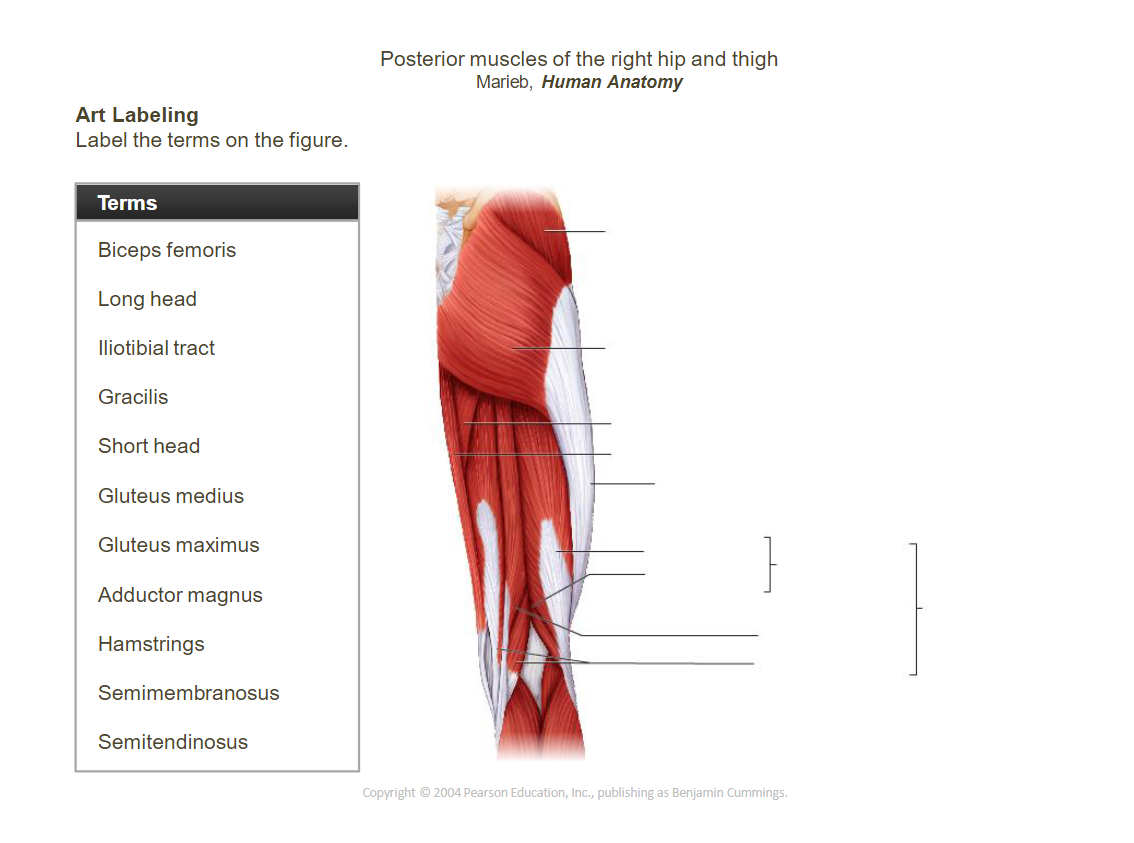
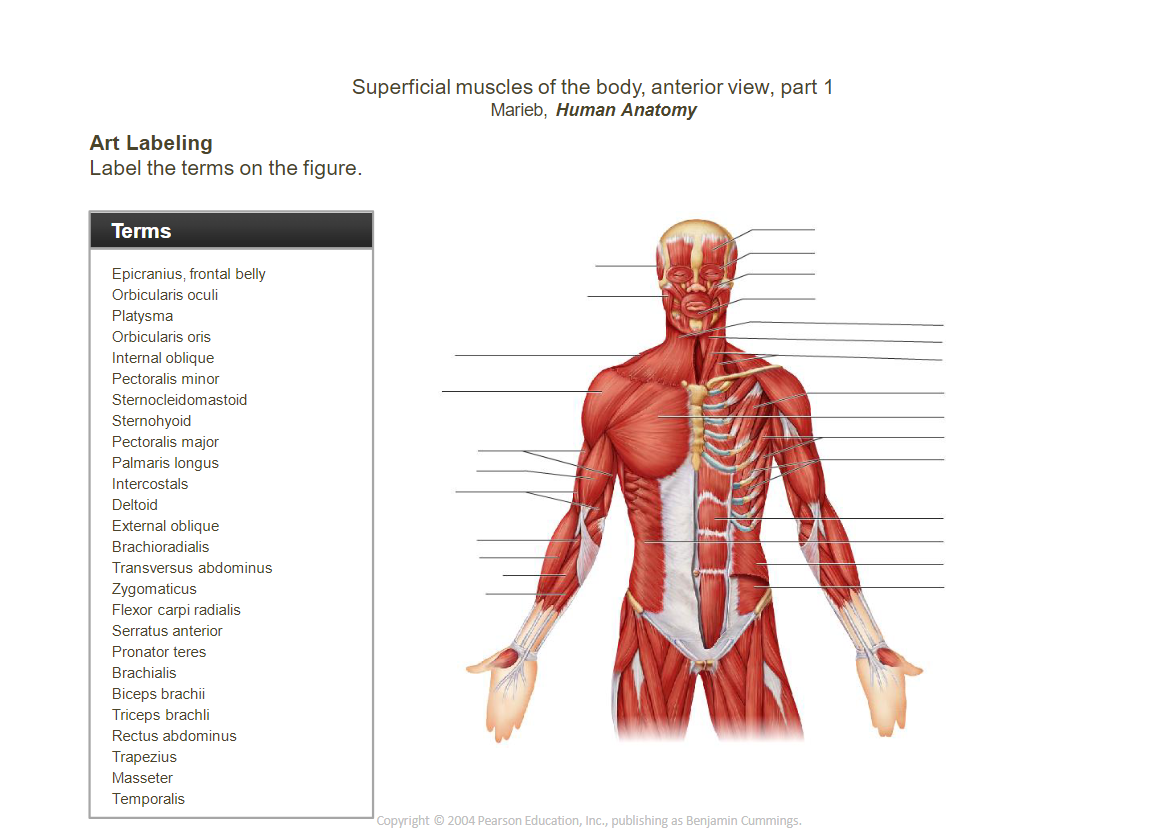
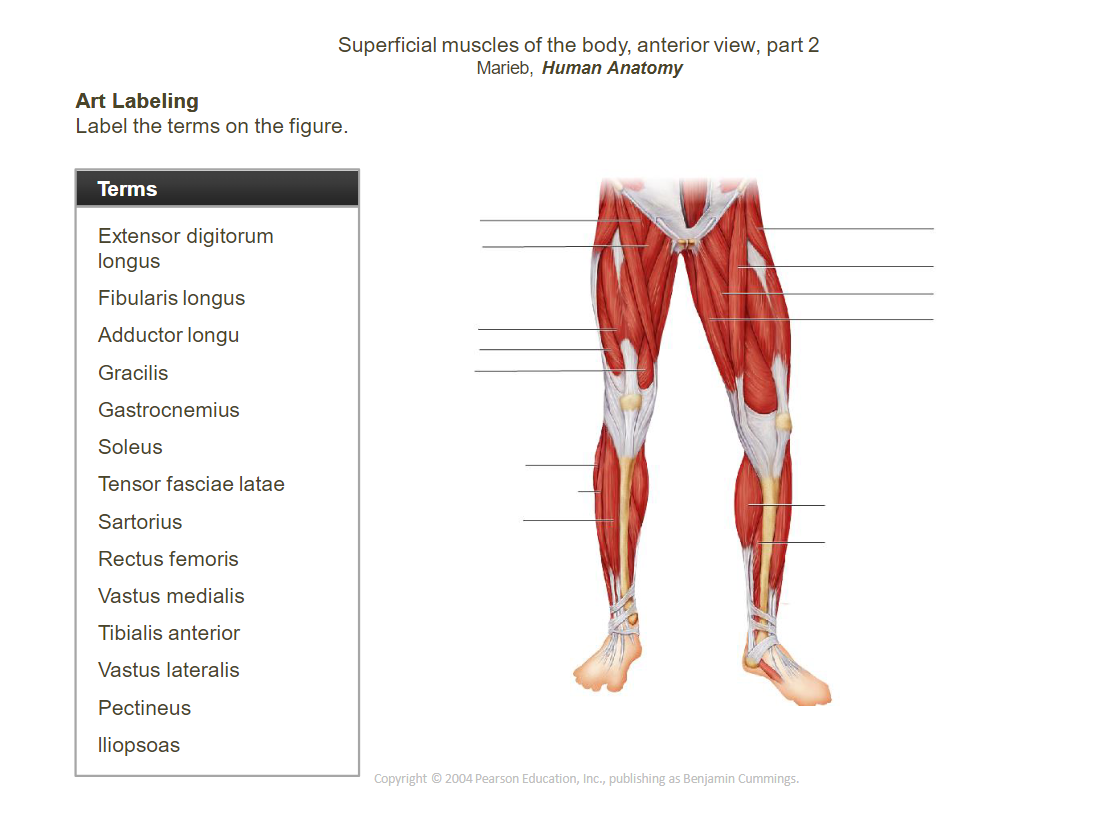
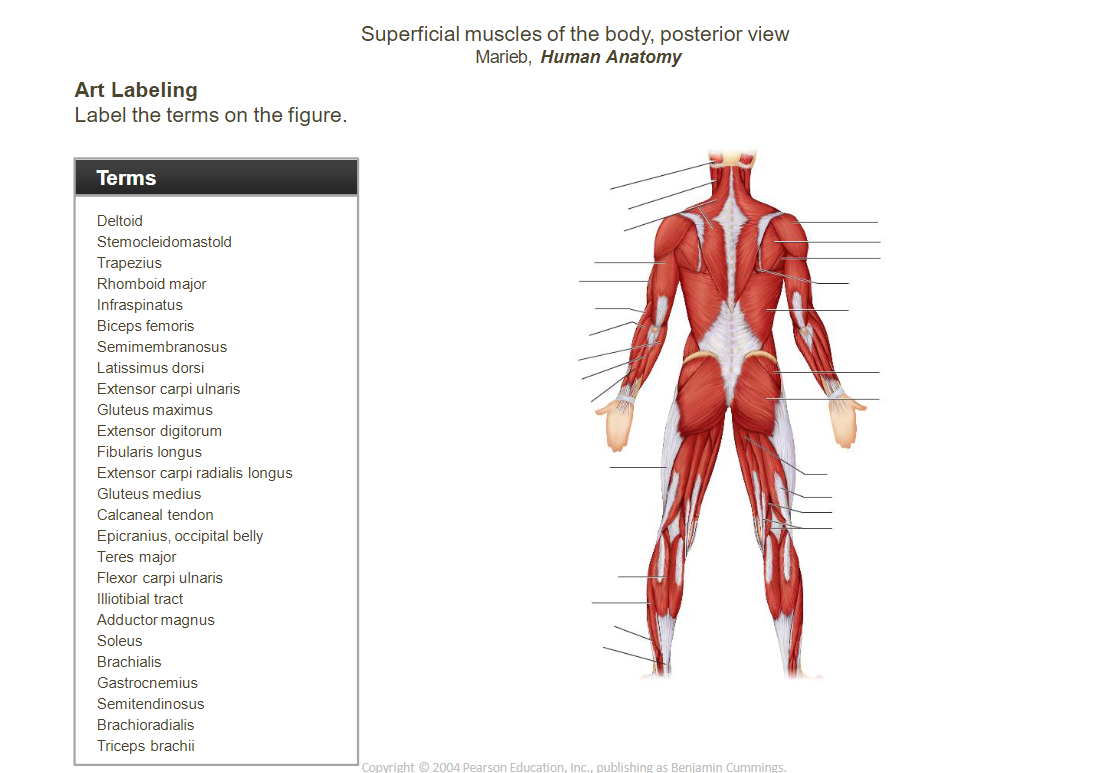
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Occipitofrontalis (epicranius):
- ______________________________belly: Raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead.
- ______________________________belly: Pulls scalp backward.
- ____________________________________________________________: Closes the eye (blinking, squinting).
- ____________________________________________________________: Closes and protrudes the lips (kissing muscle).
- ____________________________________________________________: Elevates upper lip (smiling).
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Elevates the corners of the mouth (smiling).
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Lowers corners of the mouth (frowning).
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Lowers lower lip.
- ______________________________: Elevates and retracts the mandible (chewing).
- ______________________________: Elevates the mandible (chewing).
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes neck, rotates head.
- ______________________________: Elevates, retracts, and rotates the scapula.
- ______________________________intercostals: Elevate ribs during inhalation.
- ______________________________intercostals: Depress ribs during forced exhalation.
- Pectoralis ______________________________: Adducts and medially rotates the arm.
- Pectoralis ______________________________: Stabilizes the scapula by drawing it anteriorly.
- ____________________________________________________________: Protracts and rotates the scapula.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the arm.
- ______________________________: Prime mover for inhalation, contracts to flatten and enlarge the thoracic cavity.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the vertebral column.
- ____________________________________________________________: Fibrous structure running down the midline of the abdomen.
- ______________________________obliques: Flex and rotate the vertebral column.
- ______________________________obliques: Flex and rotate the vertebral column.
-____________________________________________________________: Retracts and elevates the scapula.
- ______________________________: Laterally rotates the arm.
- ______________________________: Abducts the arm.
- ______________________________: Medially rotates the arm.
- Teres ______________________________: Medially rotates and adducts the arm.
- Teres ______________________________: Laterally rotates the arm.
- ______________________________: Abducts the arm.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the elbow, supinates the forearm.
- ______________________________: Flexes the elbow.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the elbow.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the forearm.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Extends and abducts the wrist.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the fingers.
-__________________________________________________________________________________________: Extends and adducts the wrist.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Flexes and adducts the wrist.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the wrist.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Flexes and abducts the wrist.
- ____________________________________________________________: Pronates the forearm.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends and laterally rotates the thigh.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Abducts and medially rotates the thigh.
- ____________________________________________________________: Provides stability to the knee.
- ______________________________: Adducts the thigh.
- ______________________________: Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates the thigh.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the knee and flexes the thigh.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the thigh, flexes the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the thigh, flexes the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the thigh, flexes the knee.
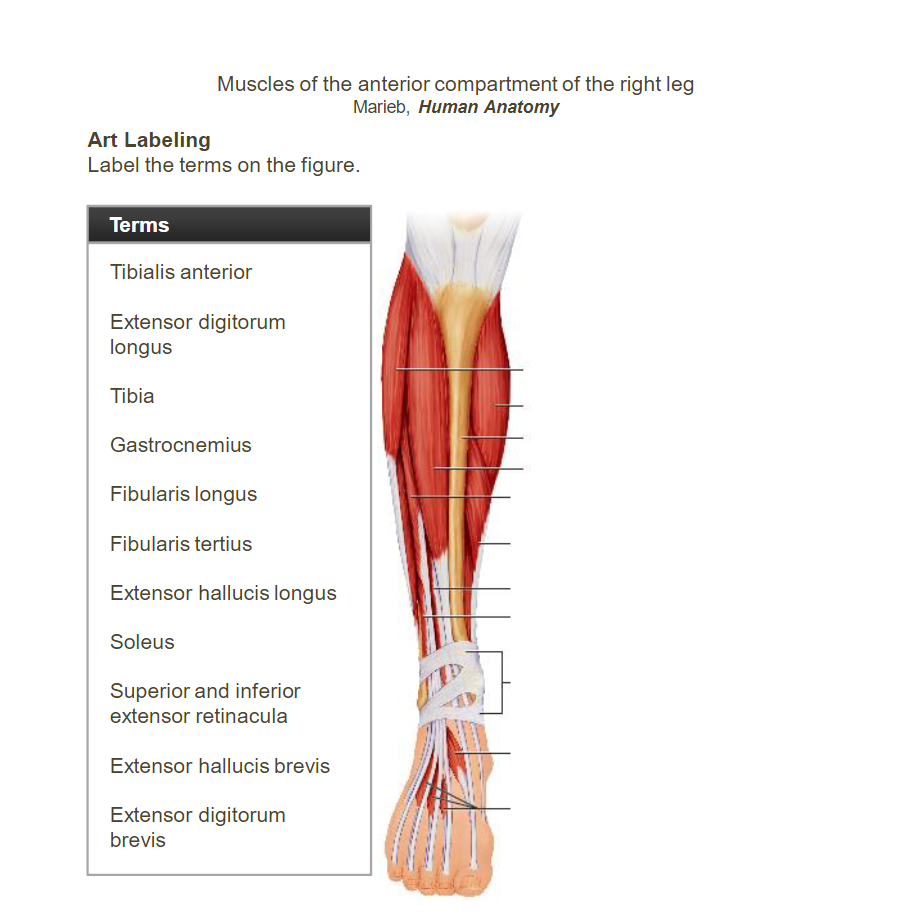
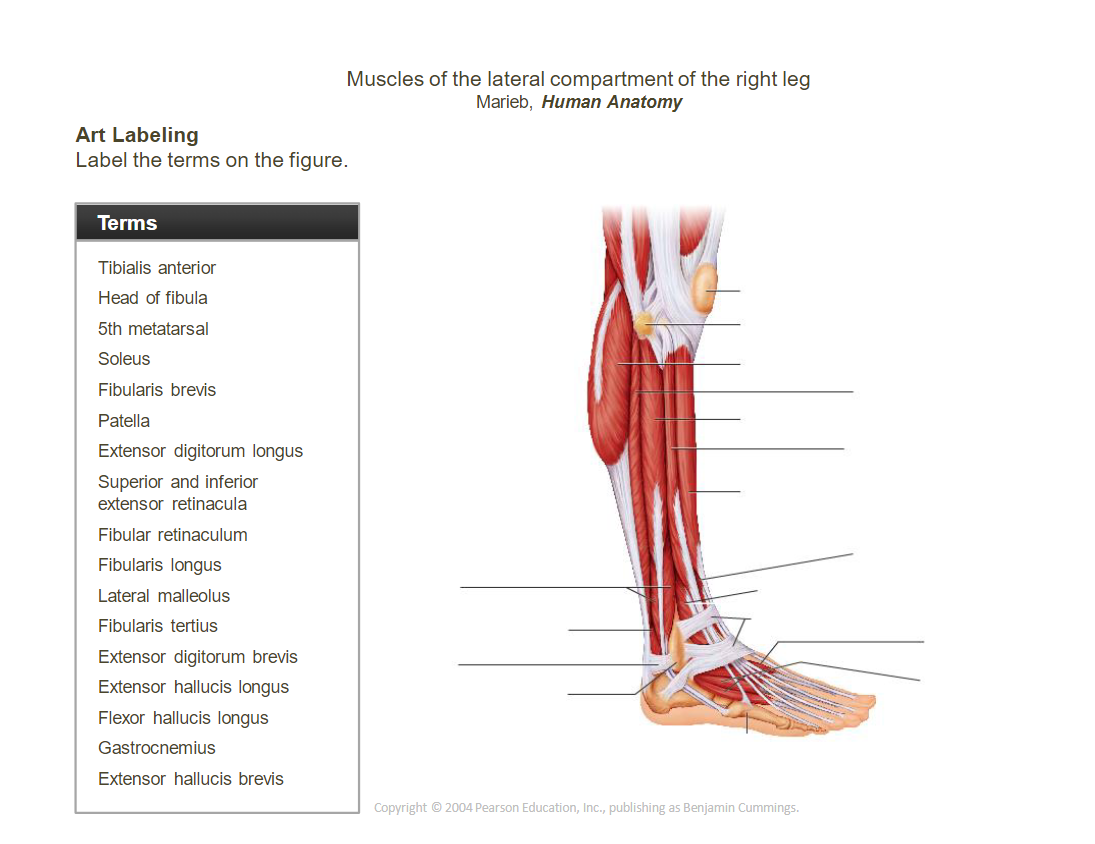
- ____________________________________________________________: Dorsiflexes and inverts the foot.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Extends the toes, dorsiflexes the foot.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Everts and plantarflexes the foot.
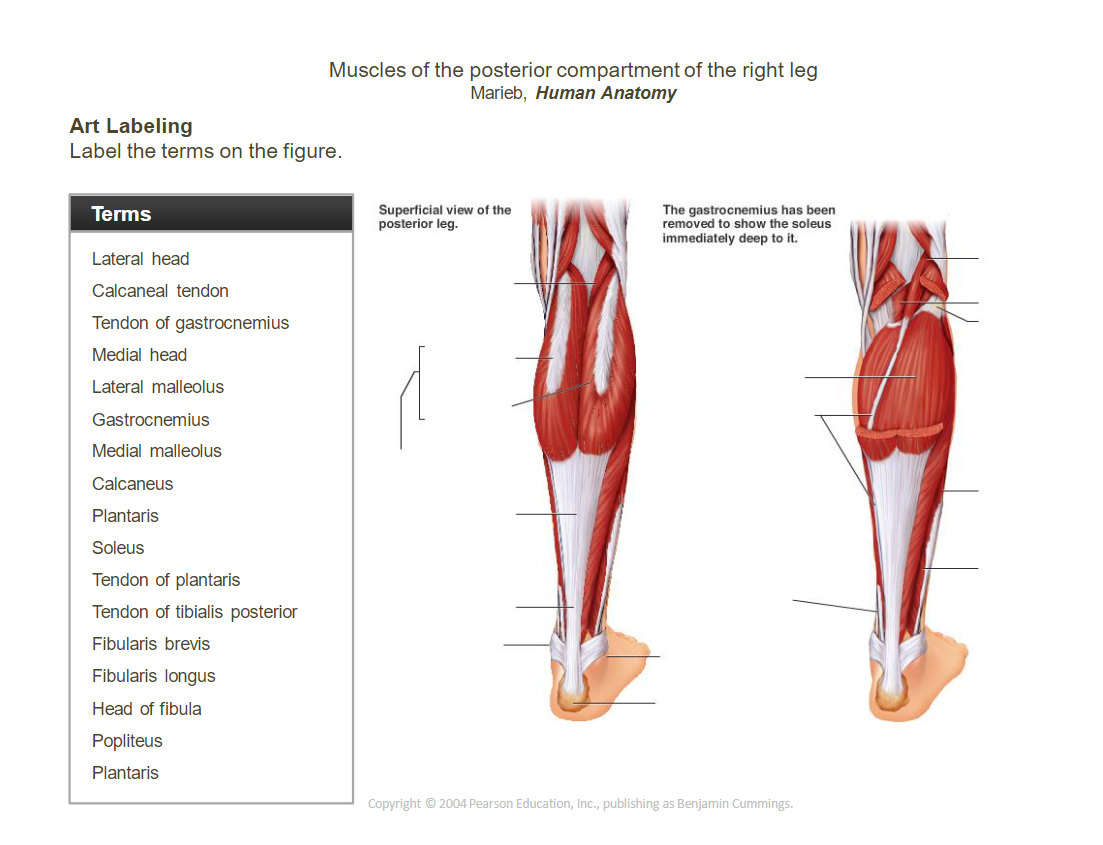
- ______________________________: Plantarflexes the foot.
- ____________________________________________________________: Plantarflexes the foot, flexes the knee.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Connects the gastrocnemius and soleus to the heel bone, aiding in plantarflexion.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________. Different fascicle arrangements include:
- ______________________________(e.g., sartorius): Muscles have fascicles running parallel to the long axis, providing extensive range of motion but less power.
- ______________________________(e.g., rectus femoris): Fascicles attach obliquely to a central tendon. This structure allows for greater power but limits range of motion.
- ______________________________(e.g., pectoralis major): Fascicles converge from a broad area to a single tendon, offering versatility in muscle movement.
- ______________________________(e.g., orbicularis oris): Fascicles are arranged in concentric rings, useful for closing openings like the mouth or eyes.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
- ____________________________________________________________: The primary muscle responsible for generating a specific movement (e.g., biceps brachii for elbow flexion).
- Antagonist: The muscle that ______________________________the movement of the ______________________________(e.g., triceps brachii for elbow extension).
- Synergist: ______________________________the agonist by providing ______________________________force or ______________________________ unwanted movement (e.g., brachialis assisting the biceps brachii).
- ______________________________: Stabilizes the origin of the agonist, enabling it to function more effectively (e.g., muscles of the shoulder girdle stabilizing the scapula).
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
The axial muscles include those located on the __________________________________________________________________________________________, while appendicular muscles are associated with the ______________________________. Use models and diagrams to study the location of these muscles.









_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Occipitofrontalis (epicranius):
- ______________________________belly: Raises eyebrows, wrinkles forehead.
- ______________________________belly: Pulls scalp backward.
- ____________________________________________________________: Closes the eye (blinking, squinting).
- ____________________________________________________________: Closes and protrudes the lips (kissing muscle).
- ____________________________________________________________: Elevates upper lip (smiling).
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Elevates the corners of the mouth (smiling).
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Lowers corners of the mouth (frowning).
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Lowers lower lip.
- ______________________________: Elevates and retracts the mandible (chewing).
- ______________________________: Elevates the mandible (chewing).
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes neck, rotates head.
- ______________________________: Elevates, retracts, and rotates the scapula.
- ______________________________intercostals: Elevate ribs during inhalation.
- ______________________________intercostals: Depress ribs during forced exhalation.
- Pectoralis ______________________________: Adducts and medially rotates the arm.
- Pectoralis ______________________________: Stabilizes the scapula by drawing it anteriorly.
- ____________________________________________________________: Protracts and rotates the scapula.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends, adducts, and medially rotates the arm.
- ______________________________: Prime mover for inhalation, contracts to flatten and enlarge the thoracic cavity.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the vertebral column.
- ____________________________________________________________: Fibrous structure running down the midline of the abdomen.
- ______________________________obliques: Flex and rotate the vertebral column.
- ______________________________obliques: Flex and rotate the vertebral column.
-____________________________________________________________: Retracts and elevates the scapula.
- ______________________________: Laterally rotates the arm.
- ______________________________: Abducts the arm.
- ______________________________: Medially rotates the arm.
- Teres ______________________________: Medially rotates and adducts the arm.
- Teres ______________________________: Laterally rotates the arm.
- ______________________________: Abducts the arm.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the elbow, supinates the forearm.
- ______________________________: Flexes the elbow.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the elbow.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the forearm.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Extends and abducts the wrist.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the fingers.
-__________________________________________________________________________________________: Extends and adducts the wrist.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Flexes and adducts the wrist.
- ____________________________________________________________: Flexes the wrist.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Flexes and abducts the wrist.
- ____________________________________________________________: Pronates the forearm.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends and laterally rotates the thigh.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Abducts and medially rotates the thigh.
- ____________________________________________________________: Provides stability to the knee.
- ______________________________: Adducts the thigh.
- ______________________________: Flexes, abducts, and laterally rotates the thigh.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the knee and flexes the thigh.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the thigh, flexes the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the thigh, flexes the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Extends the thigh, flexes the knee.
- ____________________________________________________________: Dorsiflexes and inverts the foot.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Extends the toes, dorsiflexes the foot.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Everts and plantarflexes the foot.
- ______________________________: Plantarflexes the foot.
- ____________________________________________________________: Plantarflexes the foot, flexes the knee.
- __________________________________________________________________________________________: Connects the gastrocnemius and soleus to the heel bone, aiding in plantarflexion.
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________