AICE carbohydrates unit 2 part one
General formula- (CH2O)n
n = number of carbons
ratio- equal numbers of C and O with twice H (ex C6H12O6)
most abundant biological molecule.
most ends in “-ose”
3 main types:
Monosaccharides (monomer)
Disaccharides (polymer)
Polysaccharides (polymer)
Monosaccharides
white, water-soluble, polar, solids.
Classified by # of C
5 C - pentose
6 C - hexose
Are straight chains or rings
Most common: glucose (hexose)
Main functions:
source of energy for cell respiration (broken O-H bonds release energy)
most important sugar in energy metabolism: glucose
building blocks for larger molecules
Hexose sugars to know:
Glucose- “blood sugar” immediate source of energy in cell respiration (OH on left is on bottom)
Galactose- found in dairy products (OH on left is on top)
Fructose- found in honey/fruits (pentagon shape)
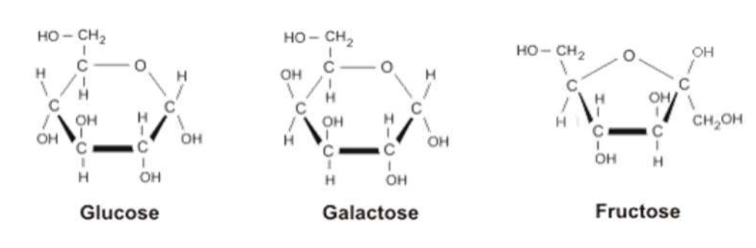
Numbering carbons: clockwise
Alpha glucose: hydroxyl on C1 points DOWN
Beta glucose: hydroxyl on C1 points UP
Disaccharides:
2 monosaccharides combined via condensation reaction
1 mono. loses a H atom and the other loses a hydroxyl group
forms a glycosidic bond
3 common disaccharides
Sucrose- (glucose + fructose)
common table sugar, and food reserve in plants
Lactose- (glucose + galactose)
sugar in mammal milk
Maltose- (glucose + glucose)
1st product of starch digestion, broken down to glucose later
Polysaccharides:
long chains of mono. combined by condensation reactions
NOT water soluble
good for long-term storage or energy or strong structures
Glycogen:
energy storage in animals and fungi
chain of Alpha glucose linked by glycosidic bonds
1-4 links, with 1-6 links that form branches
HIGHLY BRANCHED
Starches:
energy storage in plants
chain of Alpha glucose with glycosidic bonds
not soluble in water
mixture of amylose and amylopectin
amylose- linear, unbranched, Alpha glucose molecules, with ONLY 1-4 glycosidic bonds
amylopectin- branched chains of Alpha glucose with 1-4 AND 1-6 glyco. bonds
Cellulose:
most abundant organic molecule
plant cell walls
Beta glucose with 1-4 glycosidic bonds, NO BRANCHES, long strands, hydrogen bonds hold strands together to form fibers.
difficult to digest (only cows and termites have the gut to digest cellulose)
the molecules are rotated 180 degrees next to each other.
the straight chains that form bundles- microfibrils