Matter
Definition
Everything around us that has mass is matter, and matter has 3 states, which are solid, liquid and gas
Solid
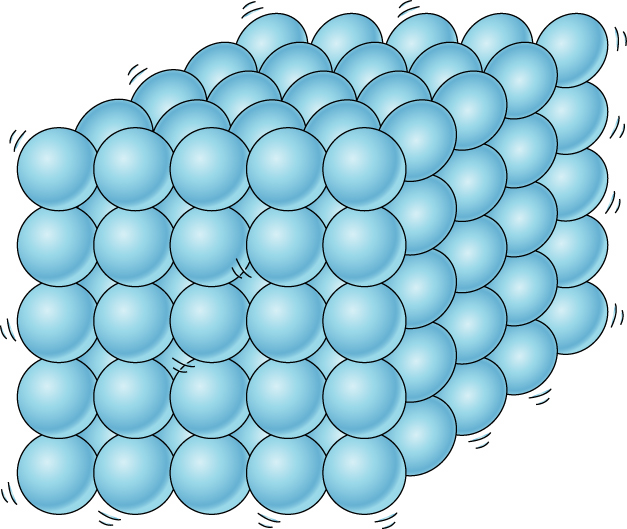
Particles in a solid structure are closely packed and rigidly arranged, and they cannot flow. Thus, they have a fixed shape. The force of attraction between particles are very strong.
Examples: ice, wood, metals, rocks, glass, concrete
Liquids
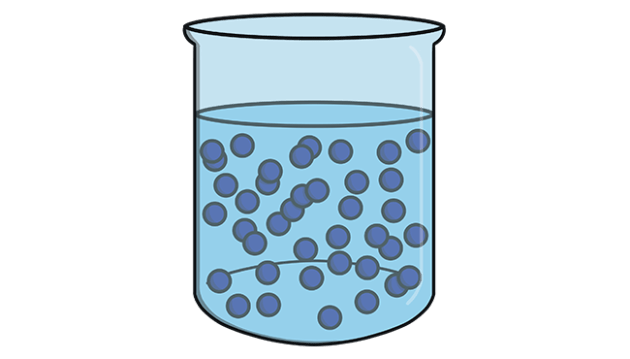
Particles are closely packed, but they are less rigid than solids. They can flow and thus, don’t have a fixed shape because they follow the shape of the container. The forces of attraction between particles are weaker than solids.
Example: water, oil, alcohol, mercury, blood, gasoline
Gas
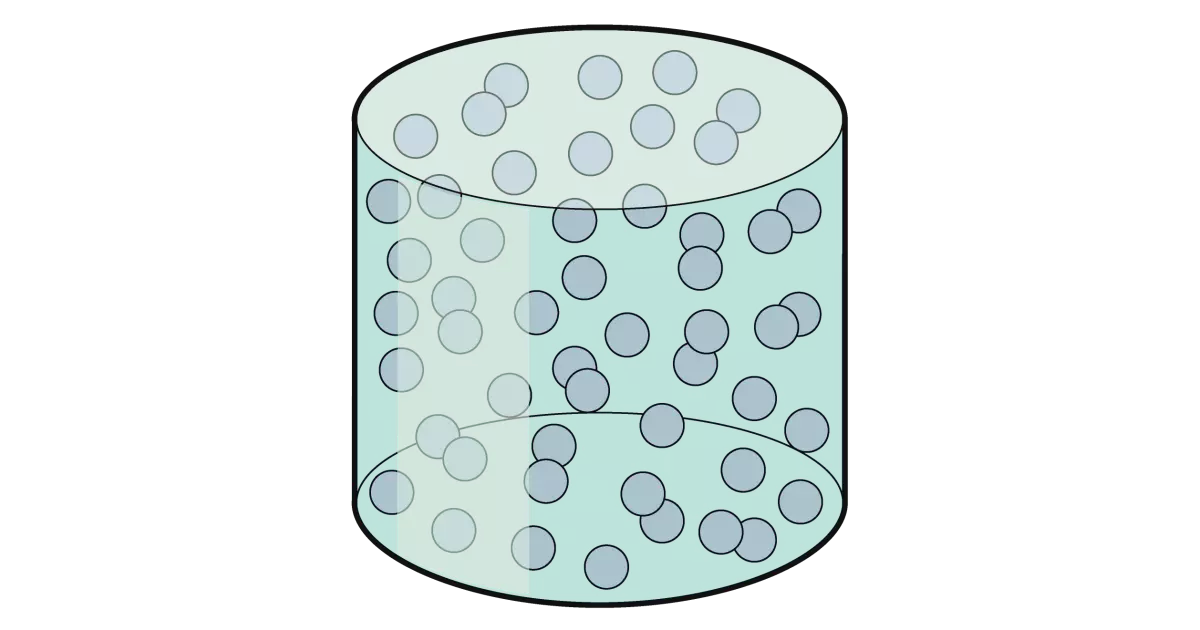
They are randomly arranged and not closely packed, and there are a lot of empty spaces between particles. They can flow more freely than liquids, and also follow the shape of their container. The forces of attraction are very weak.
Examples: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon dioxide, helium, argon
Changing States
Solid → Gas = Sublimation
Gas → Solid = Deposition
Solid → Liquid = Melting
Liquid → Solid = Freezing
Gas → Liquid = Condensation
Liquid → Gas = Evaporation