( Chapter 3 - Carbon and Life ) 9.02
Review -
╭ what we need to know is how the different structures of carbon behave and function
( . Monomers + Polymers )
need to already know prefixes
polymers are long chains of REPEATING monomer SUBunits.
atom v molecules
atom - single unit of element «—
molecule - more than one atom stuck together «—
monomers include SIMPLE sugars, amino acids, & nucleotides
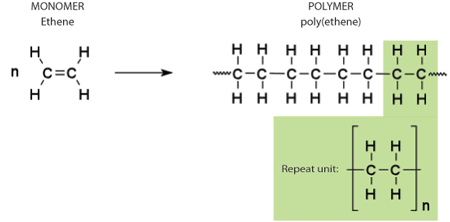
«INTRO TO ORGANIC MOLECULES AND THEIR POLYMERS
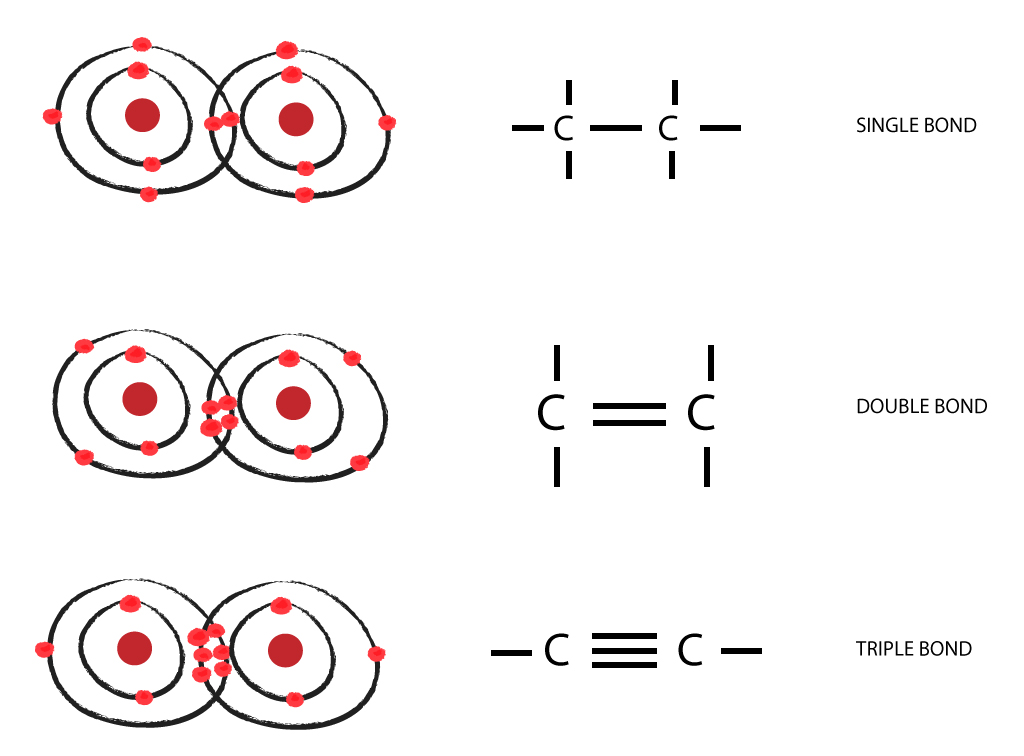
→ carbon can form up to 4 covalent bonds
leading to formation of diverse chains or backbones
chains have different functions

HYDROXYL
→ Polar(disolved in water), sticks with hydrogen bonds,

CARBONYL
→ C-C=O
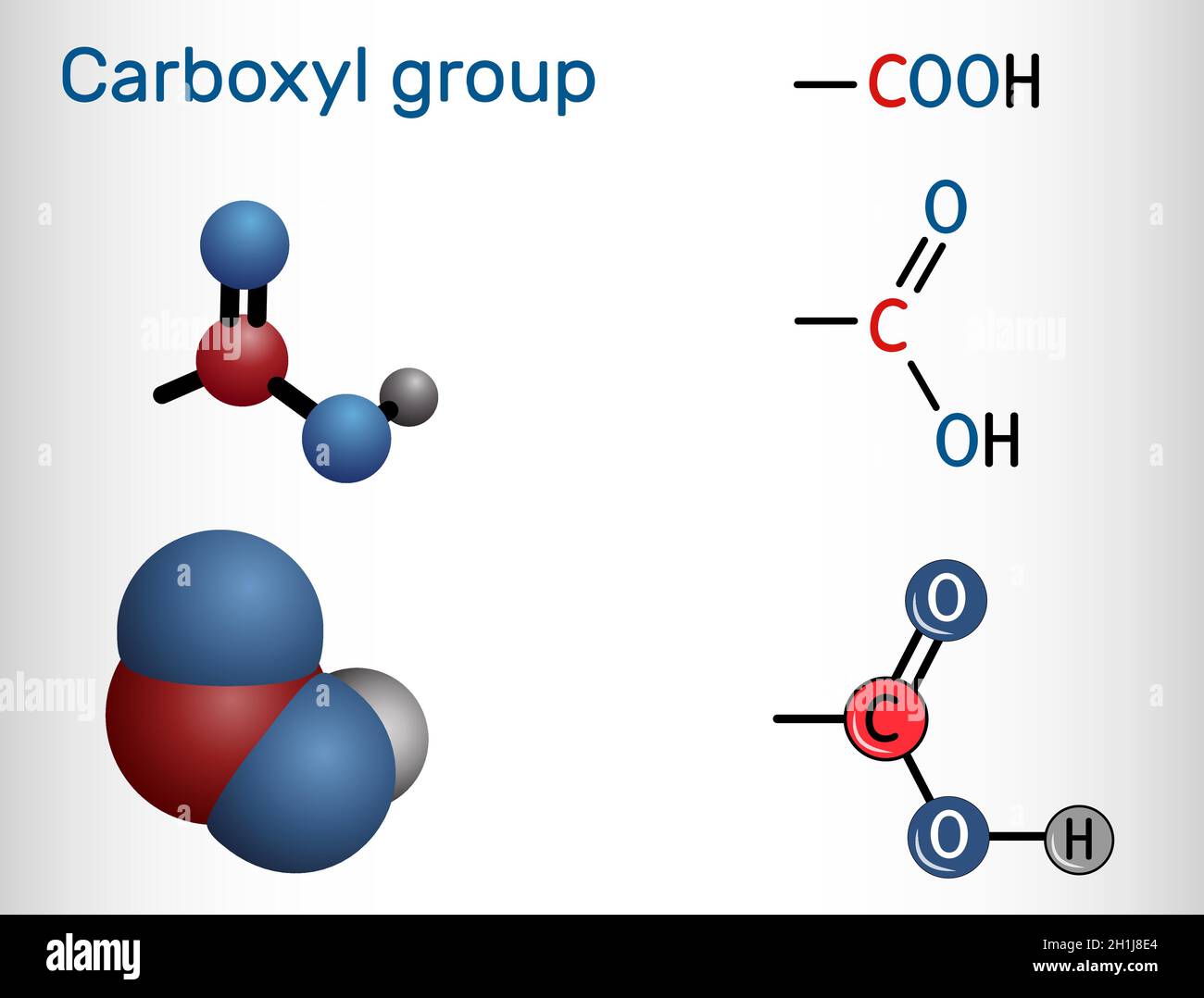
CARBOXYl
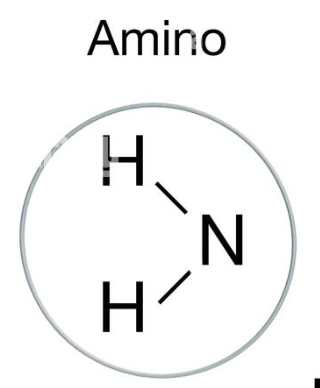
AMINO→ C-C(=O)NH2
acts as a base and accepts H+ in a solution, thus allowing for the formation of various biological molecules such as amino acids and proteins.
✦﹒enzymes are biological catalysts that speed up biochemical reactions.
enzymes often end in -ase (catalase, sucrase, lactase, amylase )
has an active site that specifically interacts with a specific substrate (like a lock and key)
this initiates a reaction (synthesis or digestion of substrate)
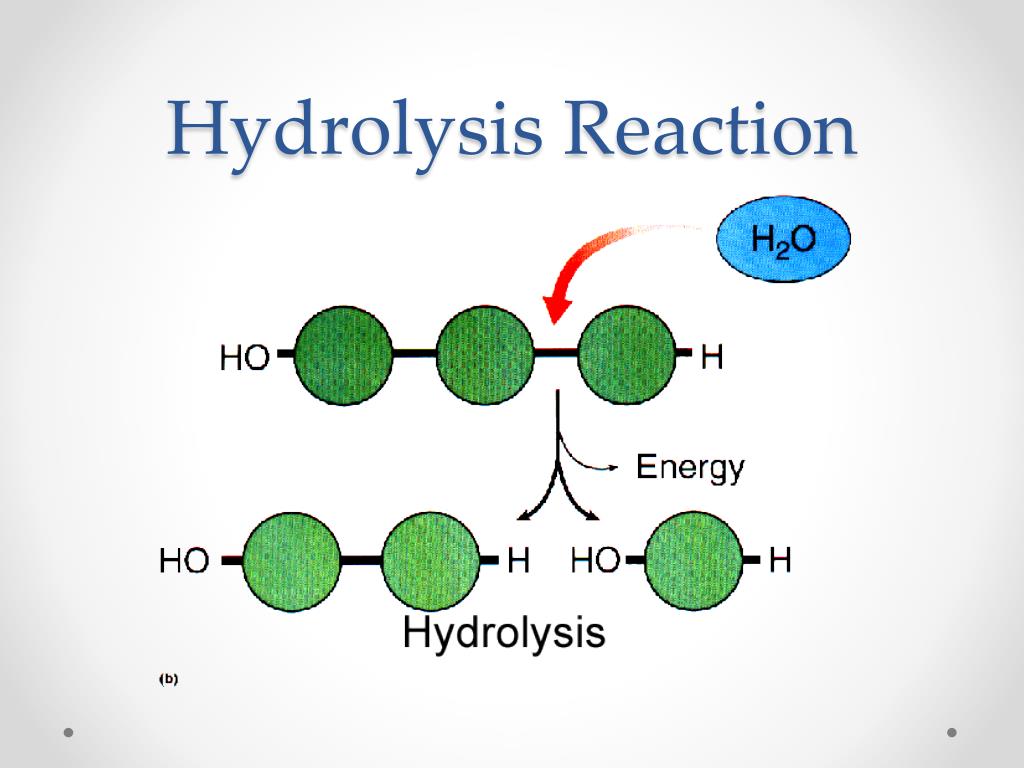
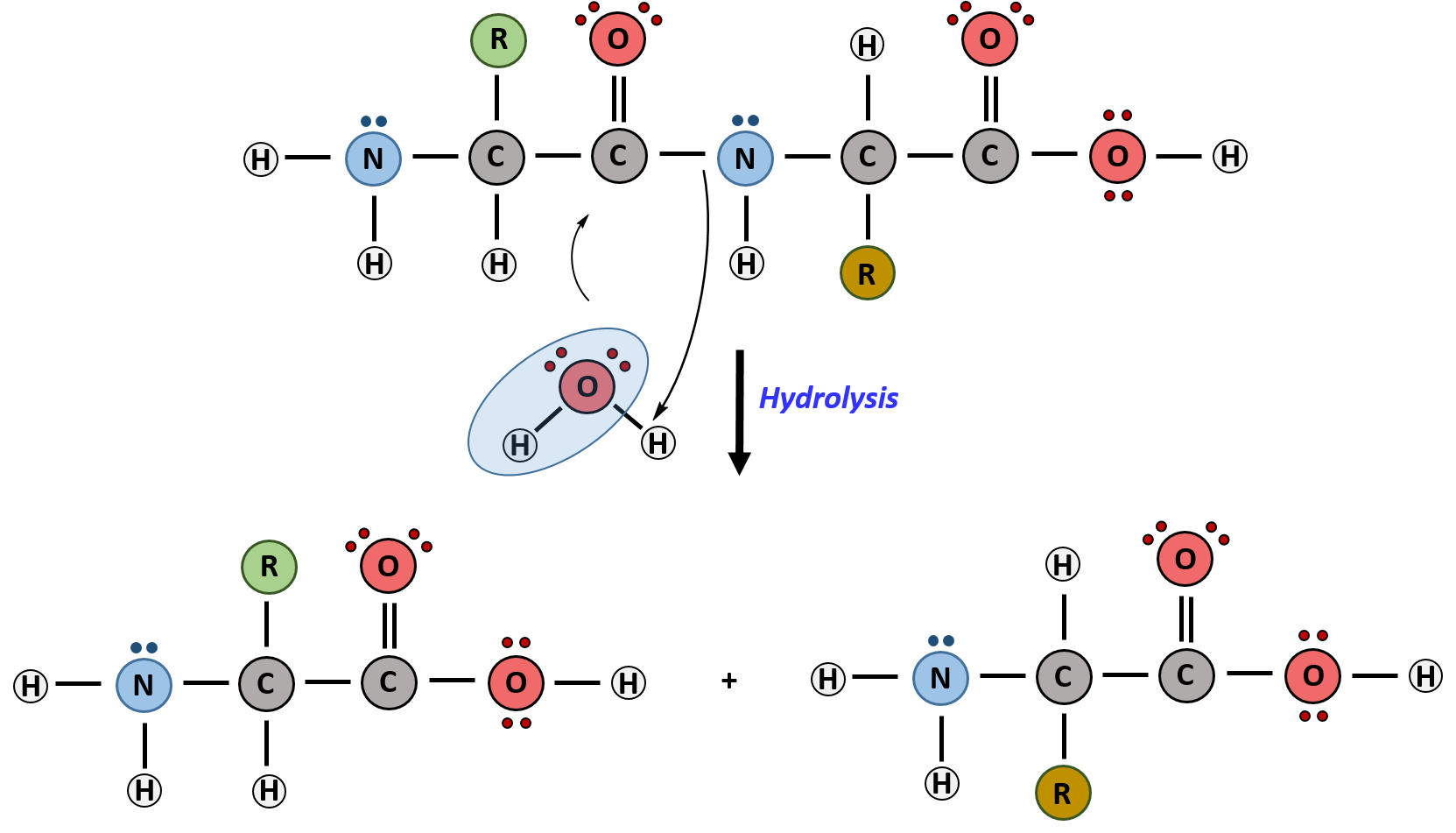
the enzymes link monomers to form polymers by DEHYDRATION SYNTHESIS - to build polymers


to break down polymers add water to it with an enzyme’s help
( . BIG 4 ORGANIC MOLECULES )
how do these all contribute? what’s the structure like?
✦﹒carbohydrates (carbs) - simple and complex
- include sugars + polymers of sugars called polysaccharides(minisugars<3)
the key function is energy, immediate and/or storage and in some cases building materials
simple sugars (monosaccharides) include glucose, galactose, and fructose
they have the same chemical formula BUT are structured completely different.
enzymes link monosaccharides to disaccharides
→ glucose+glucose=maltose
→ glucose+fructose=sucrose
→ glucose+galactose=lactose
lactose intolerant when you don’t have the ability to break the bonds into individual subunits
+ CH4 is produced when the microbes in your large intestine (microbiome) breaks it down which gives you gas
lactASE is something you can take to break down the lactose
sugars can exist in a linear form or a chain form
alpha and beta hydroxyl group changes. the beta is an isomer

complex carb (polysaccharides) are polymers of many monosaccharides
→ starch - an energy storage polysaccharides in plants. potatoes, rice, pasta, corn, grain
monomer is alpha glucose
→ glycogen - an energy storage polysaccharide in animals
monomer is alpha glucose
extensive branching: 1-4, 1-6 a Glucose
stored in the liver and muscle
negative feedback loop ex: hyperglociema
eats sugar → elevated blood sugar → pancreas detects → pancreas releases insulin → insulin tells cells to uptake glucose → glucose then goes to glycogen = lowered blood sugar

→ after a workout eat carbs
cellulose is a structural polysaccharide found in the cell wall of plants
unlike starch & glycogen, cellulose uses BETA as it’s monomer ß
most animals lack the enzymes to break down cellulose
long unbranched fibers in a 1-4 ß linkage

✦﹒lipids - fats/oils (triglycerides), steroids, phospholipids, and waxes
- carbon based macromolecules that mix poorly w water (non-polar thus hydrophobic)
- birds have oils glands to thermoregulate
triglycerides main function is long term energy storage
The glycerol backbone is found in lipids known as glycerides
fats - common in animals, solids at room temp
oils - common in plants, liquids at room temp
→ fats + oils are triglycerides
They are called fatty acids due to the carboxyl group
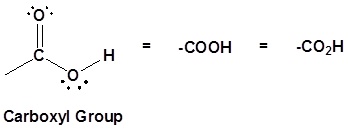

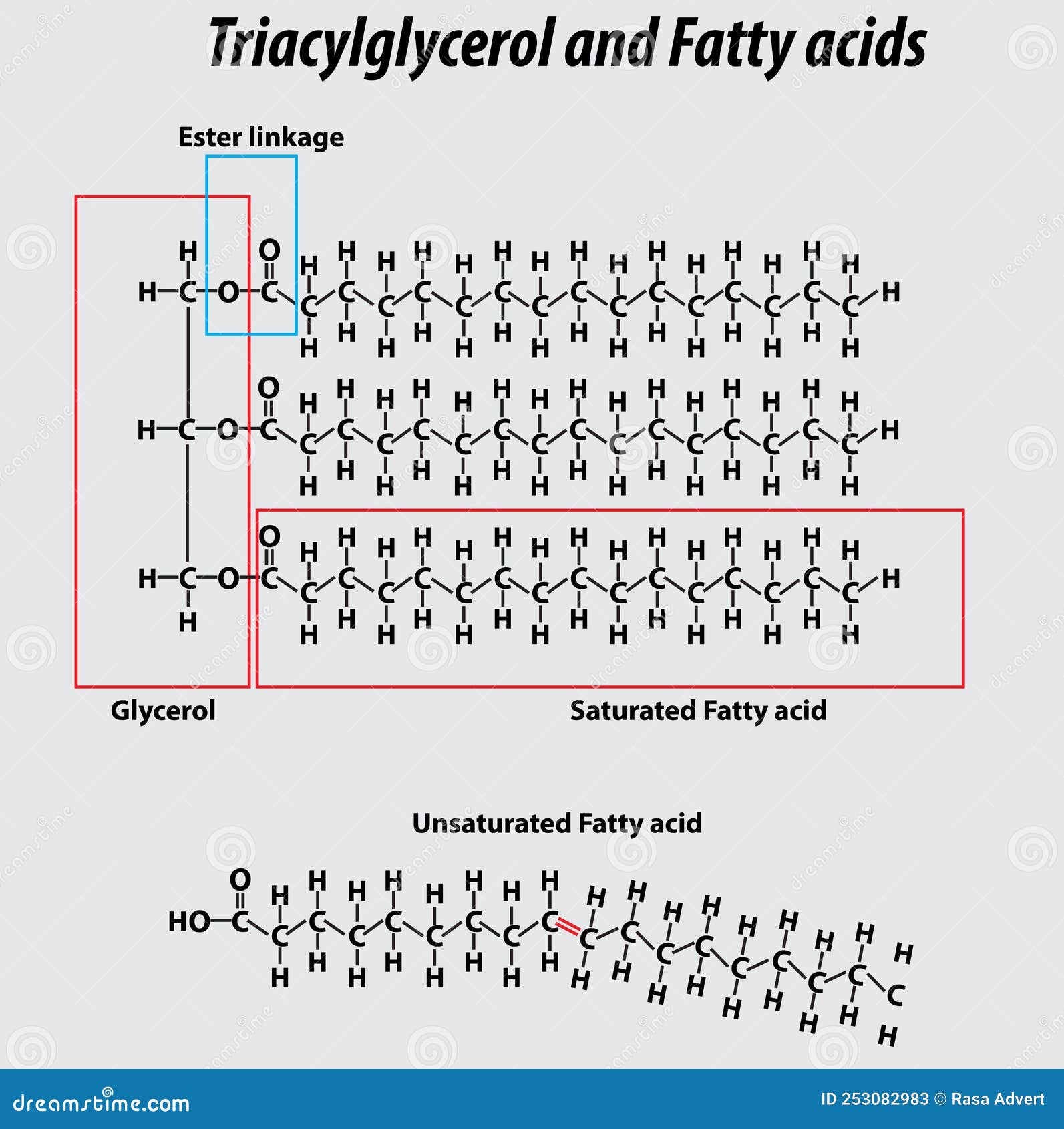
Knk occurs when hydrogens are on the same side of that doulbe bond (cis)
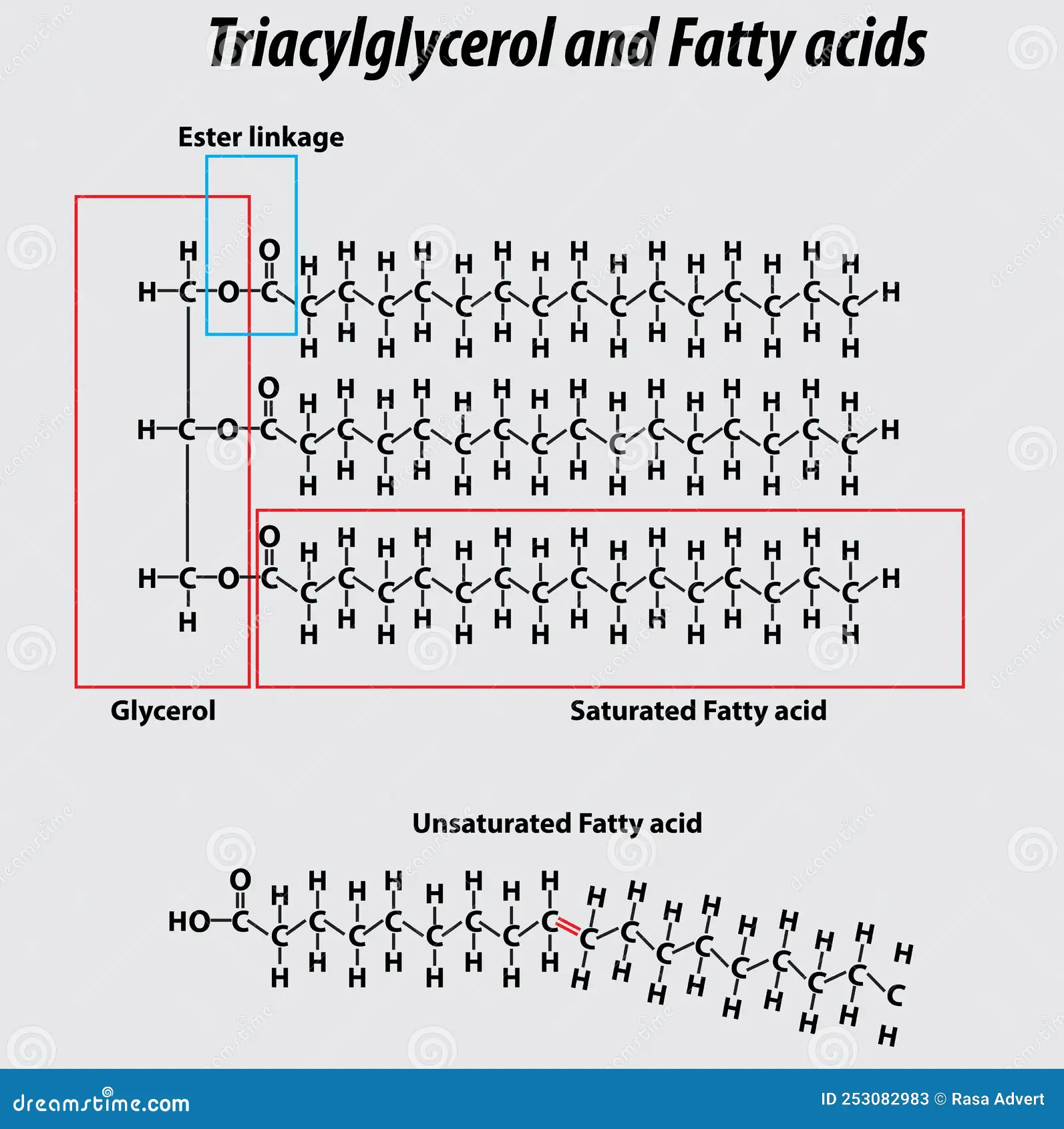
Saturated foesn’t have doulve npnda
unsaturadeted have dbopule dongs
trans fast begave as saturated fats

Fats + oils also have other purposes. Fats can also insulate us. ex otters and whales
carbs, lipids, and protiens all serve for energy. 4 cal/g, 9 cal/g, 4cal/g.
lipids/fats are x2 as important as the other two. you can store more nergy as fat
PHOSPHOKIPID
subunits for cellmembreane
phosphate gourp has negative charges thus it’s polar

streriod
lipids comprised of 4 fused carbon based rings
need to know different func groups
✦﹒proteins - diverse group with a bunch of functions

enzyme proteins were mentioned earlier.
storage proteins can store amino acids. casein is in milk. infant drinks milk and recieves those amino acids that way the infant can build their own proteins
same thing with eggs. this is why eggs are high in protein
if you wanna build muscle mass you need proteins and amino acids
defensice functiosn protect against diseases like anti bodies
transport proteins hemoglobin in iron
hormonal proteins insulin and glucagon dumped in bloodstream that go somewhere else to be used
receptor proteins responses of cell to chemical stimuli
motor/contractile proteins provide movement
structural proteins bind protiens and tissue together keratin, collagen
amino acids can be linked by peptide bpnds
amino acid?
nonpolar side chains(hydrophobic)
r poalr side chains hydrophilic can help in folding
electrically charged side chaine hydrophilic
ionic and hydrogen bonds hold protiens together becayse the hydrophilic amino acids are on the outside and hydrophiloc are in the inside
primary structure
the amino acid seqyence of the polypeptiede forms the backbone of the polypeptide and is held by peptide bonds
secondary structure
starts w the polypeptide back bone(primary) and coils+folds it.
due to hydrogen bonding btwn H and O of polypeptide backbone
alpha helix are coils & beta pleated sheets are folds
what caused it to fold and coil?
h bonds hold it in place, no R groups are involved
teriary structure
resutls from contuned folding
held via R group ineractions
h bonds
hydophibic ineteractions
ionic bonds occur between electrically charged R groups
covalent bonds form by the disulfide bridge (SH/sulfhydral groups)
quatinary structer
when two or more folded polypeptides ceom together
maintained by covalenet , ionic, AND hydrogen

DENATURATION caused by changes in temp, pH, salinity, and polarity
affects the secondary structure/foldings
doesn’t affect amino acid aequence
kinkiness and curliness of hair come from DSB
✦﹒nucleic acids - DNA + RNA- serve to store, transmit and regulate and express heredity info controlling celular actitivy
its a polymer
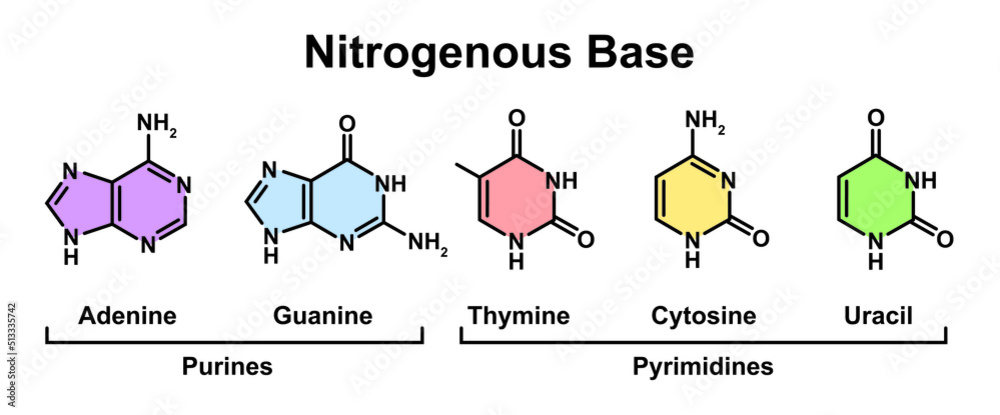
the monomer is a nucleotide: it has 3 components
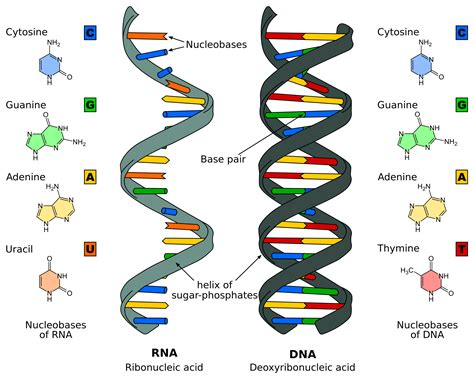
a sugar (Deoxyribose in DNA is missing an O and Ribose in RNA)
a phosphate group
and a nitrogouness base
Adenine, Guanine, Thymine, Uracil, and Cytosine
- DNA has ATCG and RNA has AUGC
we can identify the nitrogenous base by the T or U or which sugar(dexoy/ribose) it contains
The alternating formation of sugar and phosphate form the backbone for the nucleic acid with dehydration synthesis reactions
nitrogenous bases flag out from the sides of them
DNA consists of two ANTIPARRALELL polynucleotides(nucleic acids) twisted into a double helix


The Western diet can cause problems-
Pre-packaged/processed
High red meat
Sugary foods
Refined grains
High fat and fried
High preservatives, salt
Large portions
Low in fruit, veggies, whole grains, good fats...