
p. 216, #1-10.
Define the following terms: nucleotide, complementary base pairing, phosphodiester bond, and glycosyl bond.
define nucleotide -Molecules that consist of 5-carbon sugar ( deoxyribose or ribose) with a nitrogenous base attached to their 1’ carbon and a phosphate group attached
define complementary base pairing: -pairing of the nitrogenous base of one strand of DNA with the nitrogenous base of another strand; adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T); guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C)
phosphodiester bond: -a bond formed between the 3' carbon of one sugar and the 5' carbon of the next sugar by way of an intervening phosphate group 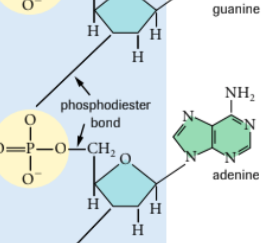
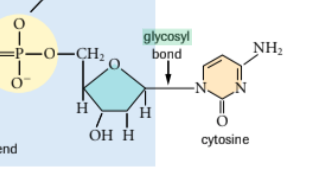
glycosyl bond: -a bond between a sugar and another organic molecule by way of an intervening nitrogen or oxygen atom
In a DNA molecule, a purine pairs with a pyrimidine. If this is the case, then why can’t A–C and G–T pairs form? - Despite the fact that a purine is opposite to a pyrimidine, this base pairing cannot occur because the pairing does not allow for hydrogen bonding. Even though for example G-C pair would constitute the diameter for a DNA molecule, the lack of hydrogen bonding would make it unstable.
The following is a segment taken from a strand of DNA: 5’–ATGCCTTA–3,. Write out the complementary strand for this segment. -3'–TACGGAAT–5'
4.
Summarize the key physical and chemical properties of DNA.-DNA is a nucleic acid polymer that consists of monomer units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide comprises a deoxyribose sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. The phosphate group is negatively charged. The four nitrogenous bases are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. A DNA molecule is double stranded and takes the shape of a helix, which is approximately 2 nm wide. A complete helical turn occurs every 3.4 nm. The two strands run antiparallel to each other. The deoxyribose sugar and the phosphate group form the backbone of each strand. The nitrogenous bases pair via hydrogen bonding. Adenine only pairs with thymine on the opposite strand and vice versa, while guanine only pairs with cytosine on the opposite strand and vice versa.
Differentiate between a purine and a pyrimidine. -A purine is a nitrogenous base that is double ringed, while a pyrimidine is a nitrogenous base that contains a single ring. Adenine and guanine are purines. Thymine and cytosine are pyrimidines.
A molecule of DNA was analyzed and found to contain 20% thymine. Calculate the percentage of adenine, guanine, and cytosine in this molecule. - a = 20% G= 30% C= 30%
Table 1 shows the distribution of nucleotides that originated from analysis of single stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA. Identify which of the samples A, B, and C are most likely double stranded and which are single stranded, and record your answers in your notebook. - A is double stranded DNA, (percentage of A = T and percentage of C = G). sample B = single stranded (percentage of G is not equal to C) sample C = single stranded (percentage of G is not equal to C, and percentage of A is not equal to T 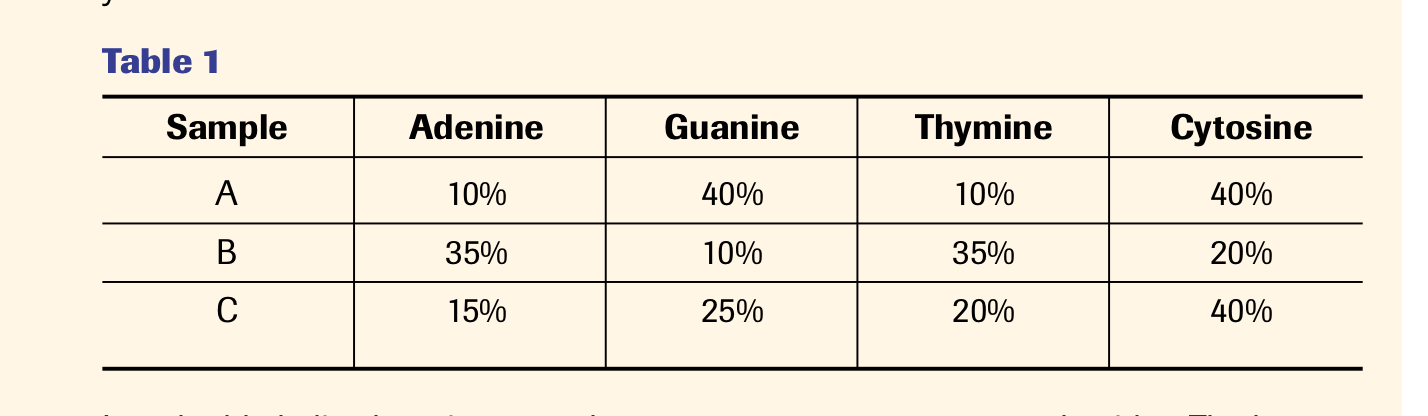
In a double helix, there is a complete turn every 3.4 nm, or 10 nucleotides. The human genome contains approximately 3 billion nucleotides. Calculate how long an average human cell’s DNA would be if its structure were unwound. Calculate how many complete turns would exist in this molecule. - A human cells DNA would be 1.02 m long. It would contain 3 × 108
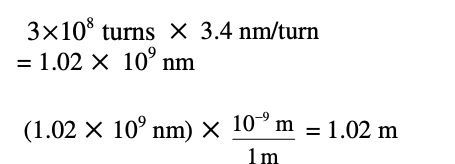

Assume that the DNA molecule in a particular chromosome is 75 mm long. Calculate the number of nucleotide pairs in this molecule has. - This molecule would contain 2.2 × 108 nucleotides.

While trying to determine the structure of the DNA molecule, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed that like bases are bonded to like bases. For example, thymine would be bonded to thymine, cytosine would be bonded to cytosine, and
so on. Explain why this proposed model would not fit with Erwin Chargaff’s observations. How would this model also contradict Rosalind Franklin’s findings in her X-ray crystallography of DNA?
The experiments of Erwin Chargaff demonstrated that the proportion of thymine was equal to the proportion of adenine and the proportion of guanine was equal to the proportion of cytosine. Furthermore, Chargaff discovered that the proportion of adenine plus guanine was equal to the proportion of thymine plus cytosine. If Watson and Crick's hypothesis were correct, it would contradict Chargaff's data. The hypothesis provided no explanation for why the proportion of T equals A or why the proportion of G equals C. The hypothesis implied that each nucleotide's occurrence is independent of another nucleotide's occurrence; thus, the proportions of each nucleotide would not be related or dependent on the proportions of another nucleotide. Rosalind Franklin's findings were also contradicted by Watson and Crick's hypothesis. The width of a DNA molecule is constant, according to Rosalind Franklin. If cytosine bonded to cytosine, thymine to thymine, and so on, the width of the DNA molecule would vary because at some points two purines would be bonded to each other and at other points two pyrimidines would be bonded to each other. Because purines are larger than pyrimidines, the width of the DNA molecule would change.
Define the following terms: nucleotide, complementary base pairing, phosphodiester bond, and glycosyl bond.
define nucleotide -Molecules that consist of 5-carbon sugar ( deoxyribose or ribose) with a nitrogenous base attached to their 1’ carbon and a phosphate group attached
define complementary base pairing: -pairing of the nitrogenous base of one strand of DNA with the nitrogenous base of another strand; adenine (A) pairs with thymine (T); guanine (G) pairs with cytosine (C)
phosphodiester bond: -a bond formed between the 3' carbon of one sugar and the 5' carbon of the next sugar by way of an intervening phosphate group 
glycosyl bond: -a bond between a sugar and another organic molecule by way of an intervening nitrogen or oxygen atom

In a DNA molecule, a purine pairs with a pyrimidine. If this is the case, then why can’t A–C and G–T pairs form? - Despite the fact that a purine is opposite to a pyrimidine, this base pairing cannot occur because the pairing does not allow for hydrogen bonding. Even though for example G-C pair would constitute the diameter for a DNA molecule, the lack of hydrogen bonding would make it unstable.
The following is a segment taken from a strand of DNA: 5’–ATGCCTTA–3,. Write out the complementary strand for this segment. -3'–TACGGAAT–5'
4.
Summarize the key physical and chemical properties of DNA.-DNA is a nucleic acid polymer that consists of monomer units called nucleotides. Each nucleotide comprises a deoxyribose sugar, a nitrogenous base, and a phosphate group. The phosphate group is negatively charged. The four nitrogenous bases are adenine, thymine, guanine, and cytosine. A DNA molecule is double stranded and takes the shape of a helix, which is approximately 2 nm wide. A complete helical turn occurs every 3.4 nm. The two strands run antiparallel to each other. The deoxyribose sugar and the phosphate group form the backbone of each strand. The nitrogenous bases pair via hydrogen bonding. Adenine only pairs with thymine on the opposite strand and vice versa, while guanine only pairs with cytosine on the opposite strand and vice versa.
Differentiate between a purine and a pyrimidine. -A purine is a nitrogenous base that is double ringed, while a pyrimidine is a nitrogenous base that contains a single ring. Adenine and guanine are purines. Thymine and cytosine are pyrimidines.
A molecule of DNA was analyzed and found to contain 20% thymine. Calculate the percentage of adenine, guanine, and cytosine in this molecule. - a = 20% G= 30% C= 30%
Table 1 shows the distribution of nucleotides that originated from analysis of single stranded DNA and double-stranded DNA. Identify which of the samples A, B, and C are most likely double stranded and which are single stranded, and record your answers in your notebook. - A is double stranded DNA, (percentage of A = T and percentage of C = G). sample B = single stranded (percentage of G is not equal to C) sample C = single stranded (percentage of G is not equal to C, and percentage of A is not equal to T 
In a double helix, there is a complete turn every 3.4 nm, or 10 nucleotides. The human genome contains approximately 3 billion nucleotides. Calculate how long an average human cell’s DNA would be if its structure were unwound. Calculate how many complete turns would exist in this molecule. - A human cells DNA would be 1.02 m long. It would contain 3 × 108
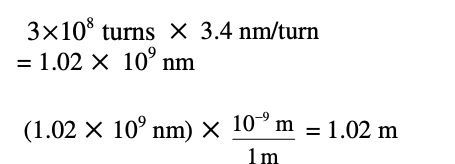

Assume that the DNA molecule in a particular chromosome is 75 mm long. Calculate the number of nucleotide pairs in this molecule has. - This molecule would contain 2.2 × 108 nucleotides.

While trying to determine the structure of the DNA molecule, James Watson and Francis Crick proposed that like bases are bonded to like bases. For example, thymine would be bonded to thymine, cytosine would be bonded to cytosine, and
so on. Explain why this proposed model would not fit with Erwin Chargaff’s observations. How would this model also contradict Rosalind Franklin’s findings in her X-ray crystallography of DNA?
The experiments of Erwin Chargaff demonstrated that the proportion of thymine was equal to the proportion of adenine and the proportion of guanine was equal to the proportion of cytosine. Furthermore, Chargaff discovered that the proportion of adenine plus guanine was equal to the proportion of thymine plus cytosine. If Watson and Crick's hypothesis were correct, it would contradict Chargaff's data. The hypothesis provided no explanation for why the proportion of T equals A or why the proportion of G equals C. The hypothesis implied that each nucleotide's occurrence is independent of another nucleotide's occurrence; thus, the proportions of each nucleotide would not be related or dependent on the proportions of another nucleotide. Rosalind Franklin's findings were also contradicted by Watson and Crick's hypothesis. The width of a DNA molecule is constant, according to Rosalind Franklin. If cytosine bonded to cytosine, thymine to thymine, and so on, the width of the DNA molecule would vary because at some points two purines would be bonded to each other and at other points two pyrimidines would be bonded to each other. Because purines are larger than pyrimidines, the width of the DNA molecule would change.