electricity and magnetism I
Positive and negative charges
- When two charged objects come together they create an electric force
- Opposite charges attract; Similar charges repel.
- Charges are measured in Coulombs (C)
- Most objects are neutral, they have equal amounts of negative and positive charges.
- Number of protons = Number of electrons → Neutral
- When an atom loses electrons it becomes positive
- When an atom gains electrons it becomes negative
- When an atom has unbalanced charges, they try to balance out with charge motion.
- THe forces between charges decreases as they drift apart.
Demonstrating electric charges
Charging by friction
Use two insulators that rub with silk, since rubbing creates friction which takes away electrons.
this needs to be done with insulators since charges cannot move so they will remain charged, and you can prove the charging.
if the insulators are attracted then they have a different charge, if they repel each other then they have the same one.
Electric fields
Space surrounding a charge in which another charge will experience a force always goes from a positive charge to a negative one.
- Electrons move oppositely, from negative to positive.
- It is possible to have an electric field with only a negative or positive charge; it is not possible to have a magnetic field with only a north or south pole.
Electrons
Electrons are subatomic particles that are negatively charged.
| conductors | insulators |
|---|---|
| allows the electrons or charges to flow through it. | does not allow charges to flow through it. |
| metals | plastics |
| graphite | glass |
| most non-metals |
Charging by induction
when a charged object is held close to a conductor, the charges will try to balance out by moving into or out of the charged object.
then, the part of the conductor held close to the charged object will become either positively or negatively charged, and the other part, oppositely charged.
Both objects, then, are likely to be attracted due to the new arrangement of charges.
Current (I)
When two oppositely charged conductors are connected by a wire (another conductor), charges will flow trying to balance the charges in both conductors.
This flow is called an electric current.
- the greater the flow, the greater the current
Charge, current, and time
Current is the charges passing a point in a circuit every second. Or the charge per second.
Charge (C) = Current (A) * Time
Q = I * t
- Current is measured in Amps, using an ammeter.
- The ammeter needs to be located in series with the part of the circuit you wish to measure the current through.
Current and electrons
In a metal, the current is caused by a flow of delocalized electrons.
- Electrons flow from negative to positive while the conventional current flows from positive to negative.
Electromotive force
The potential difference or voltage of the power source in a circuit.
- The electromotive force is measured in Volts (V)
- Is the amount of energy (joules) supplied to each Coulomb (c) of charge passing through that power supply.
Potential difference
As charge flows around a circuit, energy is transferred to or from the charge.
The potential difference is the amount of energy transferred between two points in the circuit by each unit of charge.
It is related to potential difference given to transform into Kinetic energy.
Measured in Volts (V) which is the same as 1J/C
^^V = E / Q^^
Measured using a voltmeter. which should be connected in parallel with the part of the circuits you want to measure the potential difference of.
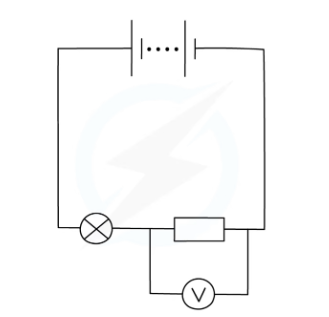
Resistance
The opposite of current: The higher the resistance, the lower the current.
Potential difference = Current * Resistance
- Is measured in Ohms (Ω)
Resistance of wires
Depends on:
- Length: shorter, less resistance.
- Material’s traits.
- Thickness: The thicker, the less resistance
The electrons face resistance on a wire due to the other ions
Electrostatic
It is the result of an imbalance between charges. Mostly in an insulator since the charges cannot move, and hence are static.
This event might produce a spark.
Dangers
- Lightning
- Refueling a car
- Electric and electronic devices might get damaged.