Fluids and Electrolytes
Fluids and Electrolytes
Body fluids consist of water, electrolytes, blood plasma and component cells, proteins, and other soluble particles called solutes.
40% to 60% of the average adult’s weight is composed of water
Females have higher proportion of BW as water
Infants have 75% to 80% water
Maintaining fluid and electrolyte balance
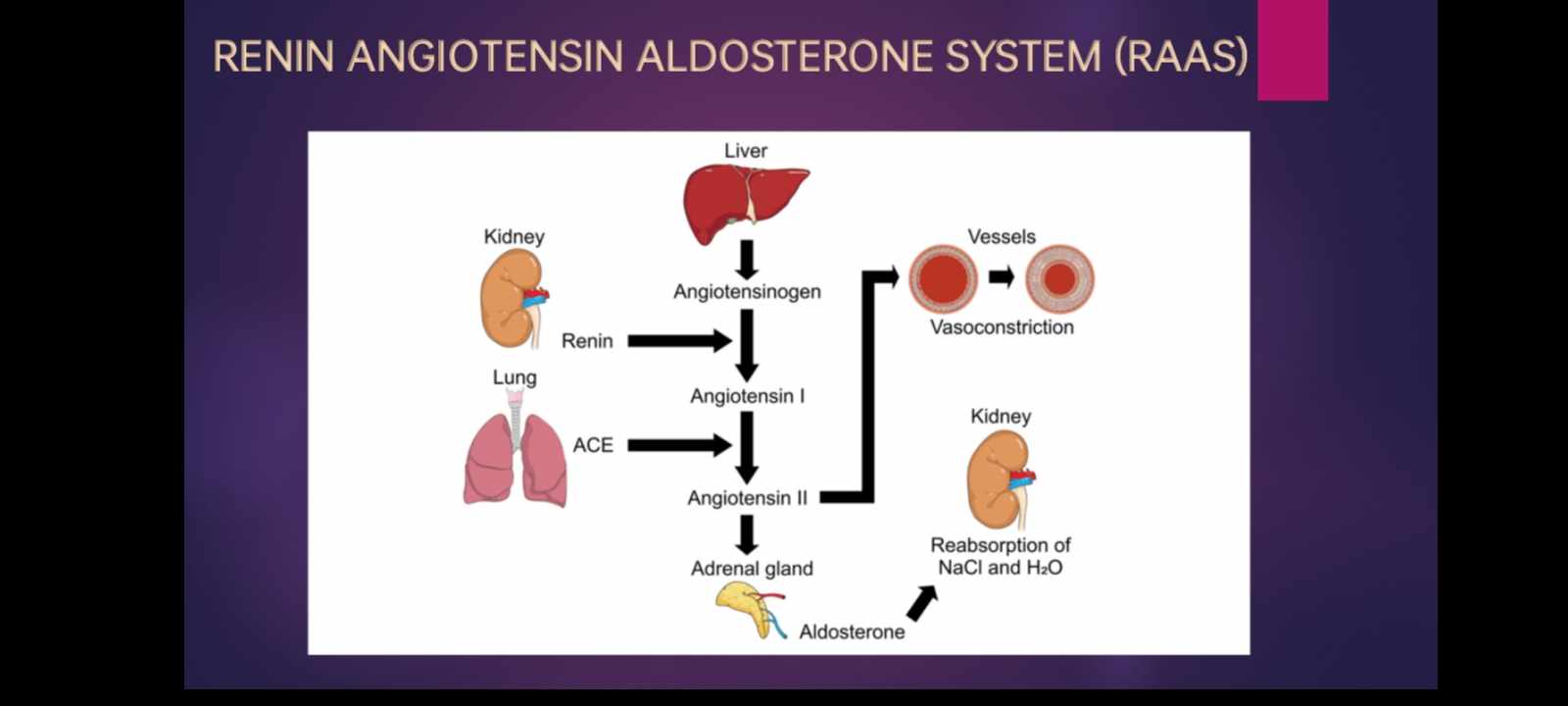
Kidneys - play a major role in controlling all types of balance
ADH - from the pituitary gland regulates the osmotic pressure of extracellular fluid by regulating the amount of water reabsorbed by the kidney
Adrenal Gland - Through the secretion of aldosterone, the adrenal glands also aid in controlling extracellular fluid volume by regulating the amount of sodium reabsorbed by the kidneys
Renin Angiotensin Aldosterone system (Raas)
Fluid Balance
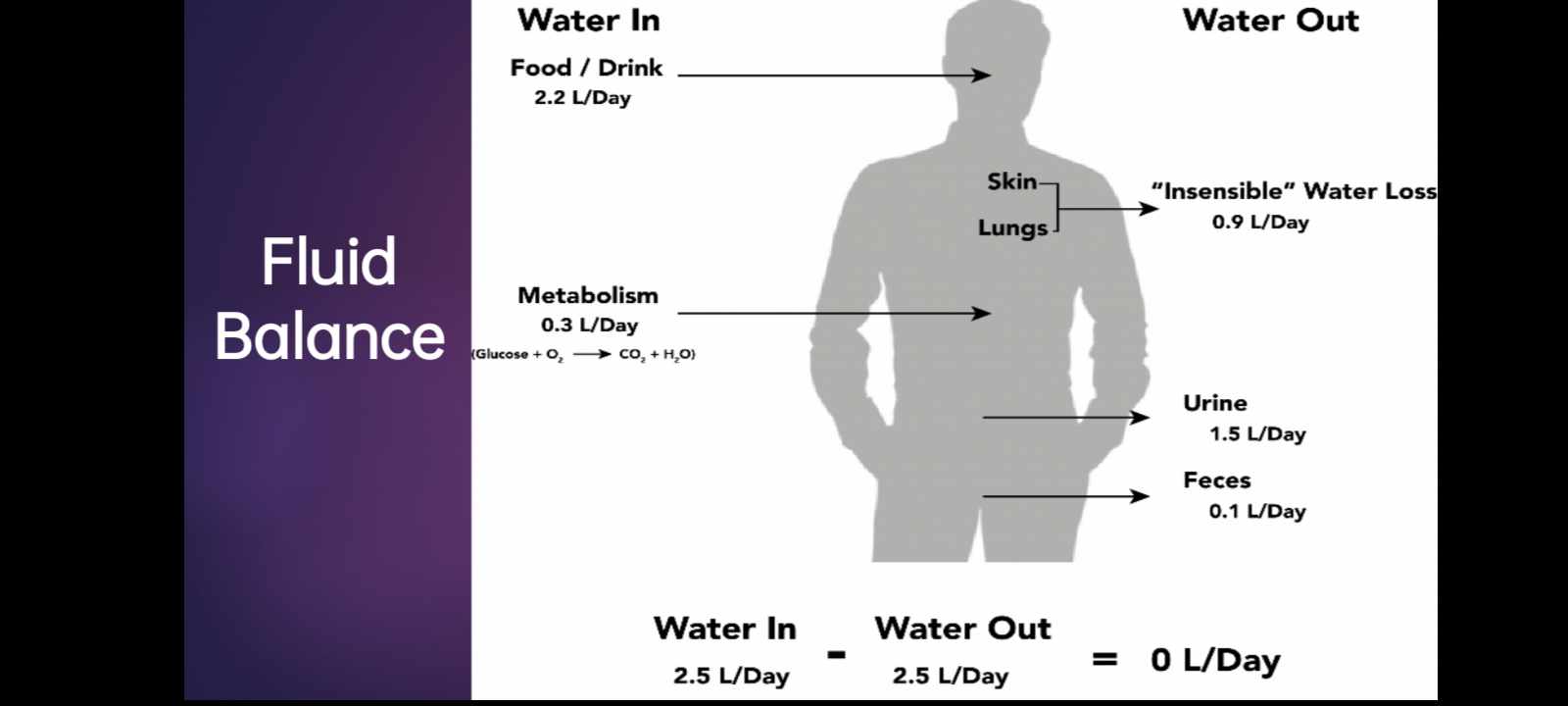
Water in
Food/Drink - 2.2L/day
Metabolism - 0.3L/day
Water Out
“Insensible” water loss = 0.9L/day (skin or lungs)
Urine - 1.5L/day
Feces - 0.1L/day
Total
2.5L/day - 2.5L/day = 0L/day
Movement of Body Fluids and Electrolytes
Filtration - fluid and solutes move together across a membrane from one compartment to another
FLUID IMBALANCE
FLUID VOLUME DEFICIT
occurs when loss of fluid is greater than fluid input
common causes of fluid volume deficit are diarrhea, vomiting, excessive sweating, fever, and poor oral fluid intake
High risks
Older adults
Infants and children
Patients with chronic diseases such as diabetes mellitus and kidney disease
Patients taking diuretics and other medications that cause increased urine output
Individuals who exercise or work outdoors in hot weather
Adult symptoms of dehydration
Feeling very thirsty
Dry mouth
Headache
Dry skin
Urinating and sweating less than usual
Dark, concentrated urine
Feeling tired
Changes in mental status
Dizziness due to decreased blood pressure
Elevated heart rate
Infant and young symptoms of dehydration
Crying without tears
No wet diapers for three hours or more
Being unusually sleepy or drowsy
Irritability
Eyes that look sunken and sunken fontanel

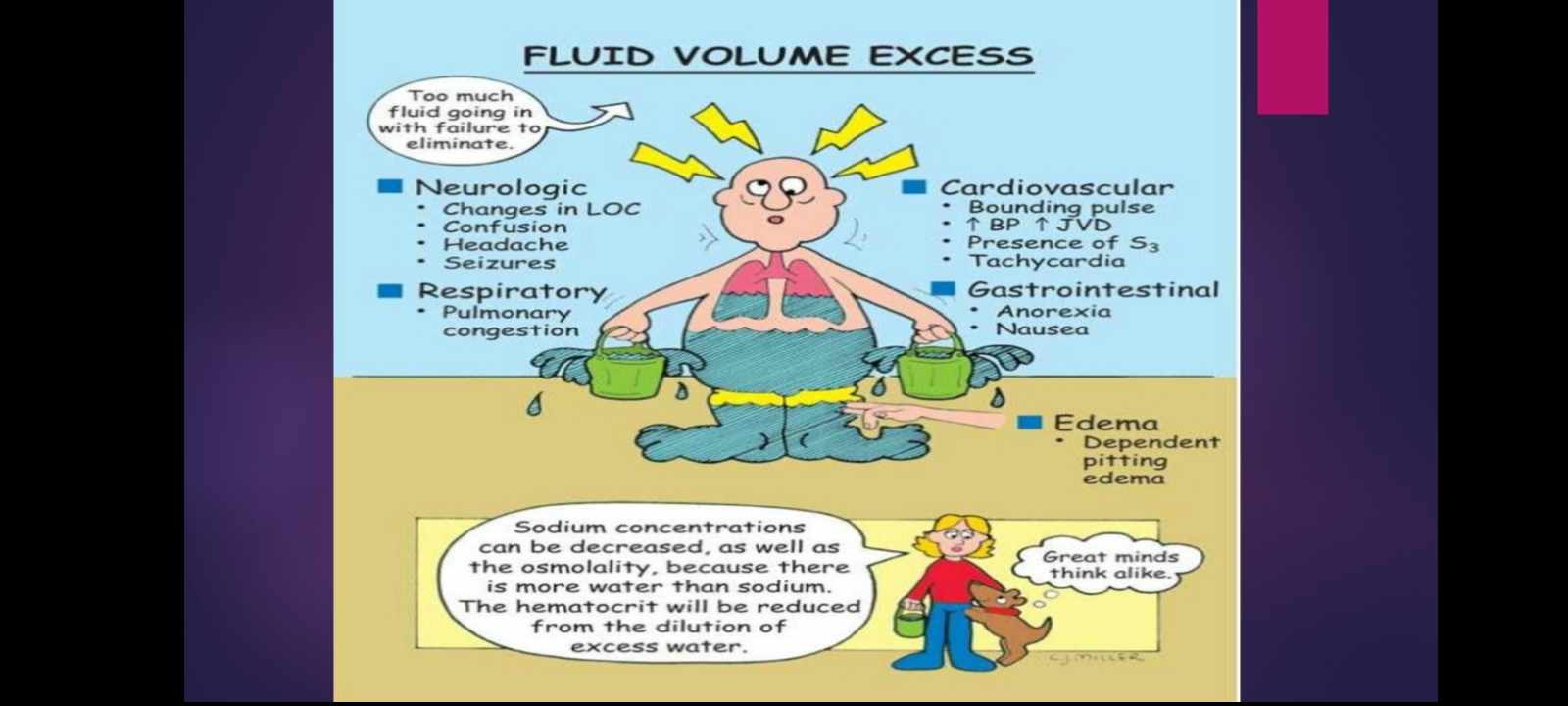
FLUID VOLUME EXCESS
occurs when there is increased fluid retained in the intravascular compartment
High risks
Heart Failure
Kidney Failure
Cirrhosis
Pregnancy
signs and symptoms
pitting edema
ascites
dyspnea
crackles from fluid in the lungs.
Treatment
Depends on the cause of the fluid retention
Sodium and fluids are typically restricted
Diuretics are often prescribed to eliminate the excess fluid.
Management
enteral fluid and electrolytes replacement
fluid intake modifications
dietary changes
oral electrolyte supplements
parenteral fluid and electrolyte replacement
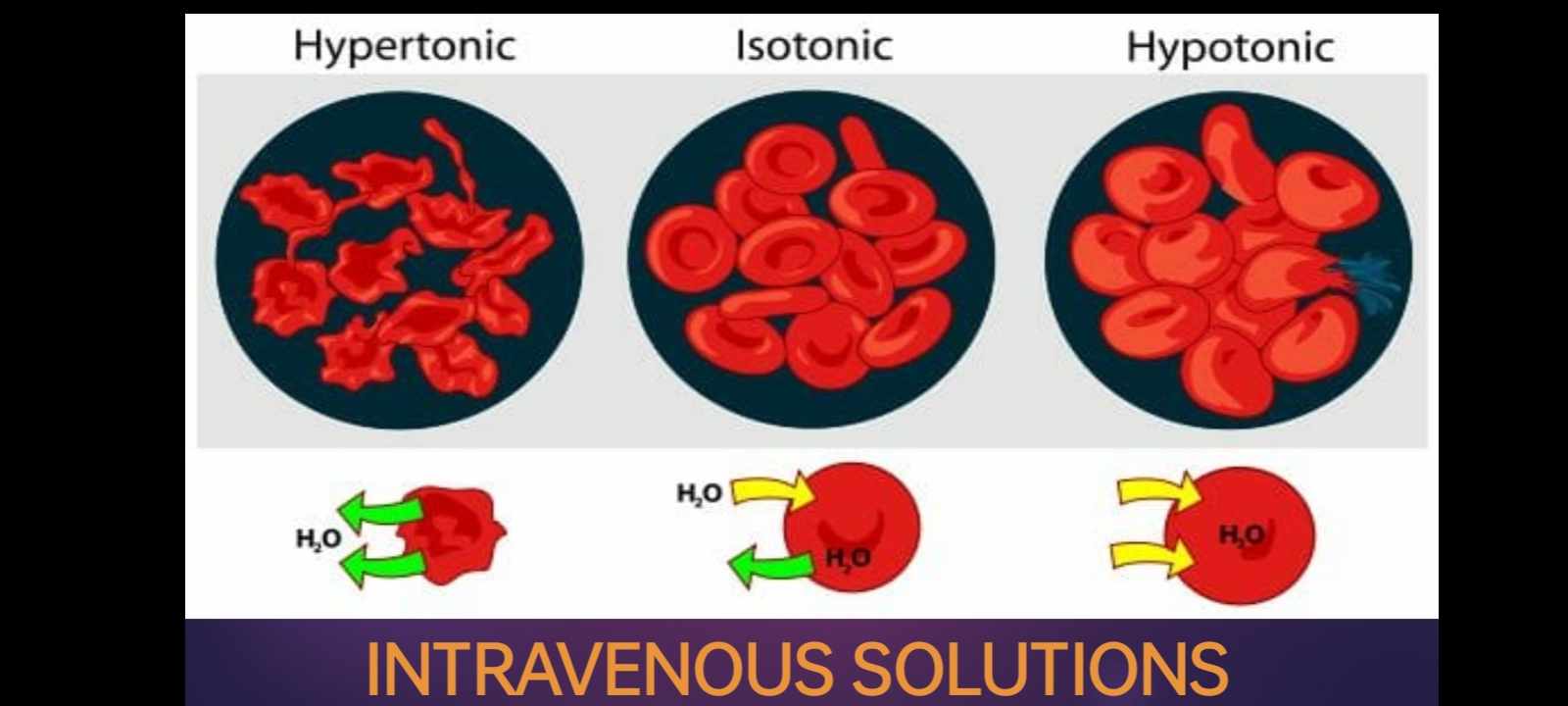
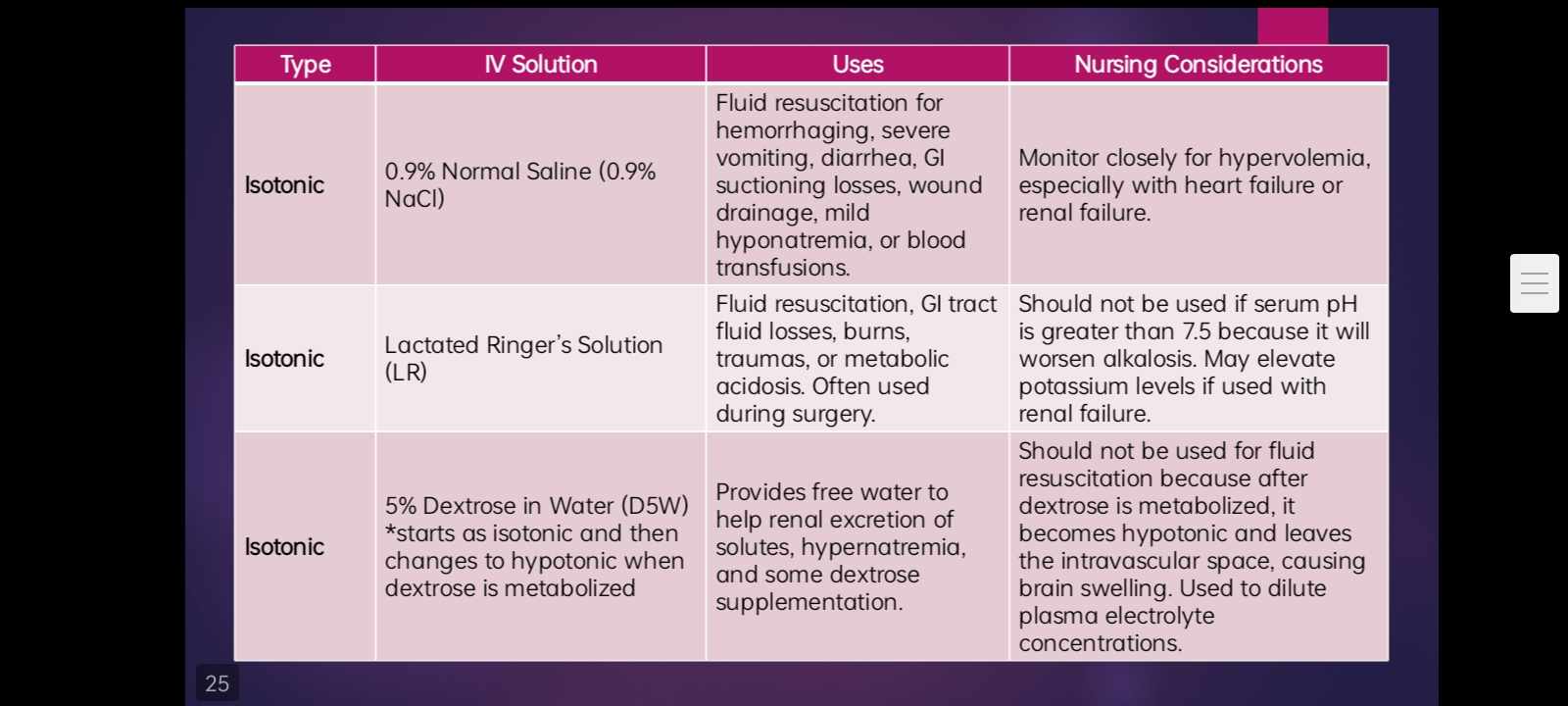
INTRAVENOUS SOLUTIONS - ISOTONIC
IVF that have a similar concentration of dissolved particles as blood.
used for patients with fluid volume deficit (also called hypovolemia) to raise their blood pressure
0.9 NaCl - Green
0.9% Normal Saline (0.9% NaCl)
Plain Normal Saline Solutions (PNSS)
Lactated Ringer’s Solution (PLR) - Blue
5% Dextrose in Water (D5W) - Red
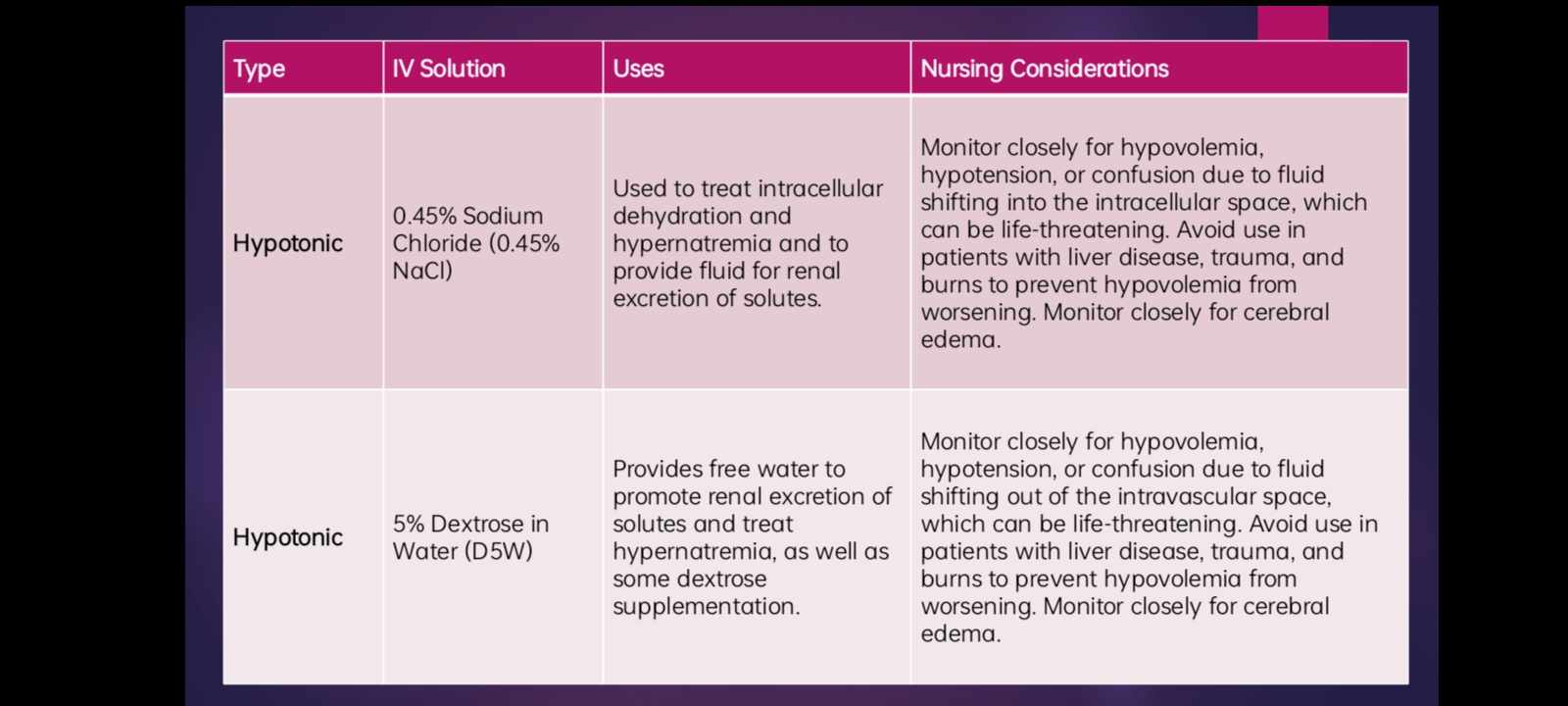
INTRAVENOUS SOLUTIONS - HYPOTONIC
have a lower concentration of dissolved solutes than blood.
hypotonic fluids are used to treat cellular dehydration.
0.45% NaCl
D5W
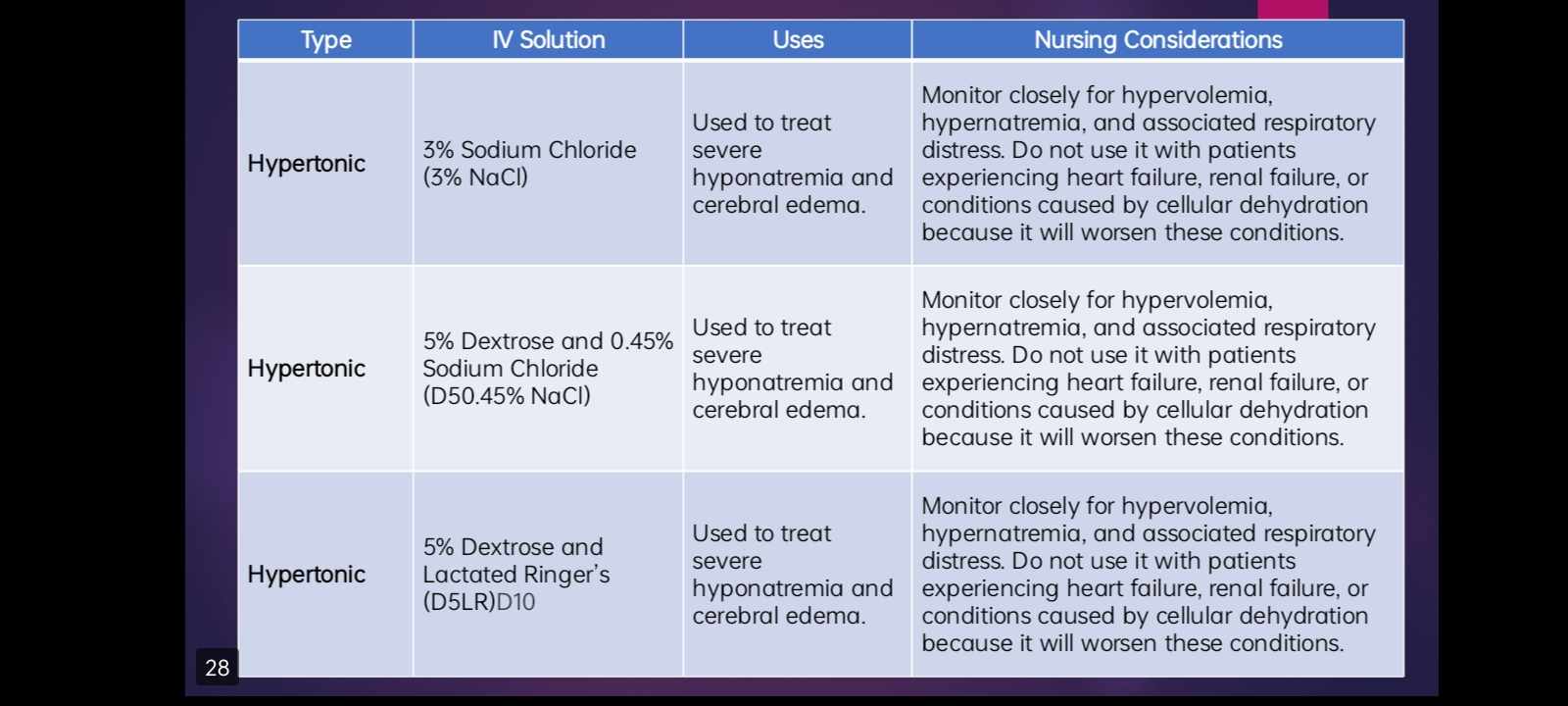
INTRAVENOUS SOLUTIONS - HYPERTONIC
IV THERAPY
administration of water, nutrients, electrolytes, blood products and medications
fluid replacement
dehydration
malnutrition
electrolyte imbalance
hyperalimentation
rapid delivery is required
drug is irritating to the tissues
drug needs to be administered over a specified period of time
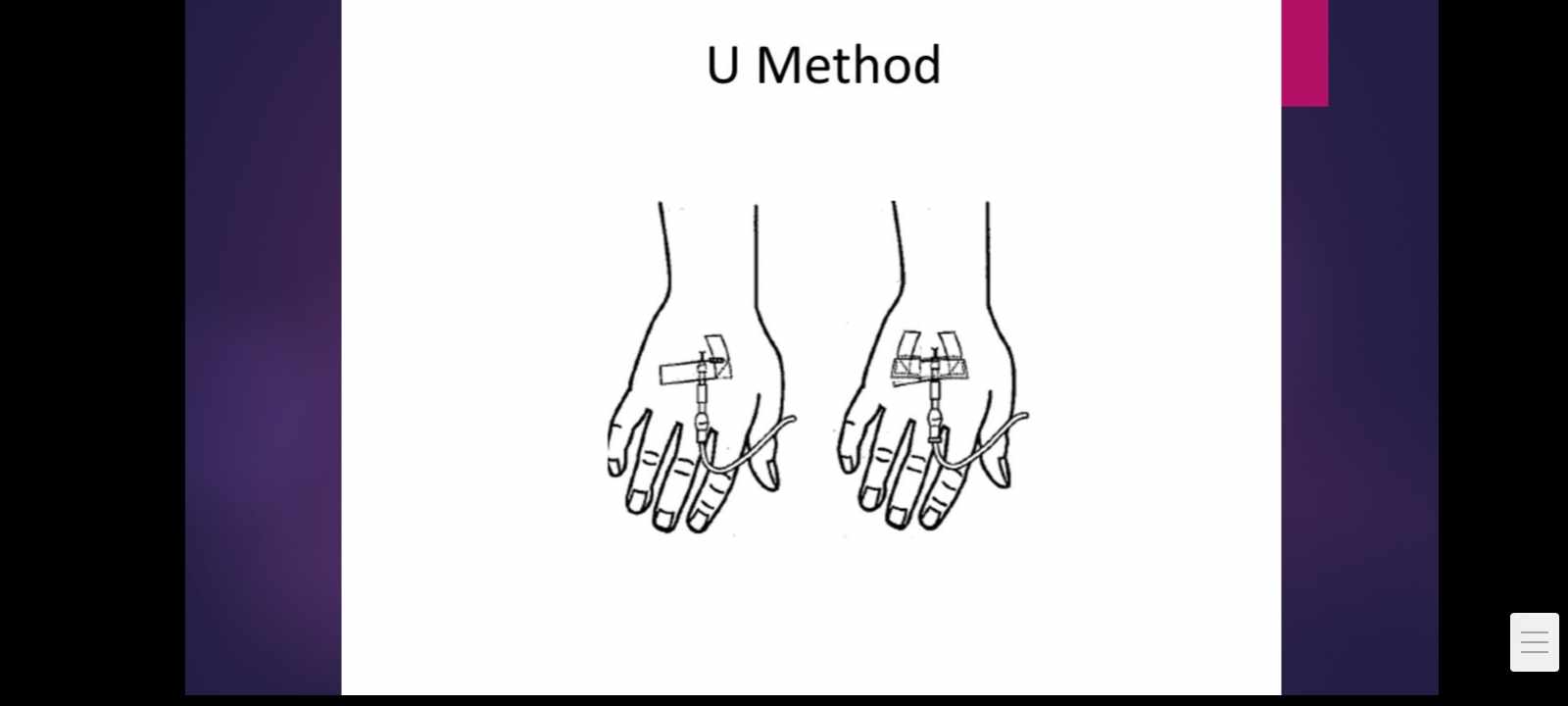
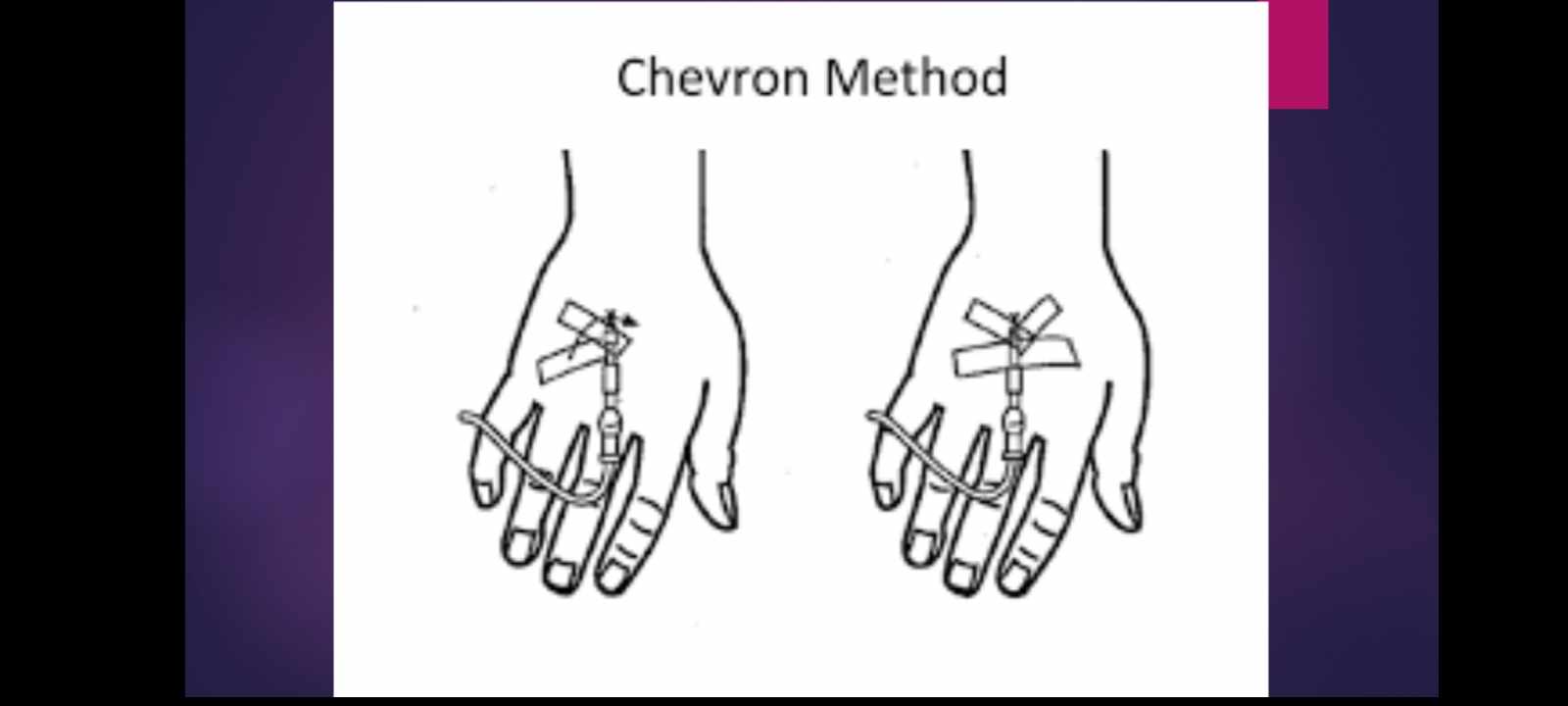
IV FLUID
Parenteral nutrition
Administration of drugs
Transfusion of blood or blood components
Equipment for IV infusion
Parenteral nutrition
Administration of drugs
Transfusion of blood or blood components
Drop Chamber/Drip Chamber
located at the site of the entrance of the tubing into the container of intravenous solution
allow to count the number of drops per minute that the client is receiving (flow rate)
Roll Valve Clamp or clip
connected to tubing and can be manipulated to increase or decrease the flow rate
Access ports
used to infuse secondary medications and to administer IV push medications. These may also be referred to as “Y ports.”
IV PIGGYBACK
administering medicines through a port in an existing IV line
used to administer small amounts of medication along with the IV solution
IV COMPUTATION
Manufacturer Drip Factor
Abbott- 15 drops per ml.
Baxter- Trevenol- 10 drops per ml.
Cutter- 20 drops per ml.
IVAC- 20 drops per ml.
McGraw- 15 drops per ml.

Complication from IV therapy
INFILTRATION - occurs when the tip of the catheter slips out of the vein. The catheter passes through the wall of the vein, or the blood vessel wall allows part of the fluid to infuse into the surrounding tissue, resulting in the leakage of IV fluids into the surrounding tissue. Infiltration may cause pain, swelling, and skin that is cool to the touch.
PHLEBITIS - inflammation of a vein
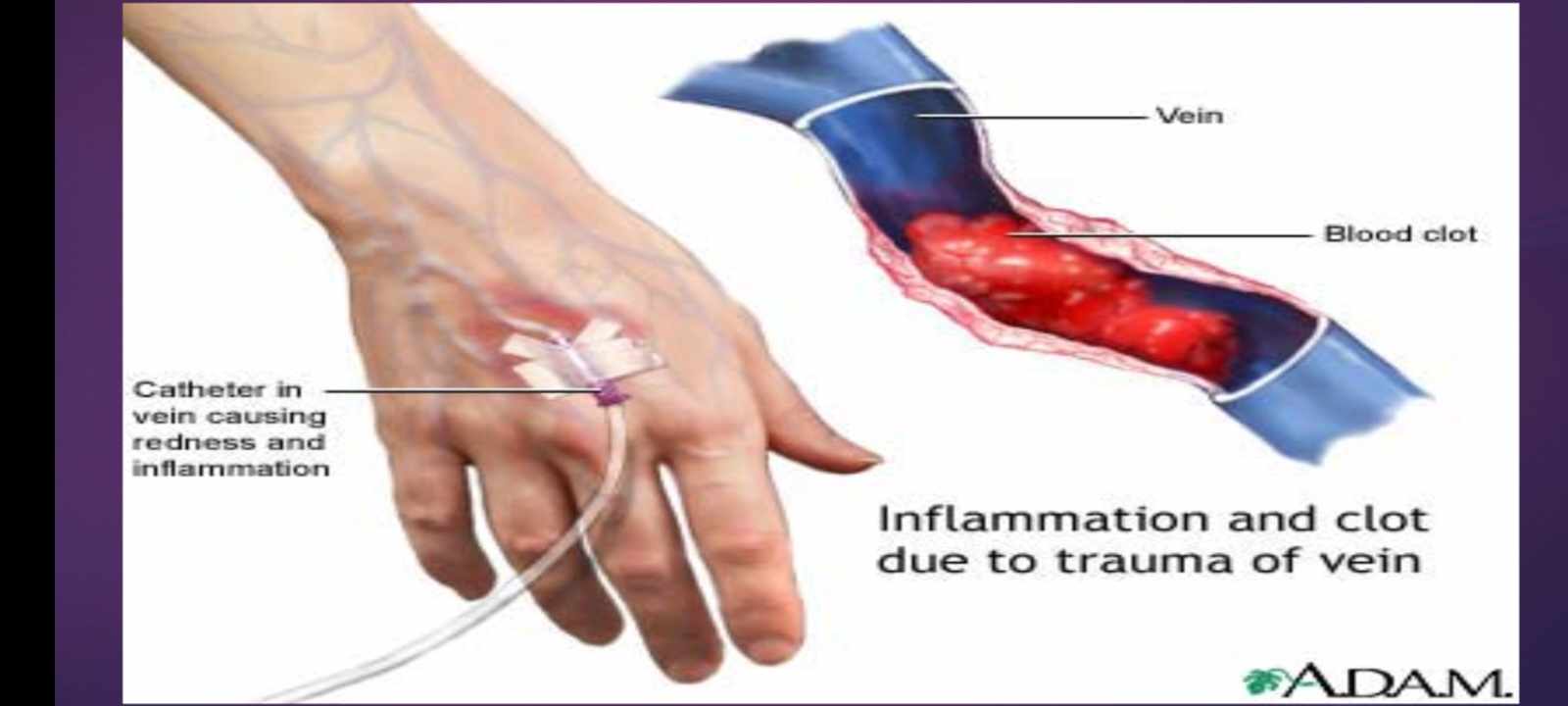
CIRCULATORY OVERLOAD
AIR EMBOLISM
CATHETER EMBOLISM
SYSTEMIC INFECTION
INFECTION OF VENIPUNCTURE
SPEED SHOCK
ALLERGIC REACTION
PULMONARY CONGESTION
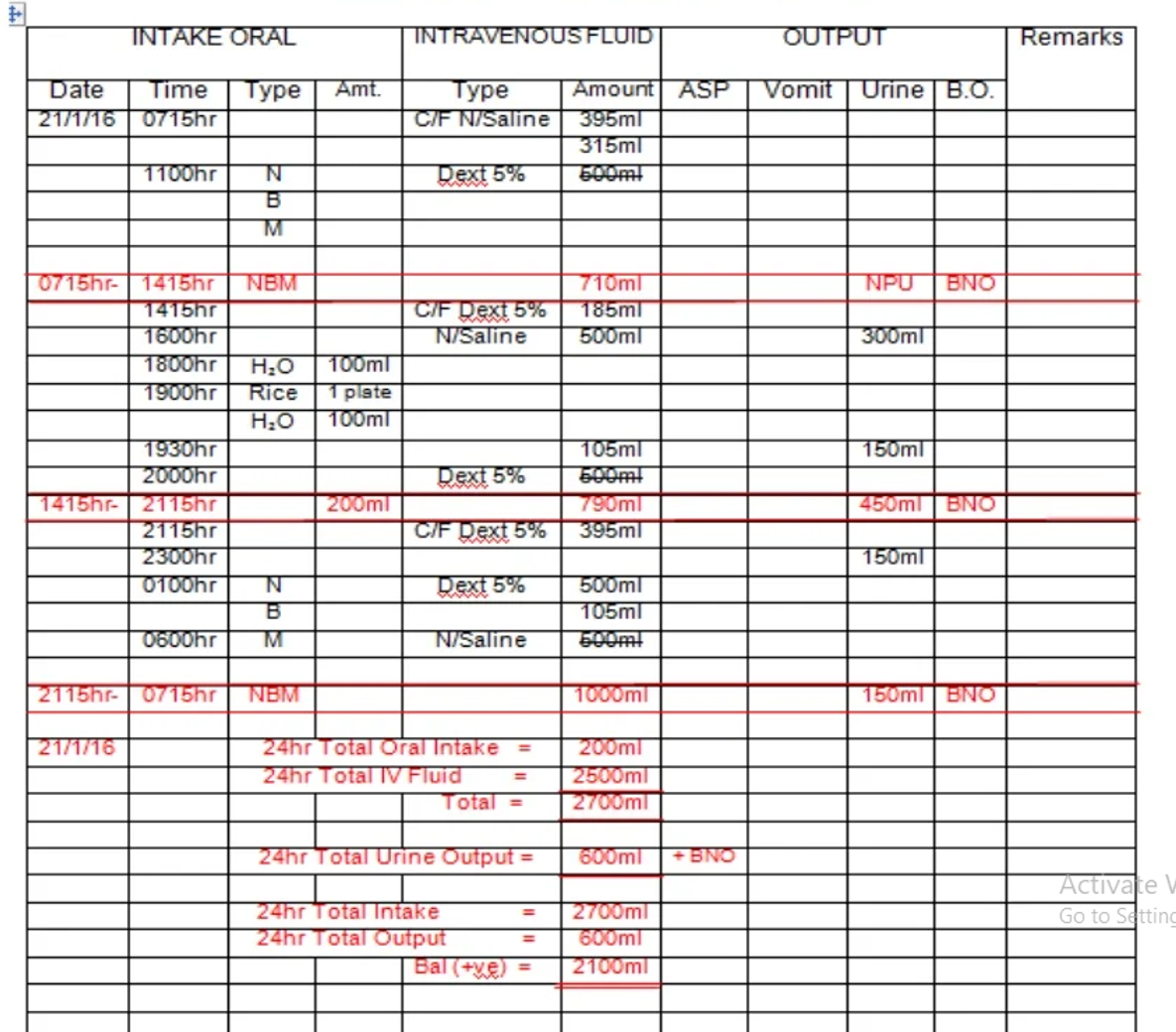
I&O SHEET