topic 3 : notes
all organisms are made of cells
most cells are too small to be seen with the naked eye
viruses “sabotage” cells
three most important parameters of microscopy
magnification : the ratio of an object’s image size to its real size
resolution : the measure of the clarity of the image or minimum distance between two distinguishable points
contrast : visible differences in parts of the sample
viruses are NOT cells but we can see them with a electron microscope
in a light microscope: visible light is passed through a specimen and then through glass lenses
lenses refract (bend) the light, so that the image is magnified


PLANT CELLS have CHLOROPLAST organelles that is responsible for photosynthesis and chlorophyll
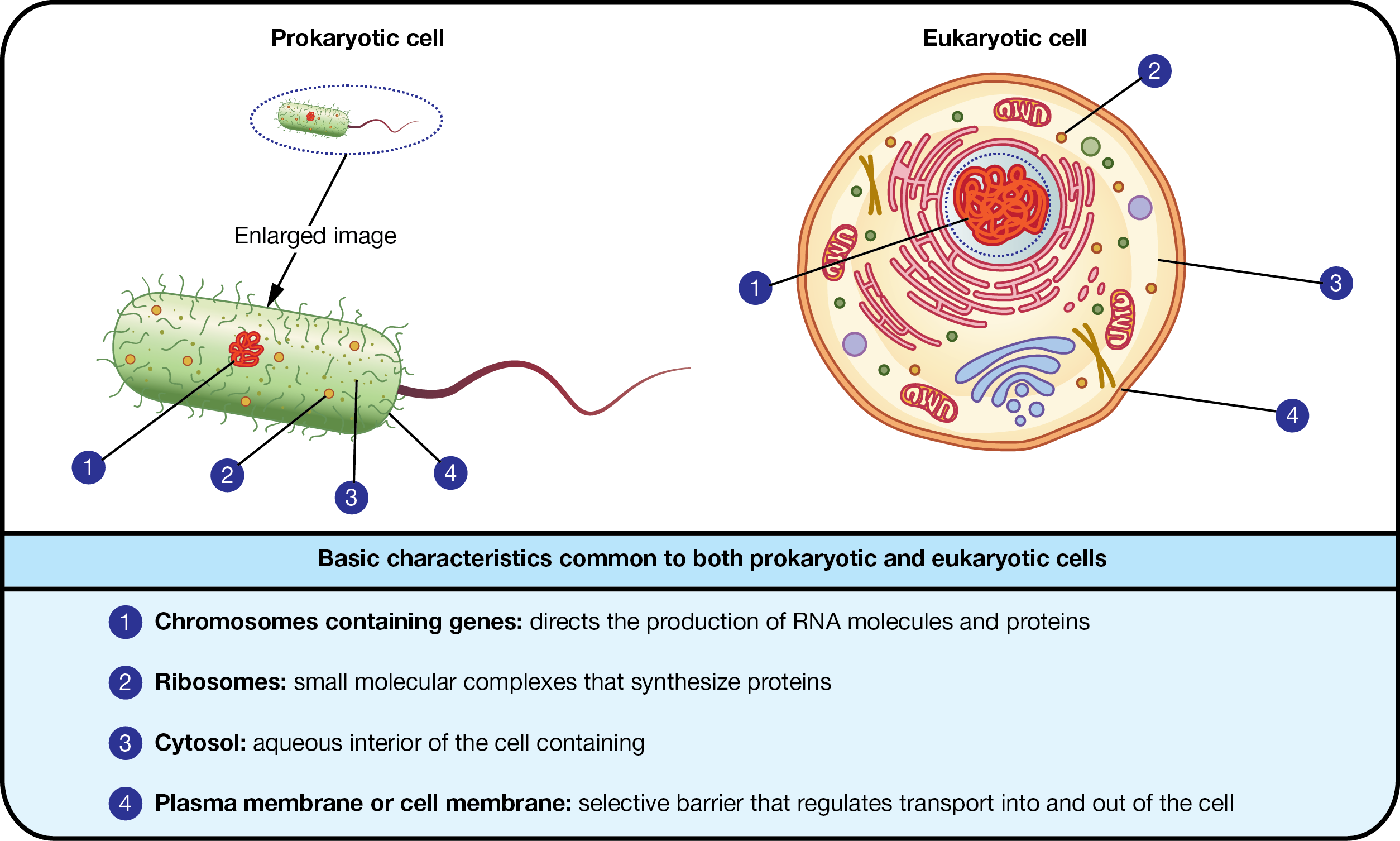
basic features of ALL CELLS
plasma membrane (boarder)
cytosol (semifluid substance in plasma membrane)
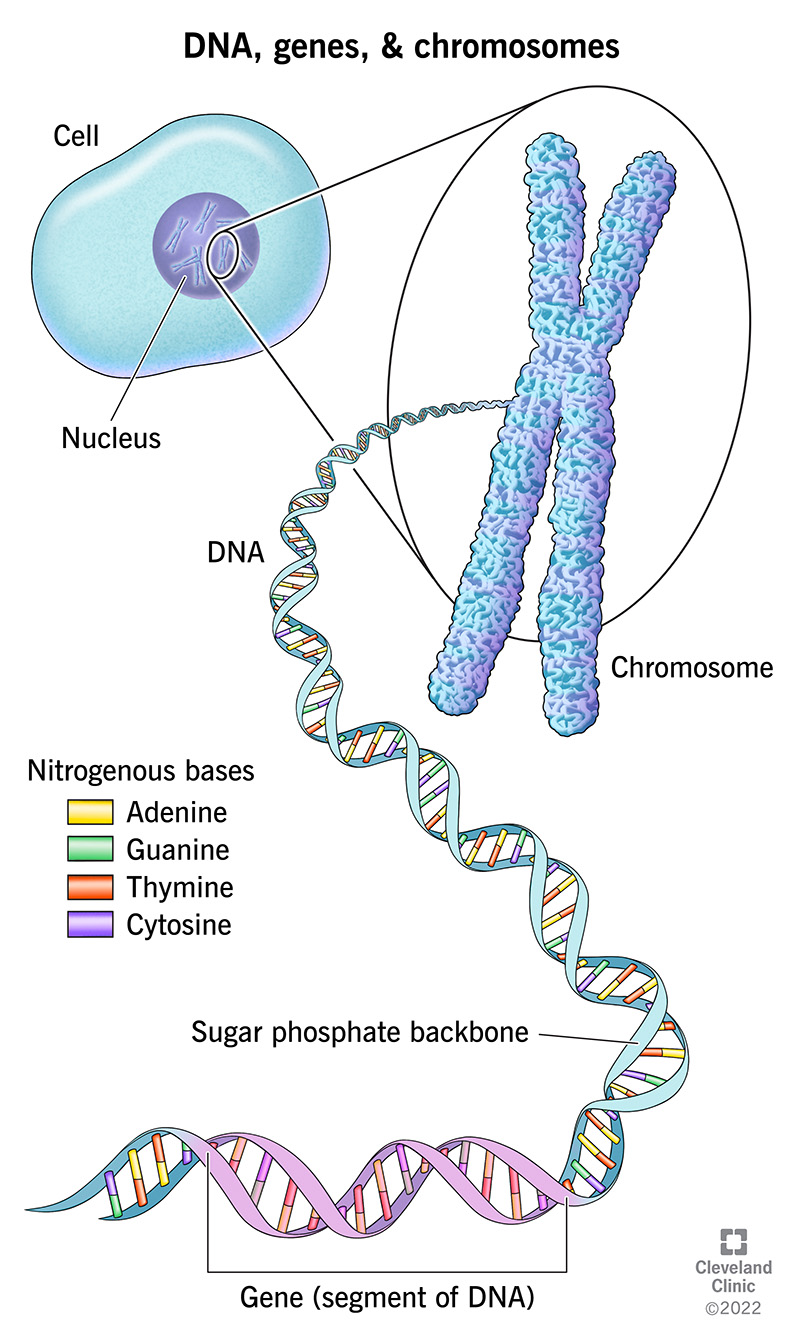
chromosomes (carry genes)
ribosomes (make proteins)
two types of cells
eukaryotic cells : most of the DNA is in the nucleus (organelle); organelles are bound by a membrane
prokaryotic cells (bacteria) : do NOT have a nucleus ; no membrane-bound organelles
Cell wall: protective layer of extracellular matrix that surrounds the plasma membrane of some cells, just outside the cell membrane
both types contain a cytoplasm bound by the plasma membrane
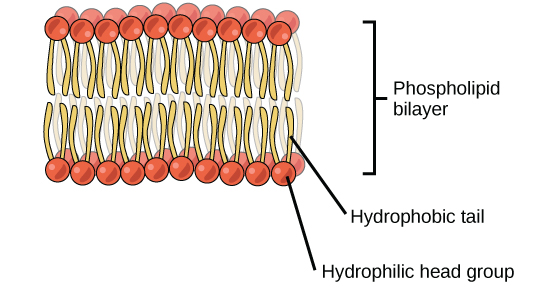
plasma membrane : selective barrier that allows sufficient passage of oxygen, nutrients, and waste to service the volume of very cell; membrane that encloses a cell and separates it from the external environment.
the general structure of a biological membrane is made of a double layer of phospholipids
cytosol : jellylike mixture of water, sugars, ions, and proteins and solutes enclosed by a cell’s plasma membrane
major part of a cell’s metabolism occurs in cytosol, and the cell’s other internal components, including organelles, are suspended in it
Organelles : structures that carry out special functions inside a cell
virus is smaller than most organelles
nuclear envelope: covers nucleus
endoplasmic reticulum: has ribosomes on surface
Golgi apparatus: modifies proteins
lysosomes: digest waste and harmful pathogens; can digest some bacteria, viruses, and worn out parts of the cell
vacuoles: contain water (plants)
plasma membrane: covers cell
cytoplasm : in a eukaryotic cell, collective term for everything between the cell’s plasma membrane and its nucleus. In a prokaryotic cell, everything enclosed by the plasma membrane.
function of the cell is dependent on the nucleus that includes DNA, the DNA includes the GENES that tell the proteins what to do
nuclear membrane: a double membrane where each membrane consists of a lipid bilayer that surrounds the nucleus
nucleus: contains DNA → organized into discrete units called CHROMOSOMES;
nucleotide : basic subunit of DNA
4 nucleotides are A, T, C, G
each chromosome is one long DNA molecule associated with proteins
DNA and proteins of chromosomes together are called chromatin
DNA is not “naked” but covered with proteins; and all DNA throughout the body are the same
ribosomes: organelle that uses the information from the DNA to MAKE proteins
can either be “free” or attached to the endoplasmic reticulum
“rough” E.R. has ribosomes
ribosomes then go through the Golgi apparatus to be modified; then goes to transport vesicle to be transported throughout the cell
“smooth” E.R. makes fats, carbs, and detox from drugs and poisons
cytoskeleton: network of fibers extending throughout the cytoplasm; gives cell its structure/frame that is like a highway that allows things to move from one organelle to the next
travels through vesicles (package truck)
differences
animal cell
has cell membrane, no cell wall
plant cell
has cell wall that surrounds membrane
vacuole: stores water
chloroplast: site of photosynthesis; contains chlorophyll and enzymes; plants photosynthesize and release oxygen network
mitochondria : powerhouse of the cell ; double-membraned organelle that produces ATP (protein) by aerobic respiration in eukaryotes
Cilia: moves in our windpipe and bronchi of our lungs → traps in debris from getting into our lungs

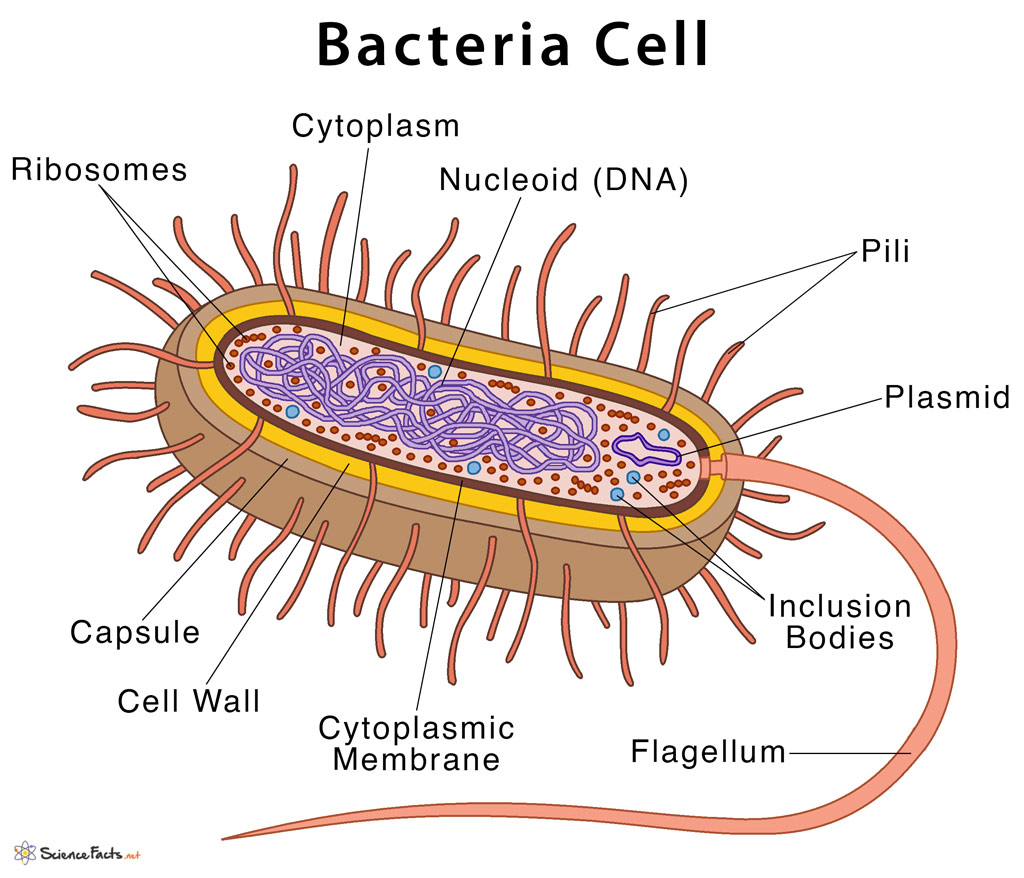
bacterial cells: some cells have flagellum and pilus that help with movement and interact with other cells ; no nuclear membrane
Cell membrane and cytoplasm: The cell is completely covered by a cell membrane that acts like a “security gate.” Only certain molecules are allowed to pass into or out of the cell. The inside of the cell (the cytoplasm) is filled with liquid (cytosol) and various organelles that do specific jobs for the cell.
Nucleus: The largest organelle in the cell is the nucleus. The nucleus acts as the “control center” or main office of the factory. Inside the nucleus, DNA is the “boss.” DNA molecules contain the plans for every protein the cell can manufacture. As the boss, DNA never leaves the office. Instead, a messenger molecule (messenger RNA) carries written instructions for building a protein to the rest of the factory.
Ribosomes are “workbenches” that work only on proteins. Ribosomes read the instructions from messenger RNA and assemble materials into a polypeptide.
Endoplasmic reticulum is part of the factory’s “assembly line.” There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. Rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER) works only on proteins. Smooth endoplasmic reticulum (SER) builds lipids.
Golgi complex: The Golgi complex is the “distribution center.” It modifies, sorts, tags, packages, and distributes the proteins and lipids.
Transport vesicles are tiny spheres of membrane that surround and carry proteins or lipids to their destination. That destination may be inside the cell, or vesicles may eject their contents out of the cell (exocytosis).
Cytoskeleton is the “skeleton” or structural components of the factory. This includes structures that act like monorails to move transport vesicles containing proteins or lipids to their destinations.
Mitochondria: All this work requires energy. The mitochondrion is an energy-generating organelle that takes in fuel (food) and mass produces the energy molecule ATP.
Lysosomes and peroxisomes are the factory’s “cleaning crew.” Lysosomes are vesicles filled with strong enzymes that digest large molecules and worn-out organelles. Similar to lysosomes, peroxisomes have enzymes that break down smaller molecules and detoxify poisons.
What structure allows only certain molecules to pass into or out of the cell?
cell membrane
What cellular structure contains most of the DNA?
nucleus
Which of the following are the only molecules built by ribosomes and rough endoplasmic reticulum (RER)?
proteins
Which of the following types of biological molecules are synthesized at the endoplasmic reticulum?
proteins
lipids
_____ & ____ are responsible for breaking down cellular components and molecules.
lysosomes
peroxisomes
On average, eukaryotic cells are approximately _____ prokaryotic cells.
10 times larger than
Which of the following characteristics is specific to prokaryotic cells?
plasmids
Mitochondria are an example of _____.
organelles found within eukaryotic cells
Which of the following structures are found only in eukaryotic cells? Select all that apply.
rough e.r.
nuclei
the Golgi complex
Which of the following are parts of both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells? Select all that apply.
plasma membrane
cytosol
DNA
In prokaryotic cells, the DNA is located in the _____ while in eukaryotic cells, DNA is located in the ______.
nucleoid
nucleus
What part of a phospholipid faces the cytosol inside a cell?
hydrophilic head
Ions and polar molecules can cross the plasma membrane in regions where the membrane has incorporated _____.
transport proteins
The plasma membrane is considered a fluid mosaic because it permits incorporated molecules such as receptors and transport proteins to _____.
move around laterally within the membrane
The word bilayer in the term phospholipid bilayer refers to which of the following?
The two layers of phospholipids that make up the membrane
The cell membrane is _______ because some molecules can travel across the membrane while others cannot.
semipermeable
Which small molecule decreases the fluidity of the plasma membrane?
cholesterol