Evolution Study Guide
Evolution
-Process by which modern organisms descend from ancient organisms
Charles Darwin
Theology became naturalistic
Took a trip around the world in 1831 at age 21
Made observations & formed his own beliefs
Galapagos Islands
Located in South America (West), Equator: Varied Climate
Observed: Finches (Beaks), Tortoises (Necks/Shells), Blue Footed Booby (Mating Rituals)
Diversity & Adapting to Environment
Could these organisms be related?
Evolutionary Roadblocks (Incorrect beliefs at the time)
Earth was only approximately. 2000 years old
Earth/Organisms were immutable (unchanging)
Natural Disasters were infrequent miracles
People That Influenced Darwin
James Hutton
Proved Earth is millions of years old through rock layering
Charles Lyell
Wrote Principles of Geology
Supported Hutton
Jean Baptiste Lamarck
Giraffes
Organisms change over time
“I think I can, I think I can”
A) Tendency Towards Perfection
B) Use & Disuse (if something goes unused, it will vanish eventually)
C) Inheritance of Acquired Traits (Tattoos passing down to offspring)
Thomas Malthus
Economist, population
More are being born than dying
War, famine, and disease regulate population
Organisms must compete
Evidence of Evolution
Fossil evidence
Provides age of planet/organisms & common ancestors
Homologous Structure
Same structure, different function
Ex) Human arm, whale fin cat leg, bird wing
Analogous Structures
Same function, different structure
Ex) Dolphin, shark, penguin’s fin; fly wing vs bird wing
Vestigial Structure
Organ you no longer need
Ex) Wisdom teeth, tailbone, appendix, whale legs
Comparative Embryology
At embryo stage, organisms have many similarities
Ex) Gills, structure
Biochemical Evidence
DNA similarities
Darwin’s Theory of Evolution
Varitation
Variation in traits
Overpopulation
Not enough resources
Competition & Struggle
Compete to survive
Survival of the Fittest
Natural Selection
Only the “strong” will survive
Species Change Over Time
Slow Process
Darwin vs Lamarck
Giraffes
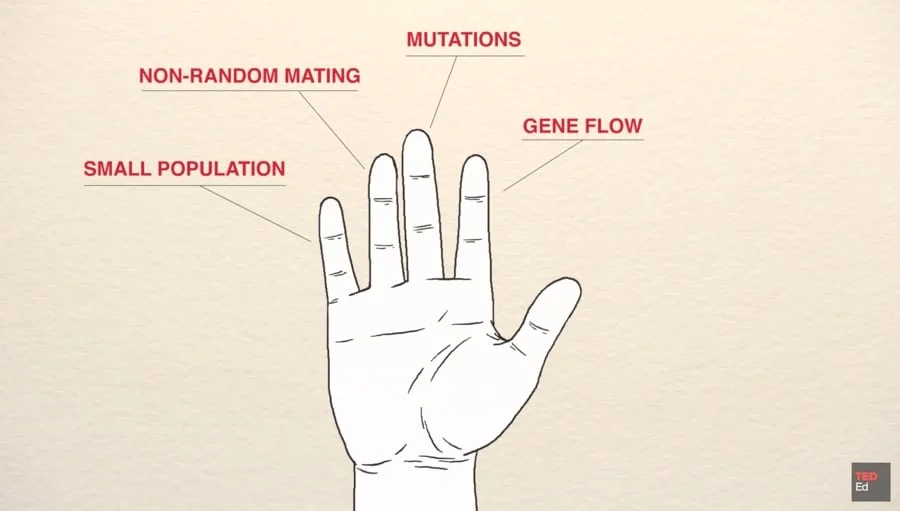
Sources of Variations
Mutations
Gene Shuffling
Crossing Over
Adaptive Radiation
Organisms adapt to environment & spread out
Ex) Finches
Evolutionary Patterns
Convergent
Species become more similar
Analogous
Ex) Shark & Dolphin
Divergent
Species become more different
Homologous
Ex) Finches
Genetic Drift, Founder Effect, Bottlenecks
How recessive traits become more prominent
Isolating Mechanisms
Behavioral
Mating hibernation
Ex) Blue Footed Boobie
Temporal
Timing
Ex) Frogs
Geographical
Geographical obstacles
Ex) Mountain
Evolutionary Paths
Gradualism
Small changes over time
Punctuated Equilibrium
Big changes over time
Five Fingers of Evolution