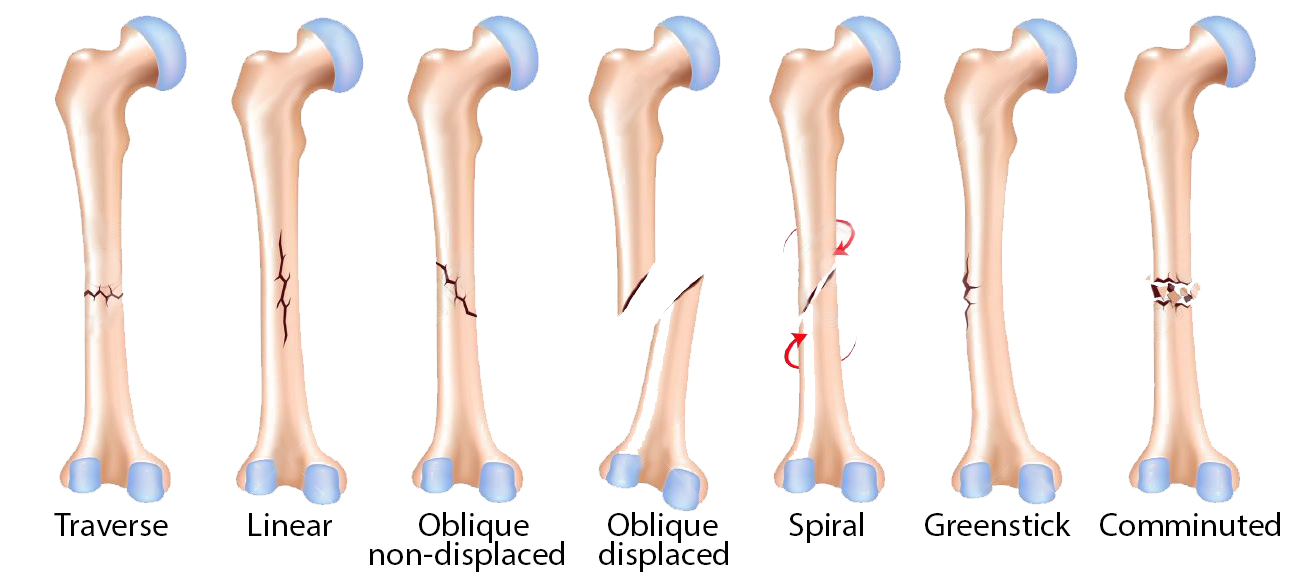
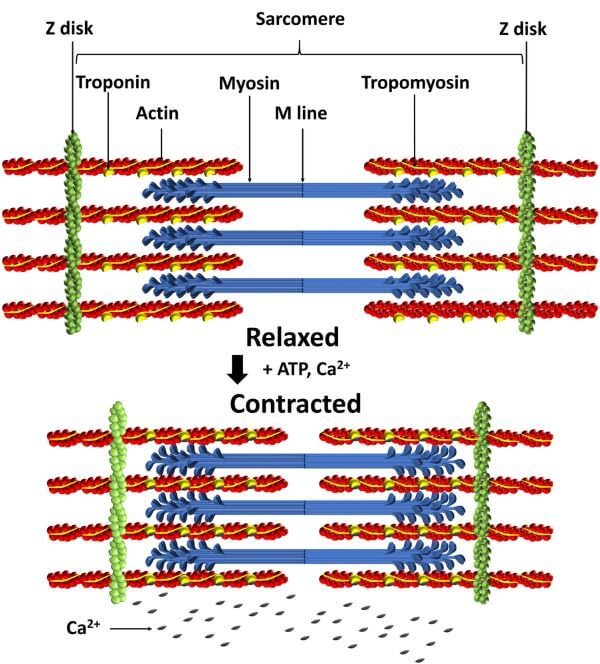
Mid-term Review
Occipital lobe (back): Responsible for vision.
Frontal lobe (front): Reason & Planning.
Parietal lobe (top): Integration and sensory perception.
Temporal (side): Processes pain auditory stimuli, emotions, and memories.
Cerebellum: Responsible for muscle coordination.
Brain stem: Hearing, vision, and other life functions.
Sagittal plane: An uneven vertical division of the body.
Plane Joint: Between carpal bones
Olfactory bulb: Smell
Connective tissue: Blood, bone, adipose
Antagonist: binds to a receptor away from the active site, preventing the normal neurotransmitter from binding.
Inverse agonist: Binds to a receptor at the active site without activating the receptor.
Reuptake inhibitor: Blocks trans-membrane proteins on pre-synaptic cells, leaving more neurotransmitters in the synapse.
Agonist: Imitates a particular neurotransmitter by binding to the receptor’s active site.
Compact bone: gives bone its strength around the diaphysis of long bones surrounding the medieval cavity.
Spongy Bone: Gives bone its lightness, found at the epiphyses of long bones
Popliteal: Inferior to gluteal region.
Sternal: Medial in the body.
Hippocampus: Memory.
Hinge: Elbow.
Orbital: The eye/eye socket
Patellar: The kneecap
Distal: Far from the joint
Scapular: On the posterior side of the body
Saddle: Base of thumb
Hypothalamus: Body of temperature
Pivot: Proximal ends of radius and ulna
Superficial: Hair is superficial to your head
Wernicke’s area: Speech production
Condyloid: Wrist
Medullary cavity: A long space filled w/ vessels and yellow bone marrow.
Yellow bone marrow: In the medullary cavity
Striated Muscle: Have lines showing the direction it moves
Which types of cells in the body would you expect to need the most ATP? Muscle cells
Fibrous Joint: Fixed/Moveable joint that connects to bone
Cartilaginous Joint: Some motion to it with hyaline cartilage in the space between articulating bones.
Synovial joints: Moveable joint with synovial fluid. Reduces friction.
CNS: Brain & Spinal cord —> Sends signals to make the body do certain actions.
PNS: Nerve cells —> Carries these signals throughout the body.
Osteoblasts: Immature; New bone formation
Osteoclasts: Breaker; Break old bone to repair new bone
Osteocyte: Cell; Produce soluble factors that help bone re-works
Neurons are similar to other cells because they both have cell membranes w/ organelles. They are different because neurons have axons and dendrites.
Explain how different types of neurons work together to sense, process, and respond to stimuli: Different neurons have different jobs.
Sensory neurons: Send information from ears, nose, eyes, etc., to the brain.
Motor neurons: Carry messages from brain to the rest of the body.
Interneurons: Connect motor and sensory neurons together.