In Class Notes 10/3: The Role of Play in Development
Play in Preschoolers 🤸♀
The Importance of Play
Play is a universal activity that has been observed in children across cultures and time. It is the most productive and enjoyable activity for kids, allowing them to learn and practice physical, cognitive, and social skills.

Types of Play
Type of Play | Description |
Solitary Play | Playing alone, unaware of others |
Onlooker Play | Watching others play, but not interacting |
Parallel Play | Playing with similar toys, but not interacting |
Associative Play | Interacting with others, but not playing the same game |
Cooperative Play | Playing together, taking turns, and following rules |

Development of Social Skills
As children progress through the preschool stage, they develop social skills through play. By the end of this stage, they should be able to engage in cooperative play, making up activities together and following rules.
The Role of Peers in Play
Peers provide an audience, role models, competition, and social information that is essential for developing social skills. Playing with peers helps children learn empathy, negotiation, and emotional regulation.
The History of Play
In the past, families had more children, and play was often informal and unstructured. Children played with siblings and neighborhood children of different ages, with older kids watching out for younger ones.
Forms of Play in Preschoolers
Rough and Tumble Play 🤼♂
"Rough and tumble play is a type of play that mimics aggression through wrestling, chasing, or hitting without intending to harm someone else."
This type of play is common in preschoolers and helps develop social understanding and lunatic system development. However, it can also increase the risk of injury.
Social Dramatic Play 🎭
"Social dramatic play is a type of play that allows children to act out different roles and themes and stories that they create."
This type of play helps children explore and understand social roles and develop their ability to explain and negotiate.
The Impact of Lack of Social Play
Research has shown that a lack of social play in preschoolers can lead to unhappiness, less learning, and fewer social skills. This is particularly relevant in the context of the COVID-19 pandemic, where many children have had limited opportunities for social play.## Screen Time and Child Development 📱
The Impact of Excessive Screen Time
Excessive screen time can have negative effects on a child's development, including:
Reduced social skills
Decreased imagination
Less time spent outdoors
Negative impact on emotional regulation and self-control
American Academy of Pediatrics Recommendations
The American Academy of Pediatrics recommends:
No more than 1 hour of screen time per day for preschoolers
Supervised screen time to ensure children are not exposed to inappropriate content
Changes in Screen Time Habits
Year | Total Screen Time | Mobile Device Screen Time |
2011 | 2 hours 16 minutes | 5 minutes |
2013 | 2 hours 30 minutes | 15 minutes |
2017 | 2 hours 30 minutes | 1 hour 15 minutes |
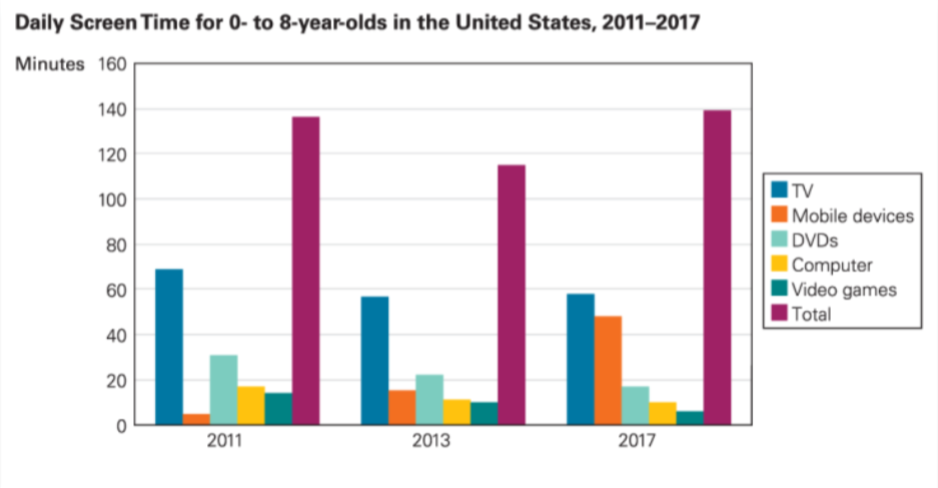
The Effects of Screen Time on Children's Behavior
70% of parents admit to using devices to calm their children down
Children who use devices to calm down may not learn to regulate their emotions themselves
Excessive screen time is associated with behavioral problems in children
Interactive Media and Learning
Interactive media, such as educational apps, can be beneficial for children's learning
Apps can teach more than just letters and numbers, including physics and problem-solving skills
Parental involvement is key to making interactive media educational
The Importance of Moderation
Parental discretion is advised when it comes to screen time
Children who have limits set on their screen time and engage in other activities, such as playdates and outdoor play, can benefit from moderate screen time
Definitions
Distractibility: The ability to focus on a task and resist distractions. Emotional Regulation: The ability to manage and regulate one's emotions. Interactive Media: Media that allows for user interaction, such as educational apps and games.
Key Takeaways
Excessive screen time can have negative effects on children's development
Interactive media can be beneficial for learning when used in moderation
Parental involvement and discretion are key to ensuring healthy screen time habits## Parenting Styles 📚
Parenting styles vary within nations, ethnic groups, neighborhoods, and even within families. Research by Von Ryan identified four important dimensions that distinguish parenting styles:
Expressions of Warmth: The level of affection or criticism shown by parents towards their children.
Strategies for Discipline: The methods used by parents to discipline their children, such as explaining, criticizing, persuading, ignoring, or punishing.
Communication: The way parents communicate with their children, either one-way or two-way.
Expectations for Maturity: The standards parents set for their children's responsibility and self-control.
Parenting Style Categories
Parenting Style | Characteristics |
Authoritarian | High behavioral standards, strict punishment, low communication, one-way communication |
Permissive | High nurturing, low discipline, two-way communication, few rules or limits |
Authoritative | Balanced approach, reasonable expectations, discipline, two-way communication |
Uninvolved/Disengaged | Few rules or limits, low communication, low warmth, neglectful |
Authoritarian Parenting
"Authoritarian parents tend to have very high behavioral standards and are not necessarily developmentally appropriate. They have very strict punishment and misconduct. Communication is low and it is one-way, the parent telling the child what to do."
Characteristics:
High expectations
Strict punishment
Low communication
One-way communication
Long-term outcomes:
Children tend to be obedient, conscientious, and quiet, but often unhappy
Adolescents may rebel and leave home at an earlier age
Adults may be quicker to blame and punish others
Permissive Parenting
"Permissive parents are kind of the opposite of authoritarian parents. They see a lot of high nurturing communication. You see a lot of two-way communication, but not enough discipline. It's a very little discipline, guidance, or control."
Characteristics:
High nurturing
Low discipline
Two-way communication
Few rules or limits
Long-term outcomes:
Children may lack self-control and emotional regulation
Peers may view them as spoiled or entitled
Adults may be unhappy and financially and emotionally dependent on their parents
Authoritative Parenting
"Authoritative parents seem to be a pretty good mix of the good things coming out of you. They're gonna set limits and enforce rules so there's definitely discipline there, but they're also flexible and communication is two-way."
Characteristics:
Balanced approach
Reasonable expectations
Discipline
Two-way communication
Long-term outcomes:
Children tend to be successful, articulate, and popular
They are well-liked by teachers and peers
Uninvolved/Disengaged Parenting
"Uninvolved or disengaged parents have very few rules or limits. Not much communication, not much of a warm nurturing relationship. You see this type of parenting most commonly in families where parents are dealing with either addictions issues or serious mental health issues."
Characteristics:
Few rules or limits
Low communication
Low warmth
Neglectful
Long-term outcomes:
Children may take care of themselves and younger siblings
Children may lack emotional support and guidance## Parenting Styles and Discipline 🤝
Parenting Styles and Long-Term Outcomes
Research has shown that children with involved and engaged parents tend to have the best long-term outcomes. On the other hand, children with uninvolved and disengaged parents are at risk of:
Being sad and lonely
Being at risk of injury or abuse, both as children and as adults
Lacking maturity or becoming overly mature
Being at greater risk for substance abuse issues
Moving away from home earlier
Discipline Methods 🚫
Punishment Rates
Punishment rates increase dramatically from infancy to early childhood. Most parents use multiple methods of discipline, and may use different methods on siblings due to expectations and personality differences.
Corporal Punishment
Corporal punishment is any discipline method that hurts the body, from spanking to actual serious child harm and abuse.
Corporal punishment is often based on personal experiences and cultural norms. Research has shown that it is ineffective in the long term, although it may work well with younger children. However, as children get older, corporal punishment can lead to:
Greater tendency to become disobedient and rebel
Issues with self-control
Increased risk of substance abuse
Prevalence of Corporal Punishment
Demographic | Prevalence of Corporal Punishment |
Southern US states | Higher |
New England | Lower |
Mothers | Higher |
Fathers | Lower |
Conservative Christians | Higher |
Non-religious families | Lower |
African Americans | Higher |
European Americans | Lower |
Asian Americans | Lower |
Hispanic Americans (US-born) | Higher |
Hispanic Americans (immigrant) | Lower |
Lower SES families | Higher |
Higher SES families | Lower |
Laws and Regulations
In 53 nations, including all of Northern Europe, corporal punishment of any sort is illegal.
In 100 nations, corporal punishment is illegal in schools.
In the US, 22 states still allow corporal punishment in schools.
Other Types of Disciplinary Techniques
Psychological Control
Psychological control involves threatening to withdraw love and support from the child, making them feel guilt and gratitude towards parents.
Time Out
Time out is used to separate the child from others in activities for a period of time.
It only works if done correctly, with a designated spot that is boring and uninteresting.
Guidelines suggest one minute of time out for every year of age.
Induction or Reasoning
Induction or reasoning involves trying to reason with the child to get them to understand why the behavior was wrong.
This method is effective with older children, but not with younger children.
Taking Away Privileges
Taking away toys or privileges can be an effective method of discipline.
As children get older, this can include taking away privileges such as watching TV, using the phone, or driving.