Eukaryotic Transcription
3/29/24
Rules of Transcription
Start with recognition and a promoter will mark the DNA to show where DNA should be transcribed- protein complex has to combine together before anything can happen
Eukaryotic Protein Coding Genes- only one region is translated in a monocistronic mRNA (Which starts out as an unprocessed pre-mRNA)
Eukaryotic Gene Structure- onle one coding region flanked by UTRs but it is broken up into exons
In the nucleus before translation-Usually in G0 (nondividing cells), G1 or G2(periods when genes coding for cellular organelle proteins are synthesized.
gets rid of the introns during this time
Transcriton will start at the +1 site and ends in the termination region (3’ UTR) (UTR= untranslated region) - Transcription does NOT start with AUG (start codon)
Only ertian parts of DNA are stranscribed
the promoter will have two parts:
Core promoter- has a sequence that is common to most genes
Proximal promoter- has a sequence that is unique to a gene
Common Promoter Features
The TATA box- seen in core promoters; recoginized by a General TF called TBP
GC-rich box- Proximal promoter
CAAT box- Proximal promoter
Transcription Factors- proteins or protein complexes that bind to promoter squences or other regulatory sequences and influene transcription initialtion by ionteracting with RNA polymerase
General TFs play a role in transcription for most genes
Specific TFs are regulatory and differ among sexes- bind to the proximal promoters
Core promoter: “on/off” switch a highly conserved sequence which serves conserved sequence which serves as the binding site for General Transcription Factors and RNA Pol II (start site of transcription)
Proximal Promoter: Contains regulatopry sequences which bind transcriptional activator proteins (Specific Transcription Factors). These stimulate and stabilize activity of the RNA pol II bound at the core promoter
RNA Polymerase II- requires many general and specific transcription factors to function
Eukaryotic Stages of Transcription
Recognition
The TATA box is recognized and bounded by a general transcription factor
First, TBP can bind to the TATA box (TBP= Tata Binding Protein) TBP is a component of the TFIID complex. this allows the complex to recognize and bind to the Tata box in the core promoter
TBP attached by interacting with negatively charged phosphates in the backbone and inserts amino acids side chains betwen the bases- stabilized by hydrogen bonds; it distorts the DNA causing it to bend and “melt”
TFIID complex recruits more transcription factors and mark the promoter
Initiation
After the TBP “melts” the DNA, this will be the landing site for other binding complexes- TFIIB recruits RNA Polyermerase II
TFIIH has helicase activity and can phosphorylate RNA polymerase II in order to activate this activity to open the bubble
Need to Know TBP, TFIID, TFIIB, and TFIIH
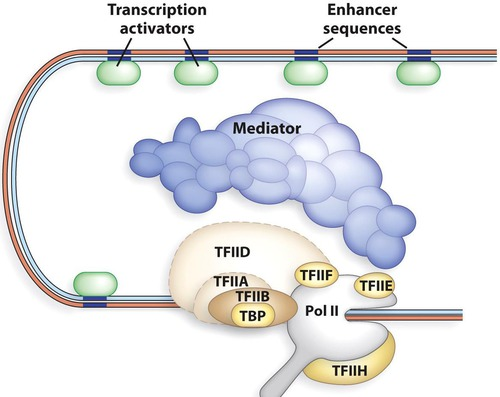
Specific Transcription Factors are bound to distal regulatory regionS in the DNA and to the Proximal Promoter in the DNA
Mediator Complex-part of the complex that bridges specific TFs bound to distal regulatory regions in the DNA and the RNA polymerase II Holoenzymes bound to the core promoter
TFIIH- Open the transcription bubble (helicase activity) and activates the RNA polymerase II
CTD tail is phosphorylated by the TFIIH resulting in active RNA pol II Holoenzyme
CTD tail- Carboxyl-Terminal Domain (this is the end of a protein)
Elongation
Some general transcription factors are released
RNA poly II- openes the bubble ahead of itself and closes it behind the transcription bibble- remember that eukaryotic DNA contains nucleosomes/ chromatosomes
Rercruits Elongation factors to evict histones anhead of RNA pol II and replace them behind it
EFsmaintian heterduplex RNA:DNA hybrid region
EFs deal with issues
Termination
Termination involves cleavage of the RNA at a specific position in the 3’ UTR and this is linked to the dephosphorylation of RNA Pol II (deactivating) and RNA Pol II drops off the DNA
By this point we have made the preMRNA ⬇