Chapter 3
Systems of the body:
Nervous System:
Endocrine System:
Respiratory System:
Circulatory System:
Integumentary System:
Muscular system:
Skeletal system:
Immune system:
Energy system:
Digestive system:
Urinary system:
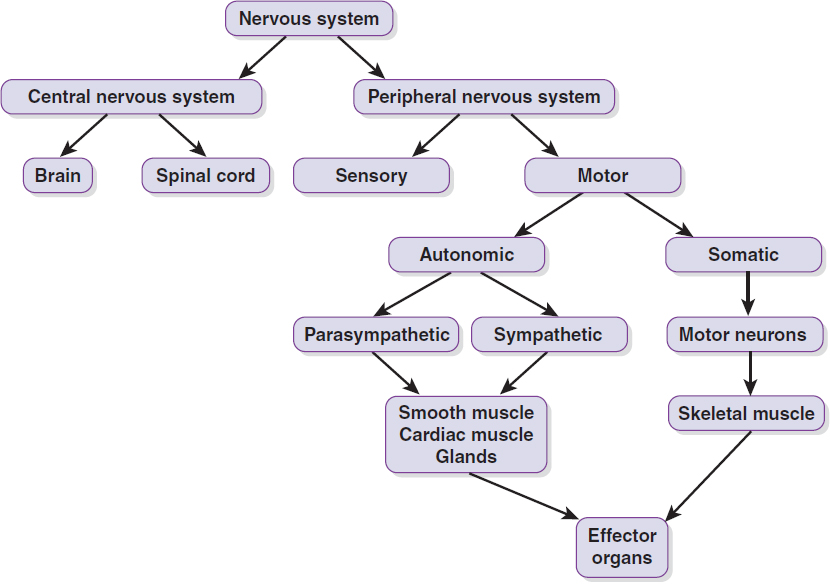
Nervous System:
One of the 2 primary control systems of the body = other one is endocrine system.
responses occur rapidly
controls voluntary and involuntary actions
responds to physical activity strenuous exercise and diseases.
CNS: Central Nervous System
Brain and spinal cord = primary components of CNS
Peripheral nervous system: afferent sensory neurons, and efferent motor neurons. It also includes motor end plates that connect efferent neurons to muscle fibers and the sensory receptors on sensory organs.
Efferent neurons: somatic neurons and autonomic neurons
2 divisions of autonomic nervous system: sympathetic and parasympathetic.
Afferent Neurons: neurons that carry electric impulses to brain and spinal cord
Efferent Neurons: neurons, carries electric impulses away from brain and spinal cord.
Somatic: part of NS, controls voluntary action
Autonomic: part of NS, regulates involuntary action
Sympathetic: part of autonomic NS, acts in opposition to parasympathetic NS (usually in conditions of stress).
Parasympathetic: part of autonomic NS, acts in opposition to sympathetic NS.

Nervous System and Exercise Science:
more exercise = more stroke volume during contraction of heart = results in higher cardiac output
Muscular System:
What systems come together to create movement of the body with the muscular system: skeletal, and nervous system.
What is the primary component of the muscular system? Muscle Fibers
Muscle Fibers: generates force through interaction of various contractile and regulatory proteins.
Types of fibers: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac.
Skeletal muscle = voluntary control
Smooth and Cardiac Muscle: controlled by autonomic NS.
Muscular System and Exercise Science:
Eccentric Muscle Actions: greater damage to the tissues and soreness and pain in the affected muscle.
muscle fibers lengthen when generating force.
High intensity resistance exercise training results in significant gains in muscle size and strength that results in improvement in sport and athletic performance.
Muscle Fiber Hypertrophy: increase in size of individual muscle fibers.
occurs in response to prolonged resistance exercise training.
this is cross-sectional size
Muscle Fiber Hyperplasia: increase in the number of individual muscle fibers.
Undifferentiated satellite cells: undeveloped cell that can convert to a developed cell.
Skeletal System:
protects underlying organs and tissues of the body
What works with the skeletal system to create movement or respond to a stimulus? Muscular System and Nervous System
Hematopoiesis: several bones of the body contain red bone marrow, that will produce blood cells (red, white, and platelets).
Skeletal System and Exercise Science:
Osteoporosis: low bone mineral density.
osteoporotic bones have a greater risk for fracture.
Erythropoietin: endocrine hormone, controls red marrow in bone when it is generating red blood cells.

Recombinant Human Erythropoietin (rEPO) demonstrated to increase RBCs formation and reduce the risk of anemia as a part of therapy.
Erythropoietin: hormone stimulates the production of RBCs and hemoglobin.
Cardiovascular System:
What does the cardiovascular system transport? blood that contains oxygen, nutrients, and:
hormones
electrolytes
drugs
Does the cardiovascular system assist in body temperature regulation? YES!
Which two system are often referred as one system? cardiorespiratory and cardiopulmonary system
What are the primary components of the cardiovascular system:
heart
arteries
arterioles
capillaries
venules
veins
blood
What is the heart compromised of?
cardiac muscle
nervous tissue = this generates force that will propel blood through body.
arteries & veins: comprised of smooth muscle; helps distribute blood through tissues of the body.
Cardiovascular System and Exercise Science:
What is the leading cause of death in the US? cardiovascular disease.
What is the primary cardiovascular disease occurring in most Americans? Coronary Artery Disease (CAD).
What is atherosclerosis? cholesterol and blood lipids builds up in the arteries supplying blood to the heart.
“Atherosclerosis, a disease process whereby cholesterol and blood lipids build up in the arteries supplying blood to the heart, results in a reduction of blood flow to cardiac muscle”
Atherosclerosis A disease process whereby cholesterol and blood lipids build up in the arteries causing a narrowing of the vessel opening.
COPD: Chronic Obstrcutive Pulmonary Disease; this includes chronic bronchitis and emphysema and it reduces the ability to perform physical activity and exercise.
Exercise-induced asthma: This asthmatic event is typically referred to as exercise-induced asthma. Exercise-induced asthma can result in airway constriction, shortness of breath, and wheezing similar to those experienced with asthma