Size and Surface Area
Exchanging Substances: Organisms in their environment
Cells need to take in oxygen (for aerobic respiration) and nutrients.
Need to excrete products (carbon dioxide, urea)
Stay same temperature, so heat exchanged
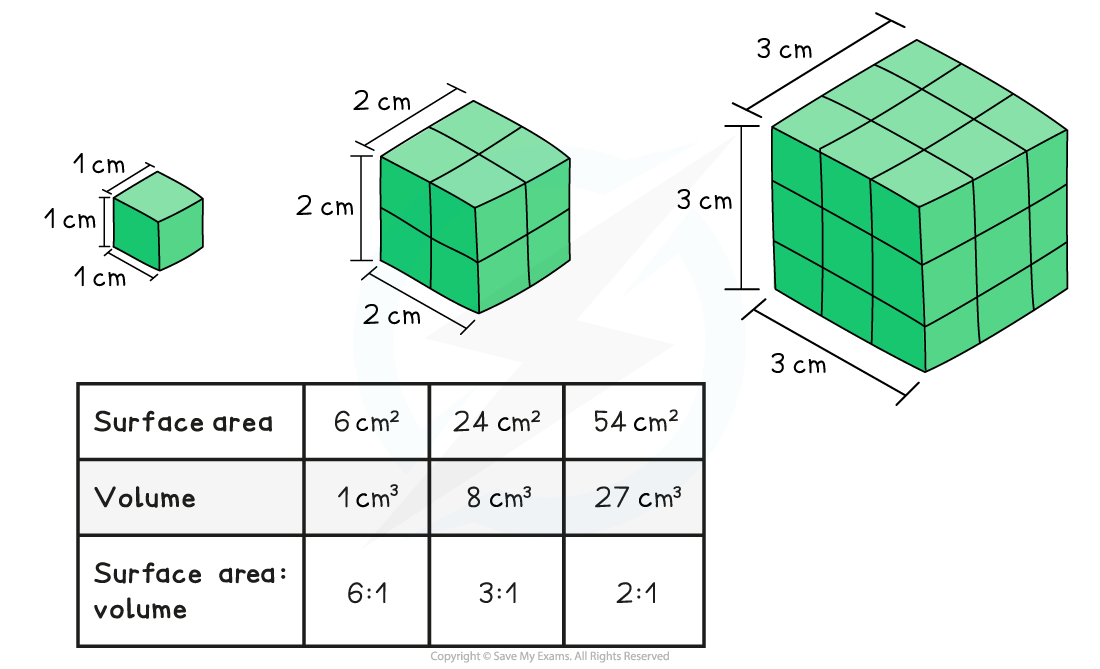
Depends on surface area to volume ratio
Surface Area to Volume ratios
Smaller animals have larger surface area to volume ratios
Larger animals have smaller surface to volume ratios
It’s a factor which affects exchange of substances in an organism
For example:
Multicellular Organisms: Exchange Organs and Mass Transport Systems
All cells need to be supplied with substances like glucose and oxygen
Also needs to remove remove waste to avoid damaging itself
Single-celled:
Substances can diffuse directly into or out of the cell
Substances travel across the cell membrane
Diffusion rate is quick as small distances needed to travel
Multicellular:
Diffusion across outer membrane is too slow as distances are too large and larger animals have low SA:V ratio where it’s difficult to exchange enough substances to supply cells
Uses exchange organs (e.g. lungs) along with an efficient system
Effects of Size and Shape on Heat Exchange
Metabolic activity creates heat inside cells, along with creating waste products.
Size:
Rate of heat loss depends on surface area
Large volume = small surface area → harder to lose heat
Small volume = large surface area → easier to lose heat
Therefore, smaller organisms need a high metabolic rate in order to generate enough heat to stay warm
Shape:
Compact shape = small surface area (relative to volume) → minimises heat loss
Less compact shape = large surface area → increases heat loss
Compact or not, it depends on the temperature of their environment:

Behavioural and Physiological Adaptations
Not all have size or shape to suit their climate, some have other adaptations
Animals with high SA:V ratio tend to lose more water (evaporates)
Small desert animals have kidney structure adaptations so they produce less urine
To support high metabolic rate, small mammals in cold areas need to eat large amounts of high energy food (seeds and nuts)
Large organisms in hot areas (elephants and hippos) have slow heat loss
Elephants have large flat ears to increase SA → lose more heat → physiological
Hippos spend much of the day in water → behavioural adaptation