AP Bio- Chapter 14 genetics
Earliest hypothesis: blending hypothesis. states that we are a perfect blend of our parents
particulate (gene) idea: parents pass on heritable particles (genes) to offspring
Introduced after Mendel’s work with pea plants
True breeding: the genes of the parent are homozygous, (AA or aa). When truebreeding plants self-pollinate, offspring are ALWAYS the same as the parents
Parent generation: P
First generation offspring: F1
Second generation offspring: F2
Rules Mendel established:
Alternative versions of genes cause variations in characters. The alternative versions of genes are called alleles.
Each organism inherits 2 alleles from each parent for each characteristic
if the 2 genes differ at the locus (location of a gene on the chromosome), then the dominant gene is the one that determines the organism’s trait
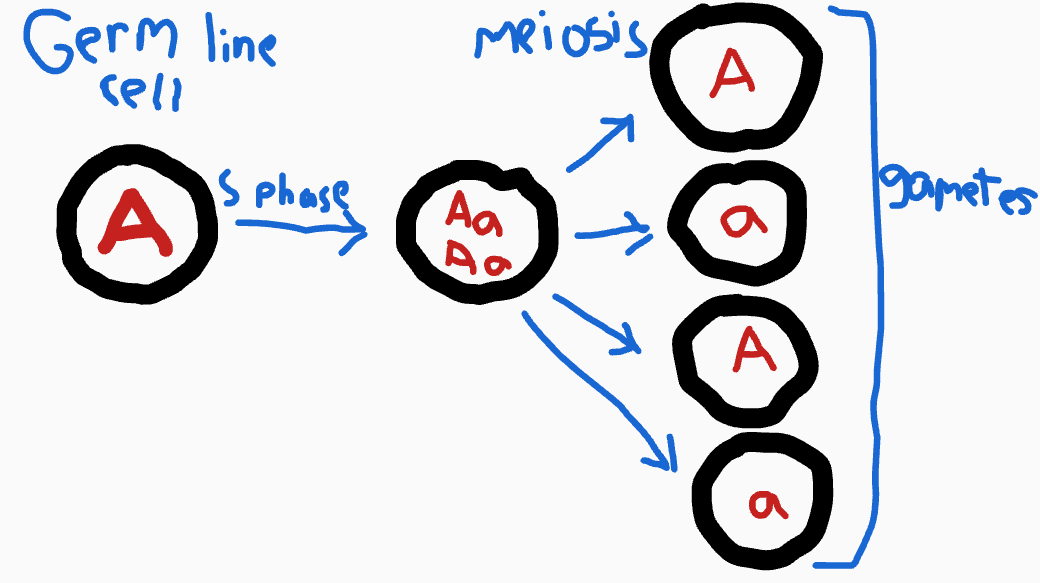
LAW OF SEGREGATION: the 2 alleles for an inherited trait separate during meiosis and end up in different gametes.
Test-cross: a test done to see if an unknown parent is homozygous dominant or heterozygous. It is always crossed with a homozygous recessive
Law of independent assortment: 2 alleles will segregate independently of each other
Common ratio in dihybrid cross: 9:3:3:1
Dihybrid: when two traits are looked at (AaBb)
Laws of probability: if a parent is Aa, there is a ½ chance a gamete will carry ‘a’ and ½ chance a gamete will carry ‘A’
Complete dominance: ex- white pea breed with red pea, offspring is red
Codominance: 2 dominant alleles are both expressed- Blood AB
Incomplete dominance: 1 dominant allele is not completely dominant over the other. (snap dragon being pink)
Pleiotropy: 1 gene can have multiple phenotypic effects- cystic fibrosis
Epistasis: one gene can override another gene- mouse color
Polygenetic inheritance: additive effect of 2 or more genes on a single phenotypic character- skin color
“Norm of reaction” for a genotype: a genotype has a range of phenotypic outcomes
Multifactoral characteristics: both genotype and the environment can change a phenotype
Recessively inherited disorders: only have it if is ‘aa’
Person with heterozygous genotype is a carrier of the disorder but doesn’t express it phenotypically
Dominant inherited disorder: have it if ‘Aa’, have it bad and most likely do not survive if ‘AA’
Testing for multifactorial disease (where genotype and environment effect the individual- heart disease)
Amniocentesis: removal of amniotic fluid to test for genetic disorders
CVS- chorionic villus sampling, where tissue is removed from the placenta
Genotype | Blood type |
|---|---|
IA IA or IA i | A |
IB IB or IB i | B |
IA IB | AB |
ii | O |