Trade-Offs and Trade
Goods and Services: Things people value and produce to satisfy wants
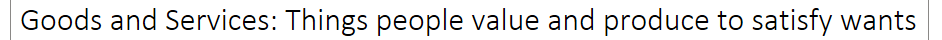
Factors of production: The resources used to produce goods and services
How are goods and services produced?
Land- A natural recourse that includes minerals, gas, coal, water, air, forests, and fish
Labor- The time and work people devote to producing goods and services
Capital: The tools, instruments, machines, buildings, and other constructions that businesses use to produces goods and services
Ex- Mining equipment, office towers, auto assembly lines
Entrepreneurship- The human recourse that organizes labor, land, and capital

The economy determines what, how, and whom goods are produced
How goods and services are produced changes over time
Education and training increase human capital
Advances in tech expand the range of automated tasks that change the role of human effort
For whom goods and services are produced
Who gets the goods and services depends on their income
People earn income by selling the services of the factors of production they own:
Land earns rent
Labor earns wages
Capital earns interest
Entrepreneurship earns profit

Economic problem: To make the best choices
Production efficiency: When it is not possible to produce more of one good or service without producing less of something else
Production inefficiency= wasting recourses
"There is no such thing as free lunch" When production is efficient, we can’t get something for nothing for free
With no wasted recourses, we face
Tradeoff: An exchange
Opportunity cost: The best thing you must give up to get it

PPF: A description of the limits to what can be produced given the available resources and technologies
All points inside the PPF and on the PPF are attainable. All points outside out unattainable

Economic growth: The expansion of production and possibilities
Technological change: The development of new goods and of better ways of producing
Capital accumulation: The growth of capital recourses, including human capitalComparative advantage: When someone can produce a good at a lower opportunity cost
Absolute advantage: When someone is more productive than others and can outperform in many activities


Economic life is organized by 2 categories:
Households: Individuals or people living together
Firms: Institutions that organize the production of goods and services

Market: Any arrangement that brings buyers and sellers together and enables them to get information and do business with each other
Goods markets: Goods and services are sold
Factor markets: Services of factors of products are bought and sold
Market Price: Coordinates the choices made by buyers and sellers of a good

