Chemistry Notes
Matter that has Chemical and Physical Properties
Matter has many forms
matter - anything that has mass and volume
mass is a measure of quantity of an object (g, kg)
volume is a measure of space taken up (mL, L)
mater can be found as a solid, liquid, or gas (can also be a combination)
The Particle Theory of Matter
1. All matter is composed of very tiny objects called particles
2. Each pure substance unique particles
3. Particles present in matter are always in motion
4. The particles in a substance attract each other
Classification of Matter
PURE SUBSTANCES
pure substances: only made up of 1 kind of matter
unique set of properties
color, hardness, boiling point, etc
a pure substance is either an element (gold) or a compound (sugar)
elements are a pure substance that cannot be broken down into any simpler substance by chemical means
each element has its own symbol and name (gold (Au))
compounds are a pure substance that is made from 2 or more elements that are combined together chemically
(H2O)
MIXTURES
a mixture is a combination of pure substances
each substance remains in its original pure form
Homogeneous Mixtures
Solutions
Saltwater
Sugar dissolved in water
Alloys
Brass (Copper + Zinc)
Bronze (Copper + Tin)
Heterogeneous Mixtures
Suspensions
Sand in water
Oil and water
Colloids
Milk
Fog
Observing Physical Properties
Physical properties
Color and luster - The light the substance reflects gives it color and luster (shine)
Conductivity - Conductivity is the ability of a substance to conduct electricity or heat. A substance that conducts electricity or heat is called a conductor. A substance with little or no conductivity is an insulator
Density- amount of mass in a given volume of a substance (d = m/v)
Ductility - any substance that can be stretched into a wire is ductile
Hardness - ability of a substance to resist being scratched
Malleability - A substance that can be pounded or rolled into sheets is said to be malleable.
Physical Change
substance remains same chemically and may change state or form
most physical changes can be reversed
Chemical properties
Combustibility is the ability of a substance to burn. In
order to burn a substance requires Oxygen
Light sensitivity is a chemical property of that can cause
new substances to form when light hits it.
Reacting with an acid is a chemical property where
when acid is poured on a substance it produces a gas and
bubbles.
The Periodic Table Organizes Elements by Patterns in Properties and Atomic Structure
Evolving Models of the Atom
John Dalton (1766–1844)
Proposed that all matter is made of small, indivisible particles called atoms.
Suggested that atoms of an element are identical in size and mass.
Stated that atoms of different elements have different properties and can combine to form new substances.
J. J. Thomson (1856–1940)
Discovered that atoms are not the smallest particles and contain smaller particles within.
Proposed the "raisin bun" or "plum pudding" model of the atom, with a positively charged sphere and negative charges embedded in it.
Ernest Rutherford (1891–1937)
Discovered the atomic nucleus, a tiny, positively charged part containing most of the atom's mass.
Subatomic Particles
Atoms consist of protons (positively charged), neutrons (neutral), and electrons (negatively charged).
Protons and neutrons are located in the nucleus, while electrons orbit in energy levels around the nucleus.
Niels Bohr (1885–1962)
Developed a model with electrons in specific energy levels or shells around the nucleus.
Subatomic Particles
Protons- Heavy positively charged found in the nucleus
Neutrons -are neutral particles that have the same mass as protons and are located in the nucleus
Electrons- Negatively charged particles with almost no mass. They circle the nucleus at different energy levels.
The elements
Elements are pure substances that consist of atoms.
The periodic table consists of over 100 elements all of which have a certain spot on the table.
Non-Metals
Found on the right side of the periodic table.
Generally non-conductors of electricity in solid form, and most are gases or solids at room temperature.
Non-metal solids are brittle and lack the luster of metals.
Metalloids
Located near the middle-right of the periodic table.
Have properties of both metals and non-metals and are known as semiconductors.
Commonly used in electronics due to their semi-conductive properties.
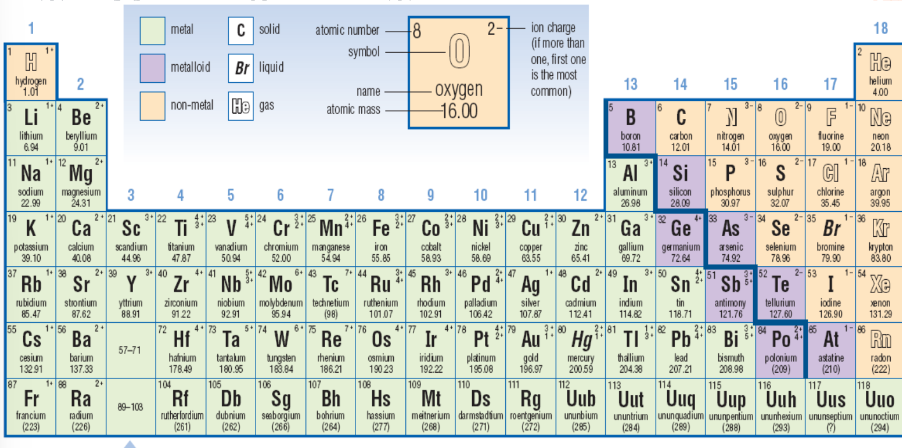
Ion Charge
Elements with atoms that can form similar ions are grouped together in the periodic table. Metals generally lose electrons and become positive ions.
Many non-metals can gain electrons and so become negative ions.
Determining the number of neutrons
Subtract the atomic number (# of protons) from the Atomic mass (# of protons and neutrons)
Atomic mass – atomic number (A – Z = N)
Example: Iron
55.85 – 26 = 30 neutrons
Metals and Non-metals
Metals tend to lose electrons to form positive ions (cations).
Non-metals gain electrons to form negative ions (anions).
Electron arrangements in ions resemble those of noble gases.
Ionic Compounds
This leaves the metal ion as a cation and the non-metal ion as a anion. The two oppositely charged ions are attracted to each other by a force called a ionic bond.
The smallest amount of substance that has the composition given by its chemical formula is the formula
Ionic properties
Ionic compounds are solids at SATP. In their solid form they form solid ionic crystals. These are more commonly known as salts.
The cross over rule
write the symbols, with the metal first (the element with the positive charge)
Write the Ionic charge above each symbol to indicate the stable ion that each element
Draw an arrow from the metals charge to the non-metal and an arrow from the non-metal charge to the metal. (Cross over the arrows)
Fill in the number of atoms from each element will have by following the arrows.
If need be reduce to lowest terms (in other words, if they are the same number, you don’t write those numbers down because you could divide the whole molecule by that number which would = 1)
Molecular Compound
When non-metals combine, a pure substance called a molecular compound is formed. In molecular compounds, the atoms share electrons to form covalent bonds. The atoms bonded together are called molecules.