Chapter 8 - Gases
8.1 - Properties of Gases
- In a gas, particles are so distant and moving that their attractions are insignificant.
- The physical characteristics of pressure (P), volume (V), temperature (T), and quantity in moles describe gas (n)
- A gas exerts pressure, the strength of the gas particles hitting the container surface’
- Units like torr, mmHg, atm, and Pa measure the gas pressure
8.2 - Pressure and Volume (Boyle’s Law)
- If there is no change in temperature and quantity of gas, the volume (V) of a gas changes inversely with the gas pressure (P).
- When the volume decreases, the pressure increases and decreases as the volume increases.
8.3 - Temperature and Volume (Charles’s Law)
- When there is no change in pressure and gas volume, the (V) volume of a gas is directly related to its kelvin temperature (T).
- Increasing the temperature of a gas will increase the volume while decreasing the temperature, volume.
8.4 - Temperature and Pressure (Gay-Lussac’s Law)
- If no change is made in volume and gas quantity, the pressure (P) of the gas is directly related to its Kelvin (T) temperature.
- With increasing gas temperature, its pressure increases; if the temperature drops, the pressure falls.
8.5 - The Combined Gas Law
- When the quantity is not changed, the combined gas law is the relationship between pressure (P), volume (V), and temperature (T).
- The combined gas law shall be used to assess the effect of change on the third in two of the variables.
8.6 - Volume and Moles (Avogadro’s Law)
- The volume (V) of a gas is directly related to the number of moles (n) of the gas when the pressure and temperature of the gas do not change.
- Increasing the volume of the gas moles; decreasing the gas moles must decrease the volume.
- 1 mole of any gas has a volume of 22.4 L at Standard Temperature (273 K) and Standard Pressure (1 atm), STP abbreviated.
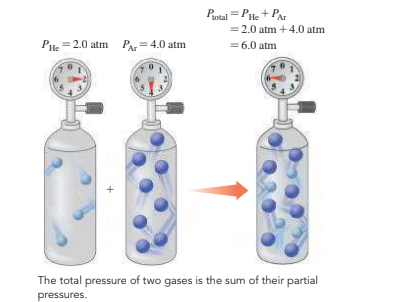
8.7 - Partial Pressures (Dalton’s Law)
The total is a combination of two or more gasses is the total of partial pressures of every single gas.
- The pressure of the partial gas in a mixture is the pressure it would exert if the gas in the container was the only gas.