4/24 - Marketing Research
When to do it?
When the value of information is worth more than the cost of conducting the research
Value = risk of negative impact to image, dollars lost, competitive gains
Cost = not just money but time and human resources
The Marketing Research Process
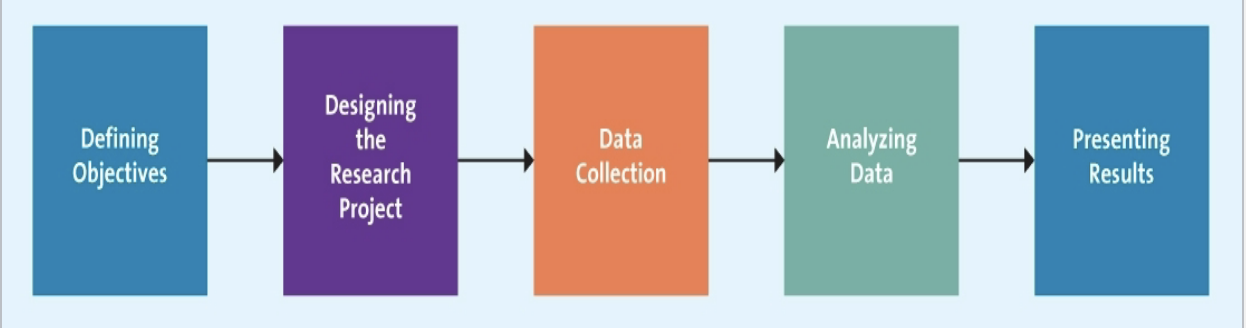
Step 1: Defining Objectives - Decision to be made
What information is needed to answer specific research questions?
What information is needed to help with a specific decision at hand?
How will that information be used?
Step 2: Designing the Research Project - Info needed
Primary Marketing Data
Done primarily for your project
Secondary Marketing Data
Data that already exists, was not collected with your project in mind
Internal secondary data includes data warehouses and data mining
Syndicated Data - Market research information collected and sold by third-party firms to multiple clients. It provides insights into market trends, consumer behavior, and industry dynamics, offering a broad overview of specific categories or industries.
Panel Research - Studying a specific group of individuals (a panel) repeatedly over time to track changes in attitudes, behaviors, or other relevant factors. (ex. record a group of consumers purchases and take surveys)
While both panel and ethnographic research involve studying human behavior, panel research focuses on gathering quantitative data from a specific group of participants over time, while ethnography is a qualitative approach that emphasizes immersion and observation in natural settings.
Scanner Research - Utilizes data collected from retail scanners, providing detailed insights into consumer purchasing habits, product performance, and market trends.
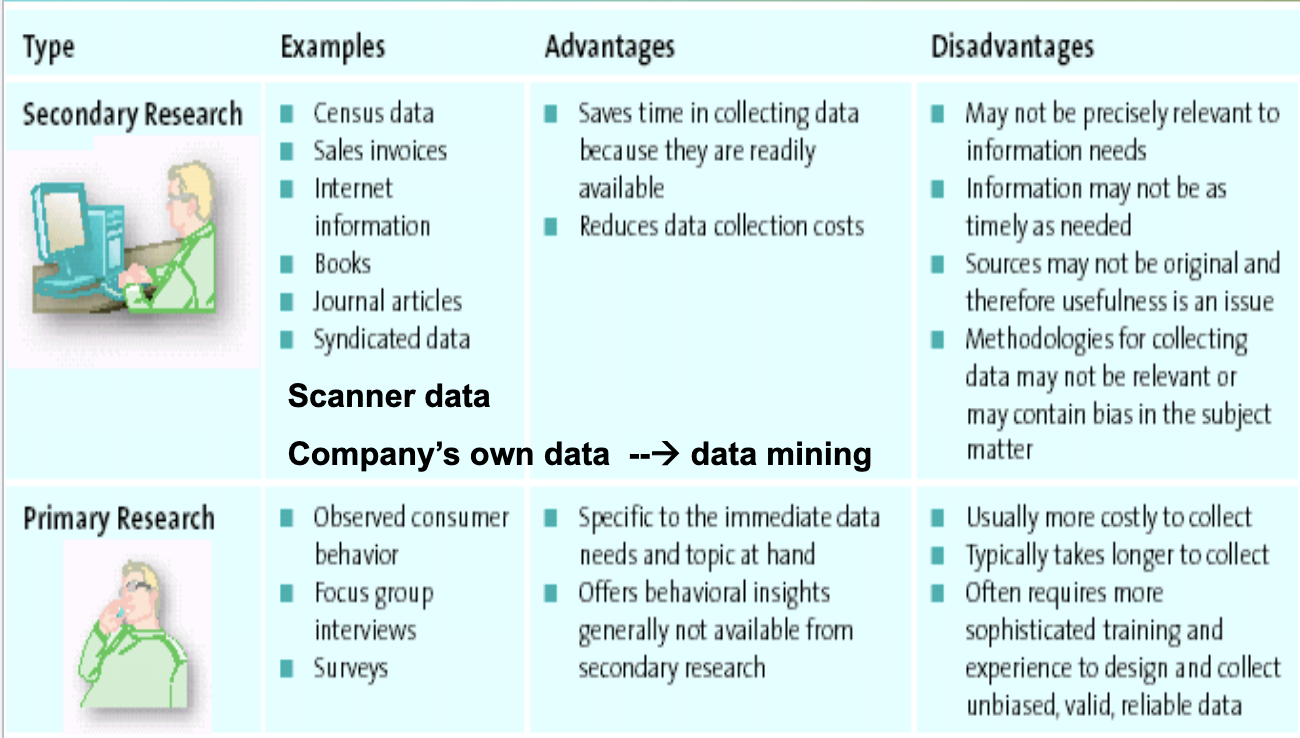
Advantages and Disadvantages of Primary and Secondary Data
Step 3: Data Collection Process
Data Collection Research
Qualitative Research
Focus Group
Ethnographic Research
Pros/Cons on Focus Group vs. Ethnographic Research
Cost more for ethnographic
Ethnographic better for “sensitive” topics
Focus groups better when you want respondents to build off each other
Ethnographic better when you want to observe in “natural” environment (say, a kitchen to view preparation).
Observation
In-Depth Interviews
Social Media
Quantitative Research
Survey
Scanner Research
Syndicated Data
Panel Research
Experiments
Variables 1 and 2 (ex. price and sales units)
Systematic manipulation of these variables
Independent variable vs. Dependent variable
Lab vs. In-Market
ex. Taking a class with two different professors and seeing which one is better
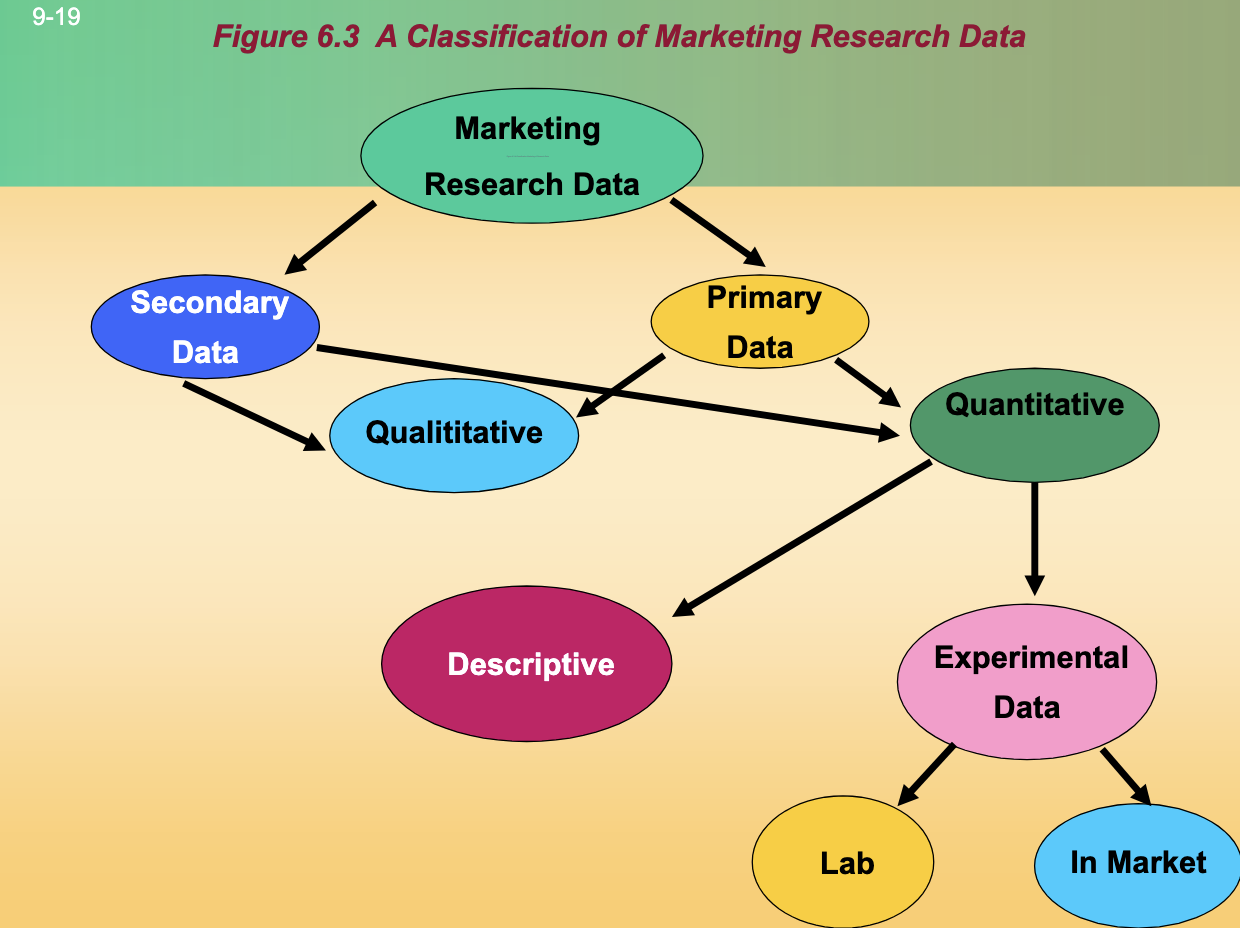
Quantitative Research Methods can be either descriptive or experimental
Step 4: Analyzing Data
Step 5: Presenting Results - Recommendations and insights “DJ Metaphor”