
BUSINESS ENTERPRISE SIMULATION
INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENTAL SCANNING
Internal Analysis of The Environment
How Businesses Conduct Internal Scanning:
WHAT CAN BE USED TO ASSESS THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT?
-interviews, surveys, discussions, evaluations
SWOT- a widely used strategic planning tool that organizations use to perform a comprehensive and competitive analysis of various internal and external factors
Strengths - things your company does well
Weaknesses - things company lacks
Opportunities - underserved markets for specific products
Threats - emerging competitors
EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS SCANNING
Industry - a group of companies offering products or services that are close substitutes for each other (soft drinks, mobile phones, sportswear)
Market Segment - distinct groups of customers within a market that can be differentiated from each other based on individual attributes and specific demands.
Supply Chain - the system involved in converting a product or service from raw materials into finished goods and then transporting finished goods from the supplier to the consumer
WHY DO BUSINESSES NEED TO CONDUCT A THOROUGH EXTERNAL ANALYSIS AND ANALYZE ITS SUPPLY CHAIN?
PESTEL ANALYSIS - to round off external analysis, a company must conduct a examination of the Political, Economic, Social and Technological landscape of the industry
Political - Political Stability, Corruption, Foreign Trade Policy, Tax Policy, Funding grants
Economic - Economic Growth, Interest Rates, Inflation, Disposable Income of Consumers, Labour Costs
Social - Population Growth, Age Distribution, Cultural Barriers, Consumer Views, Workforce Trends
Technological - Emerging Technologies, Maturing Technologies, Copyright and Patents, Production and Distribution, Research and Investment
Legal - Regulation, Employment Loans, Consumer Protection Law, Tax Policies, Antitrust Laws
Environmental - Climate, Environmental Policies, Availability of Inputs, Corporate Social Responsibility
IMPORTANCE OF PESTEL ANALYSIS - helps determine steps to take in starting business and bases of SWOT analysis
THE NATURE OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
STAGES OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:
>These three occur at three hierarchical levels in a large organization: corporate, divisional or strategic business unit, and functional
INTEGRATING INTUITION AND ANALYSIS
KEY TERMS IN STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
JetBlue - “to inspire humanity – both in air and on the ground
Tesla - to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy
TED - spread ideas
LinkedIn - to connect the world’s professional’s to make them more productive and successful
Specific - make your goal specific and narrow for more effective planning
Measurable - goal and progress are measurable
Achievable - goal should be reasonably accomplished within a certain time frame
Relevant - goal should align with your values and long term objectives
Time-based - realistic and ambitious end date clarify task prioritization and increase motivation
As organization grows, it’s important to regularly form new business objectives to effectively track employees’ performance and ensure the business is progressing and improving
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT MODEL
BENEFITS OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
BENEFITS TO FIRM THAT DOES STRATEGIC PLANNING
COMPANY AND MARKETING STRATEGY
STEPS IN STRATEGIC PLANNING
PROCESS
Mission Statements should…![]()
Mission Statements guide the development of objectives and goals
Google.com - one of the leading internet search engines
Business Portfolio - collection of businesses and products that make up the company
Portfolio Design:
Step 01: Analyze current business portfolio
Step 02: Shape the future business portfolio
GROWTH SHARE MATRIX
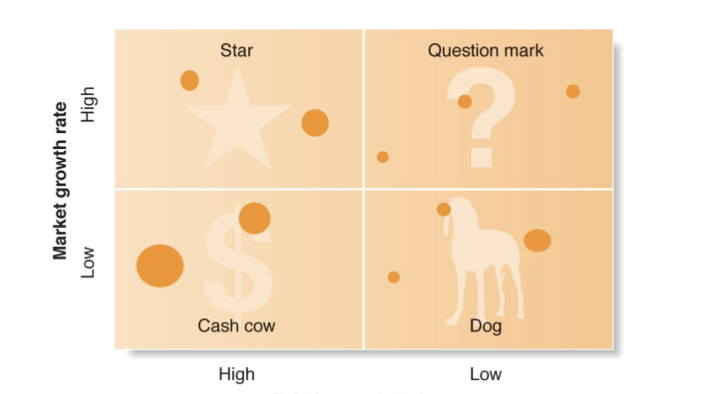
Matrix approaches to formal planning share many problems:
Designing The Business Portfolio Also Involves:
PRODUCT/MARKET EXPANSION GRID
![]()
Marketing play a key role in the strategic planning process
S- EGMENTATION: divides market into distinct groups of customers
T- ARGETING: determine which customer group to focus marketing efforts on
P- OSITIONING: create product positioning and market mix that is most likely to appeal to the selected audience
In marketing, MARKET SEGMENTATION is the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups of consumers based on characteristics
TYPES OF MARKET SEGMENTATION:
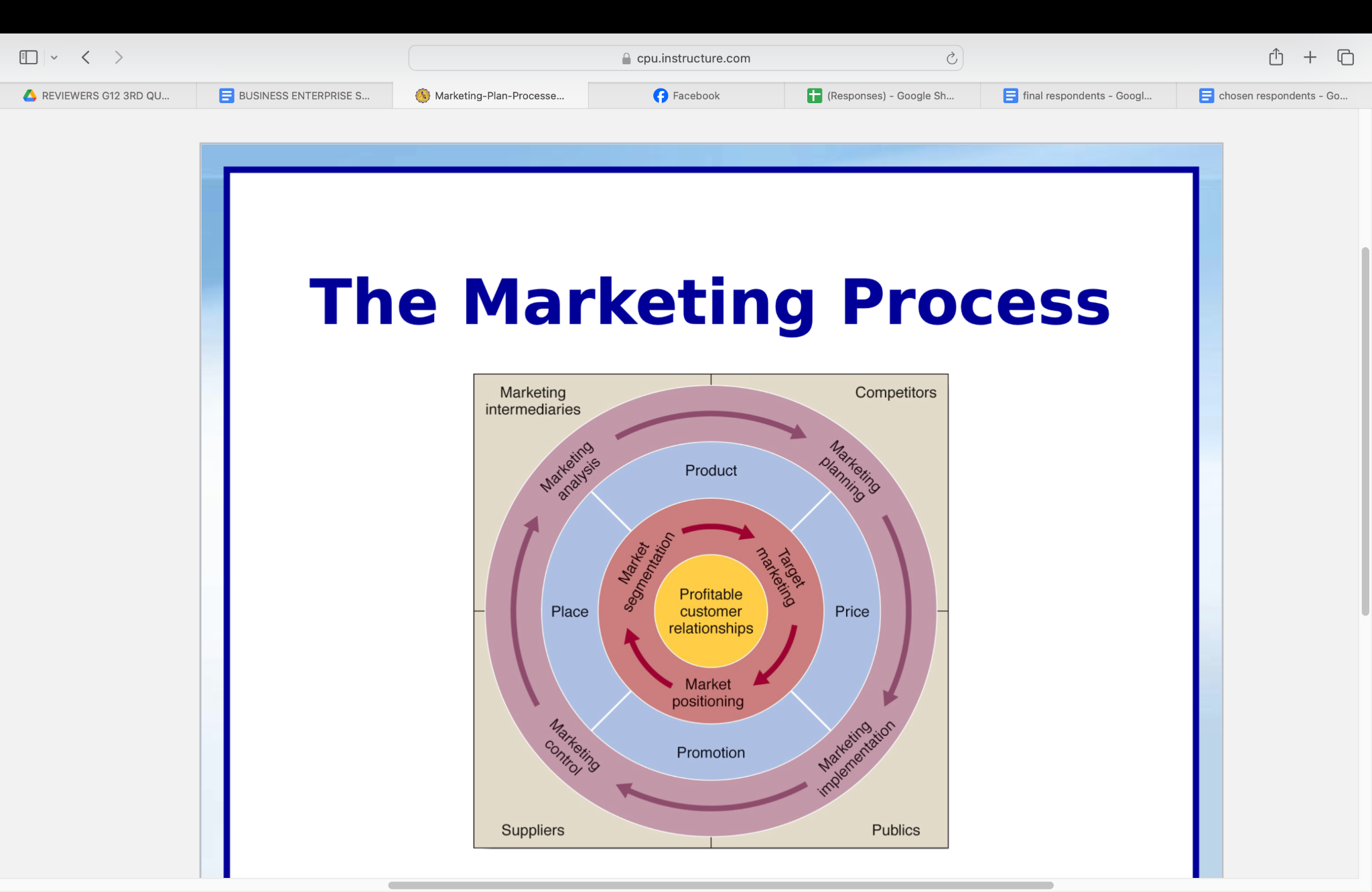
THE MARKETING PROCESS
Key Elements
Four Ps (product, place, price, promotion) and The Four Cs (customer solution, cost, convenience and communication)
THE MARKETING MIX
CREATING CUSTOMER VALUE SATISFACTION
Customer Value - how much a product or service is worth to a customer
CREATING CUSTOMER VALUE
Delivering customer value is key to maintaining long term relationships with existing customers and earning repeat business.
Creating customer value increases customer satisfaction and experience
9 WAYS TO INCREASE CUSTOMER VALUE:
Perceived Value - The customer’s evaluation of the difference between benefits and costs
Determinants Of Customer Perceived Value
Total Customer Benefit
Total Customer Cost
Loyalty - a deeply held commitment re-buy or re-patronize a preferred product or service in the future despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching position
Brand Loyalty Factors:
Value Proposition - cluster of benefits the company promises to deliver
Customer Value Propositions
Tips on how to write a value proposition:
A value proposition is not:
Customer Satisfaction - product’s perceived performance relative to customer’s expectations
Product and Service Quality - quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy needs
Total Quality Management - an organization-wide approach to continuously improve the quality of all the organization's
processes, products, and services
Framework for Customer Relationship Management
Identify prospects and customers → differentiate customers by needs and value to company → interact to improve knowledge → customize for each customer
CRM Strategies
Mass Marketing
One-on-One Marketing
PREPARATION FOR EMPLOYMENT
Application Letter
Importance:
How To Write An Application Letter?
Mock Job Interview - provides a stimulated interview experience that allows individuals to practice answering common interview questions, gain confidence, and receive feedback on their performance
INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENTAL SCANNING
Internal Analysis of The Environment
How Businesses Conduct Internal Scanning:
WHAT CAN BE USED TO ASSESS THE INTERNAL ENVIRONMENT?
-interviews, surveys, discussions, evaluations
SWOT- a widely used strategic planning tool that organizations use to perform a comprehensive and competitive analysis of various internal and external factors
Strengths - things your company does well
Weaknesses - things company lacks
Opportunities - underserved markets for specific products
Threats - emerging competitors
EXTERNAL ENVIRONMENT ANALYSIS SCANNING
Industry - a group of companies offering products or services that are close substitutes for each other (soft drinks, mobile phones, sportswear)
Market Segment - distinct groups of customers within a market that can be differentiated from each other based on individual attributes and specific demands.
Supply Chain - the system involved in converting a product or service from raw materials into finished goods and then transporting finished goods from the supplier to the consumer
WHY DO BUSINESSES NEED TO CONDUCT A THOROUGH EXTERNAL ANALYSIS AND ANALYZE ITS SUPPLY CHAIN?
PESTEL ANALYSIS - to round off external analysis, a company must conduct a examination of the Political, Economic, Social and Technological landscape of the industry
Political - Political Stability, Corruption, Foreign Trade Policy, Tax Policy, Funding grants
Economic - Economic Growth, Interest Rates, Inflation, Disposable Income of Consumers, Labour Costs
Social - Population Growth, Age Distribution, Cultural Barriers, Consumer Views, Workforce Trends
Technological - Emerging Technologies, Maturing Technologies, Copyright and Patents, Production and Distribution, Research and Investment
Legal - Regulation, Employment Loans, Consumer Protection Law, Tax Policies, Antitrust Laws
Environmental - Climate, Environmental Policies, Availability of Inputs, Corporate Social Responsibility
IMPORTANCE OF PESTEL ANALYSIS - helps determine steps to take in starting business and bases of SWOT analysis
THE NATURE OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
STAGES OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT:
>These three occur at three hierarchical levels in a large organization: corporate, divisional or strategic business unit, and functional
INTEGRATING INTUITION AND ANALYSIS
KEY TERMS IN STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
JetBlue - “to inspire humanity – both in air and on the ground
Tesla - to accelerate the world’s transition to sustainable energy
TED - spread ideas
LinkedIn - to connect the world’s professional’s to make them more productive and successful
Specific - make your goal specific and narrow for more effective planning
Measurable - goal and progress are measurable
Achievable - goal should be reasonably accomplished within a certain time frame
Relevant - goal should align with your values and long term objectives
Time-based - realistic and ambitious end date clarify task prioritization and increase motivation
As organization grows, it’s important to regularly form new business objectives to effectively track employees’ performance and ensure the business is progressing and improving
STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT MODEL
BENEFITS OF STRATEGIC MANAGEMENT
BENEFITS TO FIRM THAT DOES STRATEGIC PLANNING
COMPANY AND MARKETING STRATEGY
STEPS IN STRATEGIC PLANNING
PROCESS
Mission Statements should…![]()
Mission Statements guide the development of objectives and goals
Google.com - one of the leading internet search engines
Business Portfolio - collection of businesses and products that make up the company
Portfolio Design:
Step 01: Analyze current business portfolio
Step 02: Shape the future business portfolio
GROWTH SHARE MATRIX

Matrix approaches to formal planning share many problems:
Designing The Business Portfolio Also Involves:
PRODUCT/MARKET EXPANSION GRID
![]()
Marketing play a key role in the strategic planning process

S- EGMENTATION: divides market into distinct groups of customers
T- ARGETING: determine which customer group to focus marketing efforts on
P- OSITIONING: create product positioning and market mix that is most likely to appeal to the selected audience
In marketing, MARKET SEGMENTATION is the process of dividing a broad consumer or business market into sub-groups of consumers based on characteristics
TYPES OF MARKET SEGMENTATION:
THE MARKETING PROCESS
Key Elements
Four Ps (product, place, price, promotion) and The Four Cs (customer solution, cost, convenience and communication)
THE MARKETING MIX
CREATING CUSTOMER VALUE SATISFACTION
Customer Value - how much a product or service is worth to a customer
CREATING CUSTOMER VALUE
Delivering customer value is key to maintaining long term relationships with existing customers and earning repeat business.
Creating customer value increases customer satisfaction and experience
9 WAYS TO INCREASE CUSTOMER VALUE:
Perceived Value - The customer’s evaluation of the difference between benefits and costs
Determinants Of Customer Perceived Value
Total Customer Benefit
Total Customer Cost
Loyalty - a deeply held commitment re-buy or re-patronize a preferred product or service in the future despite situational influences and marketing efforts having the potential to cause switching position
Brand Loyalty Factors:
Value Proposition - cluster of benefits the company promises to deliver
Customer Value Propositions
Tips on how to write a value proposition:
A value proposition is not:
Customer Satisfaction - product’s perceived performance relative to customer’s expectations
Product and Service Quality - quality is the totality of features and characteristics of a product or service that bear on its ability to satisfy needs
Total Quality Management - an organization-wide approach to continuously improve the quality of all the organization's
processes, products, and services
Framework for Customer Relationship Management
Identify prospects and customers → differentiate customers by needs and value to company → interact to improve knowledge → customize for each customer
CRM Strategies
Mass Marketing
One-on-One Marketing
PREPARATION FOR EMPLOYMENT
Application Letter
Importance:
How To Write An Application Letter?
Mock Job Interview - provides a stimulated interview experience that allows individuals to practice answering common interview questions, gain confidence, and receive feedback on their performance