
Physical and Cognitive Development in Early Childhood
Physical Development in Early Childhood
Growth
slows during early childhood
a large role of biological factors and nutrition
Sleep
recommended 11-13 hours
sleep concerns:
narcolepsy
insomnia
nightmares
sleep problems have negative outcomes
Nutrition
decline in young children’s appetites
picky eating phase
fewer fruits and veggies
fewer vitamins and minerals
sensory sensitivity, temperament
picky eating
parental pressure to eat
Brain development
period of rapid growth
demonstration
Perceptual Development
3-4 boundaries of colors
4-5 close-up object focus
signs of vision problems
Motor development
gross motor skills
Increases in physical strength and coordination
Fine Motor Skills
Linked with increased independence
drawing and representational ability
Shaped by context
 Cognitive Developmental and sociocultural reasoning in early Childhood
Cognitive Developmental and sociocultural reasoning in early Childhood
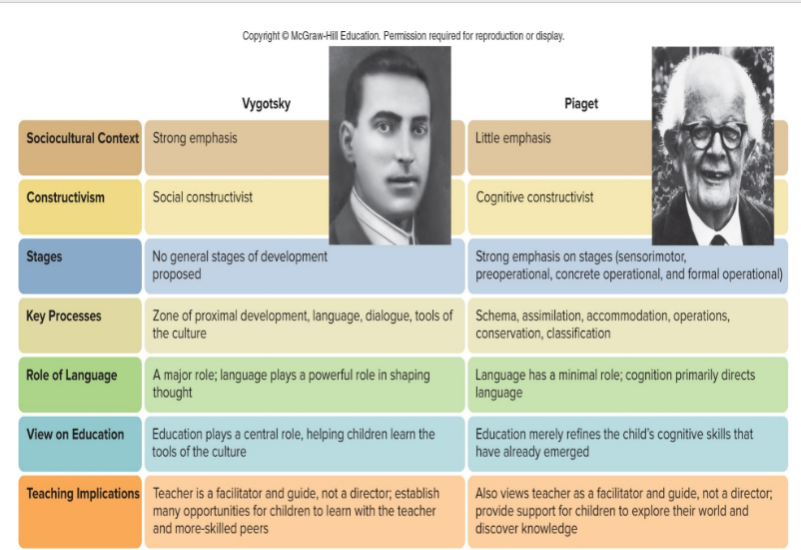
Piaget - Characteristics of Preoperational Reasoning
Egocetrism, three mutant task, animism
irreversibly and conservation
Vysgotsky’s Sociocultural Pespective
Emphasized the influence of culture
Guided participation and scaffolding
Zone of proximal development
 Information Processing in Early Childhood
Information Processing in Early Childhood
Attention
Dramatic improvements particularly in established attention
Difficulty with selective attention
at 2.5 years predicts working memory and response inhibition at age 3
Working memory and executive function
Improvements in holding information in working memory
Assessment with memory span task
Improvements in creating and carrying out a plan
Memory: memory for information
Recognition memory
recall memory
memory strategies
INFORMATION PROCESSING IN EARLY CHILDHOOD
Mostly accurate
susceptibility to suggestion
Memory: Scripts
Become more elaborate over tie
Autobiographical memory
Important or unique events are more easily recalled
Parental elaborative conversational style

Young Children’s Language Development
Early Grammar
knowledge of morphology rules
importance of parental conversations and support
overregulation errors
Children Learn Words
They hear most often
For things and events that interest them
Better in responsive and interactive contexts than in passive contexts
best in meaningful contexts
best when they access clear information about word meaning
best when grammar and vocabulary are considered
Private Speech
Serves developmental functions
Plays a role in self-regulation
Becomes inner speech
Has individual differences
Young Children Literacy (Lecture)
Positive orientation toward reading must be developed
Importance
Phonological Awareness
Readiness for School
Reading Achievement in High School
Tips
Ask Questions
Model phonics
Keep it engaging
Realistic Expectations for attention span
Moral Development
Social Learning Theory
Behavior acquired through reinforcement and modeling
more likely to imitate transgressions than good behavior
characteristics of models
powerful, competent, warm, responsive
Cognitive-Development Theory
Piaget - Heteronomous Morality 6 yoa
Immanent justice
Piaget - Autonomous Morality 10+ yoa
Kohlberg: Pre-conventional Reasoning
Conceptions of Moral Social and Personal Issues
Importance of Culture, dialogue with parents
Early Childhood Education
Project head start
Carolina Abecedarian project
Perry Preschool Project
Movement toward comprehensive pre-K
Academically centered preschool programs
Structured learning environments
child-centered preschool programs
Constructivist approach
cultural influences
Physical and Cognitive Development in Early Childhood
Physical Development in Early Childhood
Growth
slows during early childhood
a large role of biological factors and nutrition
Sleep
recommended 11-13 hours
sleep concerns:
narcolepsy
insomnia
nightmares
sleep problems have negative outcomes
Nutrition
decline in young children’s appetites
picky eating phase
fewer fruits and veggies
fewer vitamins and minerals
sensory sensitivity, temperament
picky eating
parental pressure to eat
Brain development
period of rapid growth
demonstration
Perceptual Development
3-4 boundaries of colors
4-5 close-up object focus
signs of vision problems
Motor development
gross motor skills
Increases in physical strength and coordination
Fine Motor Skills
Linked with increased independence
drawing and representational ability
Shaped by context
 Cognitive Developmental and sociocultural reasoning in early Childhood
Cognitive Developmental and sociocultural reasoning in early Childhood
Piaget - Characteristics of Preoperational Reasoning
Egocetrism, three mutant task, animism
irreversibly and conservation
Vysgotsky’s Sociocultural Pespective
Emphasized the influence of culture
Guided participation and scaffolding
Zone of proximal development
 Information Processing in Early Childhood
Information Processing in Early Childhood
Attention
Dramatic improvements particularly in established attention
Difficulty with selective attention
at 2.5 years predicts working memory and response inhibition at age 3
Working memory and executive function
Improvements in holding information in working memory
Assessment with memory span task
Improvements in creating and carrying out a plan
Memory: memory for information
Recognition memory
recall memory
memory strategies
INFORMATION PROCESSING IN EARLY CHILDHOOD
Mostly accurate
susceptibility to suggestion
Memory: Scripts
Become more elaborate over tie
Autobiographical memory
Important or unique events are more easily recalled
Parental elaborative conversational style

Young Children’s Language Development
Early Grammar
knowledge of morphology rules
importance of parental conversations and support
overregulation errors
Children Learn Words
They hear most often
For things and events that interest them
Better in responsive and interactive contexts than in passive contexts
best in meaningful contexts
best when they access clear information about word meaning
best when grammar and vocabulary are considered
Private Speech
Serves developmental functions
Plays a role in self-regulation
Becomes inner speech
Has individual differences
Young Children Literacy (Lecture)
Positive orientation toward reading must be developed
Importance
Phonological Awareness
Readiness for School
Reading Achievement in High School
Tips
Ask Questions
Model phonics
Keep it engaging
Realistic Expectations for attention span
Moral Development
Social Learning Theory
Behavior acquired through reinforcement and modeling
more likely to imitate transgressions than good behavior
characteristics of models
powerful, competent, warm, responsive
Cognitive-Development Theory
Piaget - Heteronomous Morality 6 yoa
Immanent justice
Piaget - Autonomous Morality 10+ yoa
Kohlberg: Pre-conventional Reasoning
Conceptions of Moral Social and Personal Issues
Importance of Culture, dialogue with parents
Early Childhood Education
Project head start
Carolina Abecedarian project
Perry Preschool Project
Movement toward comprehensive pre-K
Academically centered preschool programs
Structured learning environments
child-centered preschool programs
Constructivist approach
cultural influences