Plant tissues, organs and systems
Plants are made of organs like stems roots and leaves. Plant organs work together to make organ systems. These can perform various tasks that a plant needs to carry out to survive and grow.
Plant organs are made of tissues. Examples are :
Epidermal tissue - covers the whole plant
Palisade mesophyll tissue - Part of the leaf where photosynthesis takes place
Spongy mesophyll tissue - In the leaf and contains big air spaces to allow gases to diffuse in and out of the cell
Xylem and phloem - Transport things like water, mineral ions and food around the plant.
Meristem tissue - Found at the growing tips of shoots and roots and is able to differentiate into lots of different types of plant cell allowing the plant to grow.
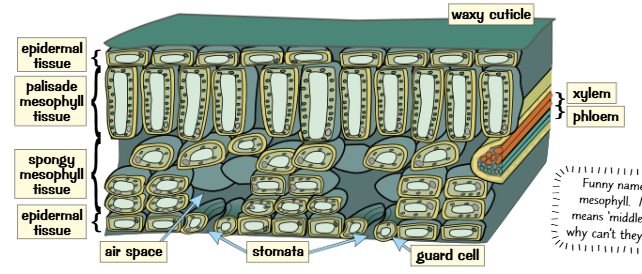
How structures of the tissues that make up the leaf is adapted to their function:
The epidermal tissue is covered with a waxy cuticle which helps reduce water loss by evaporation
The palisade layer has lots of chloroplasts meaning they are near the top of the leaf where they can get the most light
The Xylem and Phloem form a layer of vascular bundles which deliver water and other nutrients to the entire leaf taking away glucose by photosynthesis. They also help support the structure.
The tissues of leaves are also adapted for efficient gas exchange. For example, the lower epidermis is full of little holes called stomata which let CO2 diffuse directly into the leaf.
The air spaces in the spongy mesophyll increase the rates of diffusion
Phloem tubes
They transport food. They are made of collumns of elongated living cells with small pores in their end walls to allow cell sap to flow through.
They transport food substances, mainly dissolved sugars, made in the leaves to the rest of the plant for immediate use or for storage.
This transpprt goes in both directions.
This process is called is called translocation ( the movement of dissolved sugars around a plant).
Xylem tubes
Made of dead cells joined end to end with no end between them and a hole down the middle. They are strengthened with a material called lignin.
They carry water and mineral ions from the roots to the stems and leaves.
Transpiration stream is the movement of water from the roots, through the xylem and out of the leaves.
Factors affecting transpiration rate:
Light intensity - The brighter the light the greater the transpiration rate. Stomata begin to close as it gets darker. Photosynthesis cant happen in the dark meaning they dont need to open to let CO2 in. When the stomata are closed very little water can escape.
Temperature - The warmer it is the faster the transpiration rate. When its warm the air particles have more energy to evaporate and diffuse out of the stomata.
Humidity - the drier the air around a leaf, the faster transpiration happens. If the air is humid then their is lots of water in it already meaning their isnt much difference between the inside and outside of the leaf.
Guard cells are adapted to open and close the stomata. They have a kidney shape which opens and closes the stomata in a leaf.
When the plant has lots of water the guard cells fill with it and go plump and turgid. This makes the stomata open so gases can be exchanged by photosynthesis.
When the plant is short of water, the guard cells lose water and become flaccid, making the stomata close. This stops too much water vapour escaping.
Thin outer walls and thick inner walls make the opening and closing work.
There also sensitive to light and close at night to save water without losing out on photosynthesis.
You usually find more stomata on the undersides of leaves than the top. The lower surface is cooler so less water is lost through the stomata than if they were on the upper surface. .
 Knowt
Knowt