Lysosomes & Vacuoles
- Lysosomes are used to help rid the cell of waste. Vacuoles, on the other hand, are used for storage.
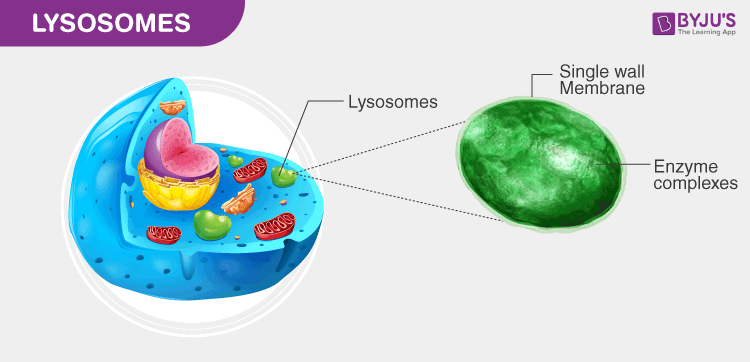
Lysosomes
Lysosomes are important parts of the cell, even though they can sometimes be forgotten. They are in charge of cleaning up the cell and getting rid of waste. Lysosomes are filled with enzymes. Enzymes are proteins that help speed up chemical reactions in cells. In lysosomes, enzymes speed up the breakdown of waste products within the lysosome.
The enzymes in a lysosome are part of the digestive part of a cell, so the lysosome keeps these enzymes contained in a membrane sack, which prevents the digestive enzymes from digesting the whole cell. These digestive enzymes can break down organic compounds, lipids, proteins, and carbohydrates, which are all relatively large molecules. The enzymes break down these large molecules into smaller molecules known as monomers (the root mono means “one”).
- For example, proteins might be broken down into their individual amino acids.
When these molecules are broken down, the cell keeps some parts in the cell for reuse. The parts that cannot be used are sent out of the cell. Cells are very small and do not have a lot of space. Thus, anything not being used by the cell leaves because the cell doesn’t have enough space for broken things to remain.
- For example, if an organelle no longer functions, the lysosome is responsible for breaking it down and removing it from the cell.
Lysosomes can also defend the cell by breaking down the cell wall of bacterial invaders.
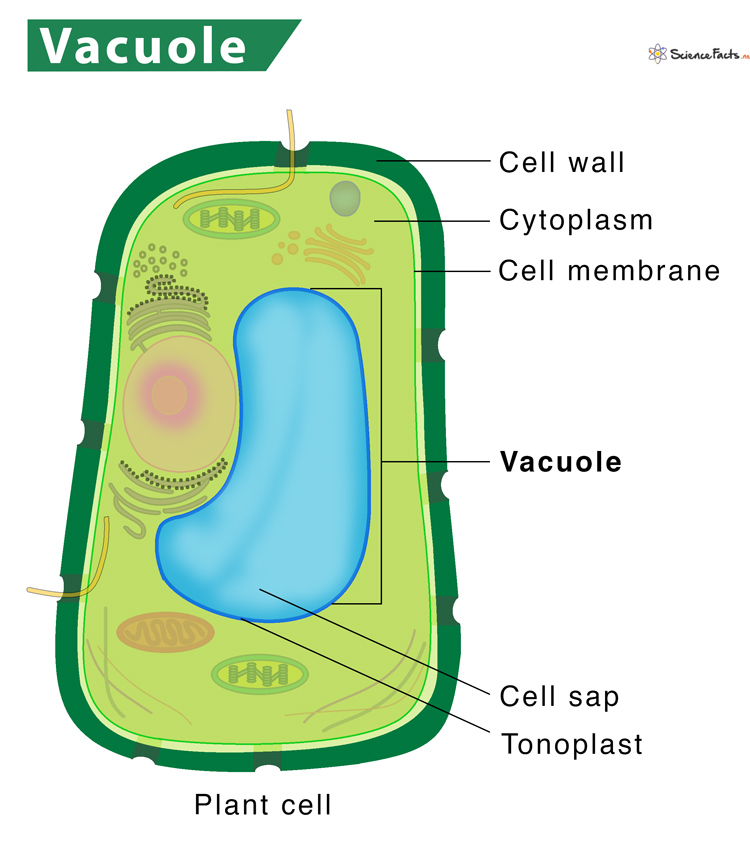
Vacuoles
Vacuoles are storage facilities in the cell. Vacuoles are most commonly found in plant cells. Plants cannot move around to get the things they need, like water and nutrients. So, when something useful becomes available to a plant, the plant likes to save it for when it is needed.
In fact, plants have a large vacuole (even larger than the nucleus) known as a central vacuole that is used to store water, salts, proteins, and carbohydrates. If a plant releases poison or toxins of some sort to deter predators, it will store that toxin in the central vacuole and if it has some sort of nectar to attract pollinators, the nectar is also stored in the central vacuole.
The central vacuole is very important because plant cells need to store water so they can remain upright.
Plants rely on something called turgor pressure to stand. Turgor pressure increases when plant cells have lots of water in them, which is stored in the central vacuole.
If a plant cell does not have enough water, it will lose turgor pressure and wilt.
Protists, single-celled organisms, can also have a vacuole. Their vacuole is called a contractile vacuole. Most protists live in freshwater, which means that water is always wanting to come into the cell, so the contractile vacuole acts as a pump for the protist and pumps out the freshwater so the cell doesn’t fill with fresh water and burst.