Chap2
Key Concepts of Accounting (Các Khái Niệm Cơ Bản Của Kế Toán)
Learning Objectives (Mục Tiêu Học Tập)
Objective 1 (Mục tiêu 1): Describe how accounts, debits, and credits are used to record business transactions.
Objective 2 (Mục tiêu 2): Explain the use of a journal in the recording process.
Objective 3 (Mục tiêu 3): Discuss how a ledger and posting enhance recording.
Objective 4 (Mục tiêu 4): Prepare and understand the significance of trial balances.
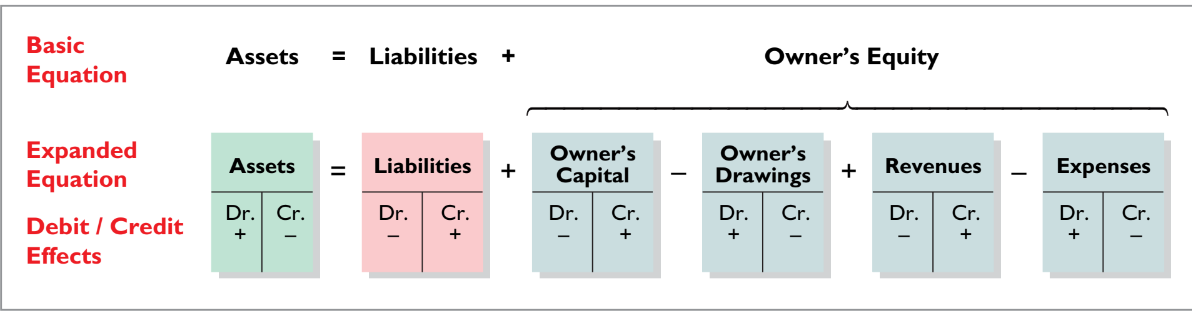
Accounts, Debits, and Credits (Tài Khoản, Nợ, và Có)
The Account (Tài Khoản)
An account is a record of increases and decreases in specific asset, liability, or owner's equity items. Examples of accounts include Cash, Accounts Receivable, Accounts Payable, etc. Each account provides essential insights into particular financial aspects of a business.
Structure of an Account (Cấu Trúc Của Một Tài Khoản)
An account has:
Title (Tên): Name of the account.
Debit Side (Bên Nợ): Left side of an account.
Credit Side (Bên Có): Right side of an account. s).
Debits and Credits (Nợ và Có)
Debit (Nợ - Dr): Indicates the left side; usually increases assets but could decrease liabilities and owner's equity. For example, charging expenses is a debit to the expense account.
Credit (Có - Cr): Indicates the right side; typically increases liabilities and owner's equity while decreasing assets. For instance, receiving cash from a sale is a credit to the revenue account.
normal balance
: The normal balance for an account is determined by whether it is an asset, liability, or equity account.
Asset accounts typically have a normal debit balance.
Liability and equity accounts usually maintain a normal credit balance.
The accounting equation (Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity) must balance.
The DEALER METHODS
Letter | Account Type | Effect of Debit | Effect of Credit |
D | Dividends | Increases dividends | Decreases dividends |
E | Expenses | Increases expenses | Decreases expenses |
A | Assets | Increases assets | Decreases assets |
L | Liabilities | Decreases liabilities | Increases liabilities |
E | owner Equity | Decreases equity | Increases equity |
R | Revenues | Decreases revenue | Increases revenue |
Recording Transactions (Ghi Nhận Giao Dịch)
The Journal (Nhật Ký)
The journal records transactions in chronological order, detailing the debit and credit impacts on specific accounts. Each journal entry consists of:
Date (Ngày Giao Dịch): Date of the transaction.
Accounts debited and credited (Tài Khoản Nợ và Có): Specific accounts involved in the transaction.
Brief explanation of the transaction (Giải Thích Ngắn Gọn về Giao Dịch): Usually underlined for emphasis and clarity. Monetary amounts are also represented with a dollar sign ($) preceding the number to indicate the currency involved.
Simple Entries: These involve just two accounts – one being debited and the other credited.
Compound Entries: Such entries involve three or more accounts. For instance, Butler Company’s purchase of a delivery truck costing $14,000, where they paid $8,000 in cash and agreed to pay $6,000 on account, is a compound entry.
Posting and the Ledger (Chuyển Ghi và Sổ Cái)
Posting (Chuyển Ghi): Posting is the transfer of journal entries to the ledger. The ledger contains all accounts and provides a running balance for each account, giving a comprehensive overview of financial activities.
Chart of Accounts (Biểu Đồ Tài Khoản)
Organizations maintain a chart of accounts, which lists account names and numbers that assist in locating them in the ledger. This organizational tool helps ensure the accurate recording of financial activities and enhances the overall financial management.
Assets
Cash: Represents money available on hand.
Accounts Receivable: Money owed by customers for services provided.
Supplies: Office supplies on hand.
Prepaid Insurance: Insurance paid in advance.
Equipment: Physical assets used for business operations.
Accumulated Depreciation—Equipment: Total depreciation on equipment over time.
Liabilities
Notes Payable: Loans or promissory notes that require repayment.
Accounts Payable: Money owed to suppliers or vendors.
Unearned Service Revenue: Revenue received before services are provided.
Salaries and Wages Payable: Salaries and wages owed to employees.
Interest Payable: Interest owed but not yet paid.
Owner’s Equity
Owner’s Capital: Owner’s investment in the business.
Owner’s Drawings: Withdrawals made by the owner.
Income Summary: Temporary account used to close revenue and expense accounts at the end of an accounting period.
Revenues
Service Revenue: Revenue earned from providing services.
Expenses
Supplies Expense: Cost of supplies used during a period.
Depreciation Expense: Cost of using equipment over time.
Insurance Expense: Cost of insurance for a period.
Salaries and Wages Expense: Cost of employee salaries and wages.
Rent Expense: Cost of renting office space or equipment.
Utilities Expense: Cost of utilities like electricity and water.
Interest Expense: Cost of interest on borrowed funds.
Trial Balance (Bảng Cân Đối)
A trial balance is a summary listing of balances in the ledger accounts at a given time and is typically prepared at the end of an accounting period. The debit and credit columns must balance, which aids in identifying any errors in the recording process.
Note that the order of presentation in the trial balance is:
Assets
Liabilities
Owner’s equity
Revenues
Expense
ALORE
Dollar Signs and Underlining in Accounting:
Dollar Signs:
Typically not used in journals or ledgers.
Present in the trial balance and financial statements.
Usually shown only for the first item in a column and the total of that column.
Underlining:
A single line (totalling rule) is placed under a column of figures to be added or subtracted.
Total amounts are double underlined to indicate final sums.
Glossary of Key Terms (Thuật Ngữ Chuyên Ngành)
Account (Tài Khoản): Recording increases and decreases in specific asset, liability, or owner's equity items.
Chart of Accounts (Biểu Đồ Tài Khoản): List of accounts and their corresponding location numbers.
Compound Entry (Ghi Chép Phức Hợp): Journal entry involving three or more accounts.
Debits/Credits (Nợ/Có): Accounting terms indicating increases or decreases in accounts.
Double-entry System (Hệ Thống Ghi Chép Kép): Accounting method recording dual effects on accounts.
Journal (Nhật Ký): Record of transactions in chronological order.
Normal Balance (Cân Đối Bình Thường): The usual balance reflecting increases in an account type.