Unit 11: Development
Gestation & Birth Reflexes
Gestation → process of carrying or being carried as an embryo or fetus through conception untill birth
Three trimesters:
1st = Last period-13 weeks
2nd = 14-27 weeks
3rd = 28-42 weeks
Birth = 37-42 weeks
1st trimester
minute ventilation increases by 40% in the first trimester
the womb will grow to the size of a lemon by eight weeks
Many symptoms and discomforts of pregnancy like nausea and tender breasts appear in the first trimester
morning sickness, miscarrages (20-25% of pregnancies result in miscarrages), ectopic pregnancy (embrio embeds itself in fallopian tube instead of uterus (rare))
2nd trimester
most women feel more energized in this period, and begin to put on weight as the symptoms of morning sickness subside
the uterus, the muscular organ that holds the developing fetus, can expand up to 20 times its normal size during pregnancy
3rd timester
final weight gain takes place, which is the most weight gain throughout the pregnancy
the women’s abdomen will transform in the shape as it drops due to the fetus turning in a downward position ready for birth
Development of the fetus:
Nutrition
Medication
Drugs
Teratogens → anything that can negitivley alter the state of the fetus
Nicotine → tobacco smoking during pregnancy can cause a wide range of behavioral, neuroligical, and physical disibilites
Inate Human Reflexes
everyone in the world holds an inherent set of instictive behaviors
primitive reflexes are displayed by normal human infants and not neurologically intact adults
Tonic neck reflex (fencing reflexe) → 4-6 months
Moro relfex → present at birth
Babinski relfex →
Rooting reflex → stops when no longer feeding through bottle or nipple
Suckling reflex
Grasping reflex →
walking reflex →
Swallowing reflex
Swimming reflex
Parachute reflex
Jean Piaget
Biography
Alfred Binet → created first IQ test
became fascinated by the way the kids brains worked
fascinated by reasoning process
Stage Theory
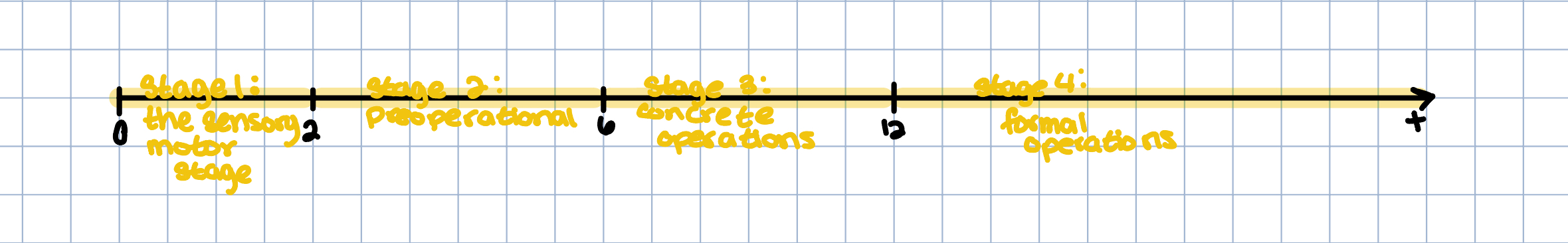
Sensorimotor
pick up everything
put things in their mouth
LACK Object Permanence
DISPLAYS “A-not-B Error” → seen in 1-2 year olds
when they realize that objects exist but may not be where they last saw it
Preoperational
DISPLAYS Egocentic thought/Egocentrism
extreme difficulty seeing things from someone elses point of view
LACK of conservation
don’t understand that things can transform
EX: same volume can look different in different cups
Concrete Operational
can’t think abstractly
can’t think hypothetically
Formal Operational
hypotheticals
see things in multiple perspectives
critical thinking
Schemas → mental framework
Disequilibrium → conflicting information with known and new information
Assimilation → adding information to schema
Accommodation → changing schema
Equilibrium → accommodation leads to equilibrium
Konrad Lorenz
Australian Biologist
Nidifugous Birds → leave the nest early and imprint on whatever live thing is around when they are born
Geese and Jackdaws
IMPRINTING
important for children to recieve touch to touch and the like to build connections while humans don’t fully imprint
Harry Harlow
Raised baby monkeys with two artificial wire frame figures
1) attached with a bottle to feed from
2) wrapped in a soft material
ATTACHMENT
found that monkeys preferred the mother that offered comfort(2)
would only go to the other mother to eat(1) and then would go back to 2
Mary Ainsworth
Strange Situation
Placed infants into strange situations
Observe their reactions when placed into the Strange Situation
ATTACHMENT STYLES
Secure Attachment(60%): confidently explore the novel enviornment while parent is present, distressed when they leave, come to parents when they returned
Avoidant Attachment(21): may resist being held by the parens and ill explore envionrment. Do not return to parents for comfort
Axious/Ambivalent(12): ambivalent reactions to parents. Show extreme stress when parents leave, but resist being comforted when they return.
Sigmund Freud
Austrian Neurologist
fled Austria to escape Nazis
Psychoanalysis
id,ego, and superego
First to develop stage thoery
Psychosexual Stages
we develop through four different psychosexual stages
if we fail to resolve a significant conflict in our lives during one of these stages, we become fixated in that stage
we would remain preoccupied with the behaviors of that stage
Stages:
1) Oral stage (0-1): In the first stage of personality development that libido is centered in a baby’s mouth. It gets much satisfaction from putting things in their mouth to satisfy the libido, and thus its id demands. Which at this stage in life are oral, or mouth oriented, such as sucking, biting, and breastfeeding.
Freud said oral stimulation could lead to an oral fixation in later life. We see oral personalities all around us such as smokers, nail-biters, finger-chewers, and thumb suckers. Oral personalities engage in such oral behaviors, particularly when under stress
2) Anal Stage (1-3): This stage develops during toilet training. If conflict around toilet training arises, a person might fixate in the stage and be overly controlling (retentice) or out of control (expulsive).
Early or harsh potty training can lead to the child becoming an anal-retentive personality who hates mess, is obseivley tidy, punctual, and respective of authority.
The anal expulsive, on the other hand, underwent a liberal toilet-training regime during the anal stage. In adulthood, the anal expulsive is the person who wants to share things with you. They like giving things away. In essence, they are ‘sharing their shit’. An anal-expulsive personality is also messy, disorganized, and rebellious
3) Phallic Stage (3-6): During this stage, babies realize their gender and this causes conflict in the family. Freud described thr process boys go through in this stage as the Oedipus Complex, when boys resent their father’s relationship with their mother. For girls, this is known as Electra Complex.
Freud(1909) offered the Litthe Hans case study as evidence of the Oedipud complex.
4) Genital Stage : Puberty
focus on several pleasure is genital
fixation in this stage Frued called normal
Erik Erikson
8 stages of psychosocial development
center on a specific social conflicts
stages have unique psychosocial task that needs resolution
faliure to pass through any stage sucessfully blocks normal development
Stage 1: Trust v Mistrust (birth-1):
basic biological needs are met, infant develop sense of basic trust
no trust = frustrated, withdrawn, suspicious, lack self-confidence
Stage 2: Autonomy v Shame & doubt (1-3):
toddlers begin to exert will over bodies for first time
begin personal responsibility feeding, dressing and bathing
Stage 3: Initiative v Guilt (3-5):
“No” to “why”
curiosity about the world
learns tasks and grapples self-control
Stage 4: Industry v Inferiority (6-puberty):
start of formal education
children develop a sense of industry and curiosity
Inferiority complex
Stage 5: Identity v Role confusion (teens-20s):
tries on different roles
identity crisis
Stage 6: Intimacy v Isolation (20s-40s):
difference in relationships
influence other stages
a timing of forming permanet relationship and sharing intimiate levels
Stage 7: Generalivity v Stagnation (40s-60s):
we look critically at our lifetime
am i living the life i want
Stage 8: Integrity v Despair (60s- up)
looking back and reflecting about our lives
able to accept the end is coming
life would feel meaningless
Parenting Styles
Diana Baumrind (1971)
Authoritarian:
high expectations, low warmth
strict, puntive style (physicial)
firm limit and control
litttle verbal exchange
low in warmth
high communication patent to child
respect work and effort
produce children who are:
less trusting
more withdrawn from peers
do well under guidance of the authoritarian, but may struggle outside the inflience of the parent
Authoritative
encourage independence
with limits and control
high warmth
moderate discipline
lots of talking/negotiating
explain reasons for rules
parents produce children who are:
more socially capable
preform better academically
are better suited to make decisions on their own
Permissive-Indifferent:
parent is uninvolved in child’s life
low warmth
low caring
low empathy
low expectations
Permissive- Indulgent
high degree of warmth
low degree of expectations
parents are highlu involved with their child but place few demands or controls on them
don’t set clear guidlines for their children
rules are constantlly changed
rules are usually not enforced
easy to get away with almost anything
children never learn to control their own behavior and always expect to get their way
produce kids with:
emotional control problems
more dependant upon parents and others
authoriative parents often produce children high in self-esteem, self-reliance, and social compitence