Bio Midterm Review
1. Properties of Water
-water is a POLAR molecule (hydrogen=slightly positive; oxygen=slightly negative)
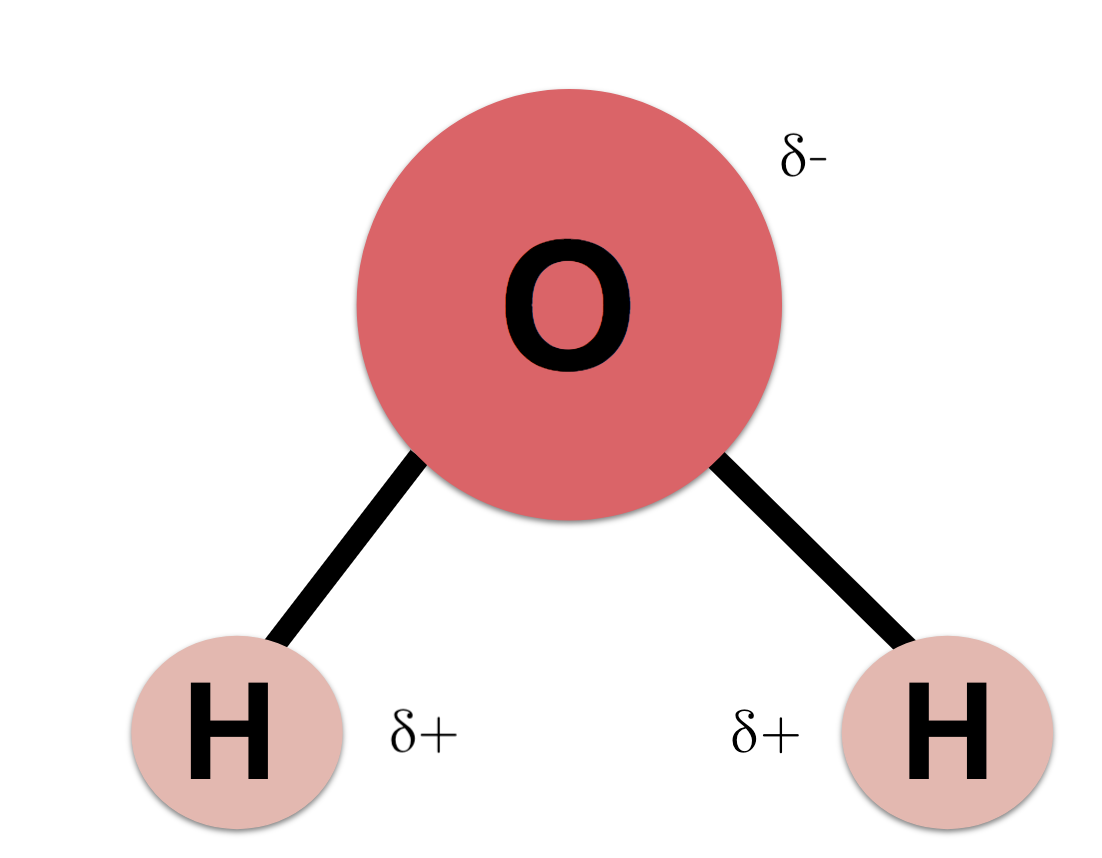
why? water has an unequal sharing of electrons between the atoms
2. Hydrogen Bonding
definition: molecules attract due to partial charges
this type of bonding has to occur with hydrogen (+) and another molecule (-)
the attraction is usually weak and not as strong as a covalent bond
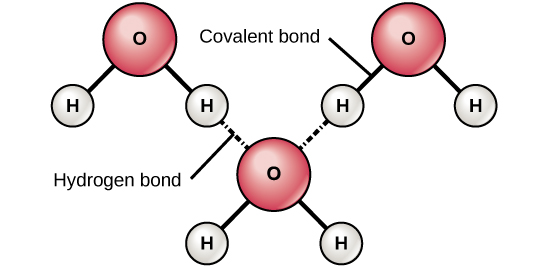
water is an example of this- if water did not have a hydrogen bond, it would not be a liquid and have the capability to sustain life
3. Types of Macromolecules
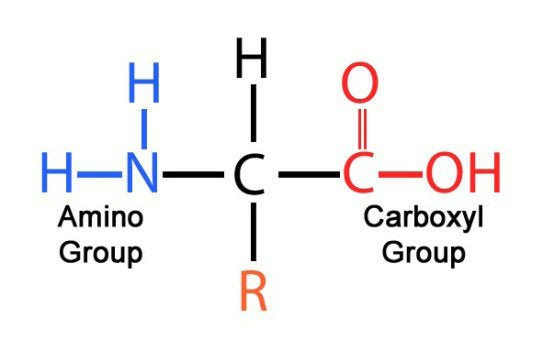
Amino Acids:
the fundamental molecule that serves as the building blocks for proteins
monomers that makeup proteins
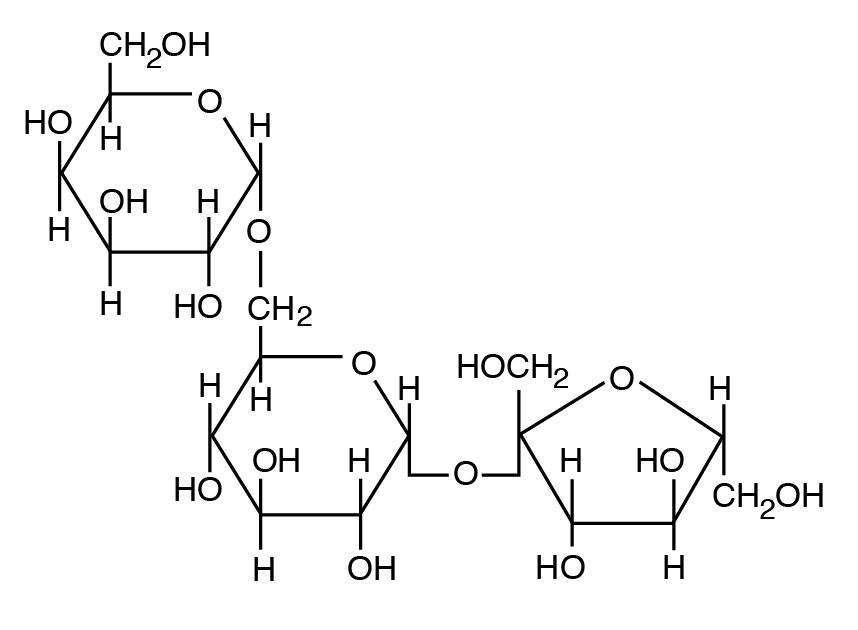
Carbohydrates:
consisting of carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen atoms
an organic compound such as sugar or starch, and is used to store energy
Nucleic Acids:
typically DNA and RNA
must have a phosphate group, a sugar, and a nitrogenous base
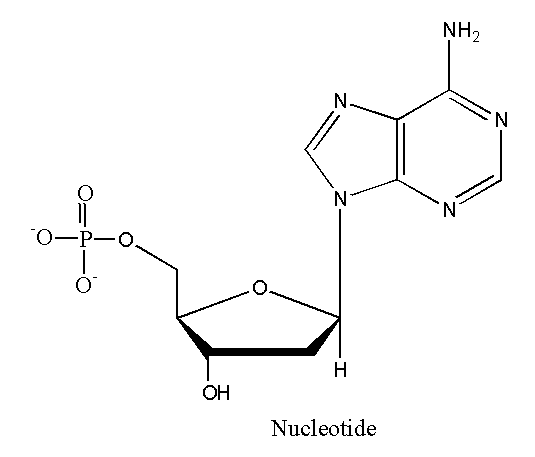
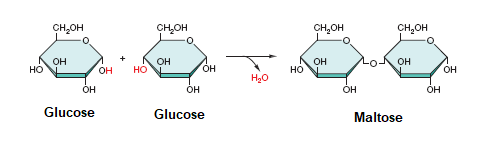
4. Monomers/Polymers in Monomerization and Polymerization
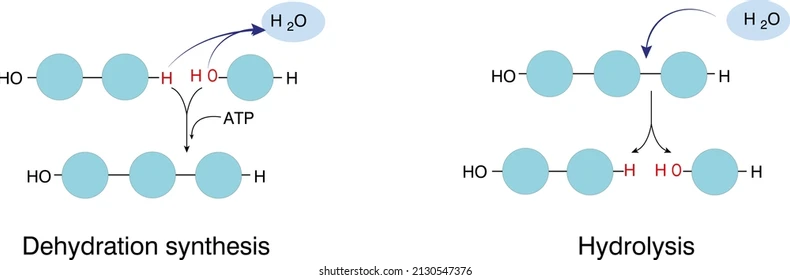
Dehydration Synthesis:
takes water out of the molecule
Hydrolysis:
water is being put into the molecule
water is “shoved” in and breaks the molecule
opposite of synthesis
ex: sugar-building carbohydrates
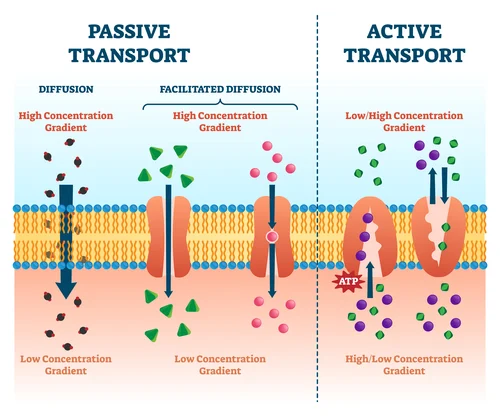
5. Cell Membrane
definition: separates and protects the interior of the cell from the outside environment
Made up of two layers:
phospholipid and the polar ends of molecules
phospholipids have a hydrophilic head and a hydrophobic tail
because of this polarity, the membrane forms in a way that water is not near the tails
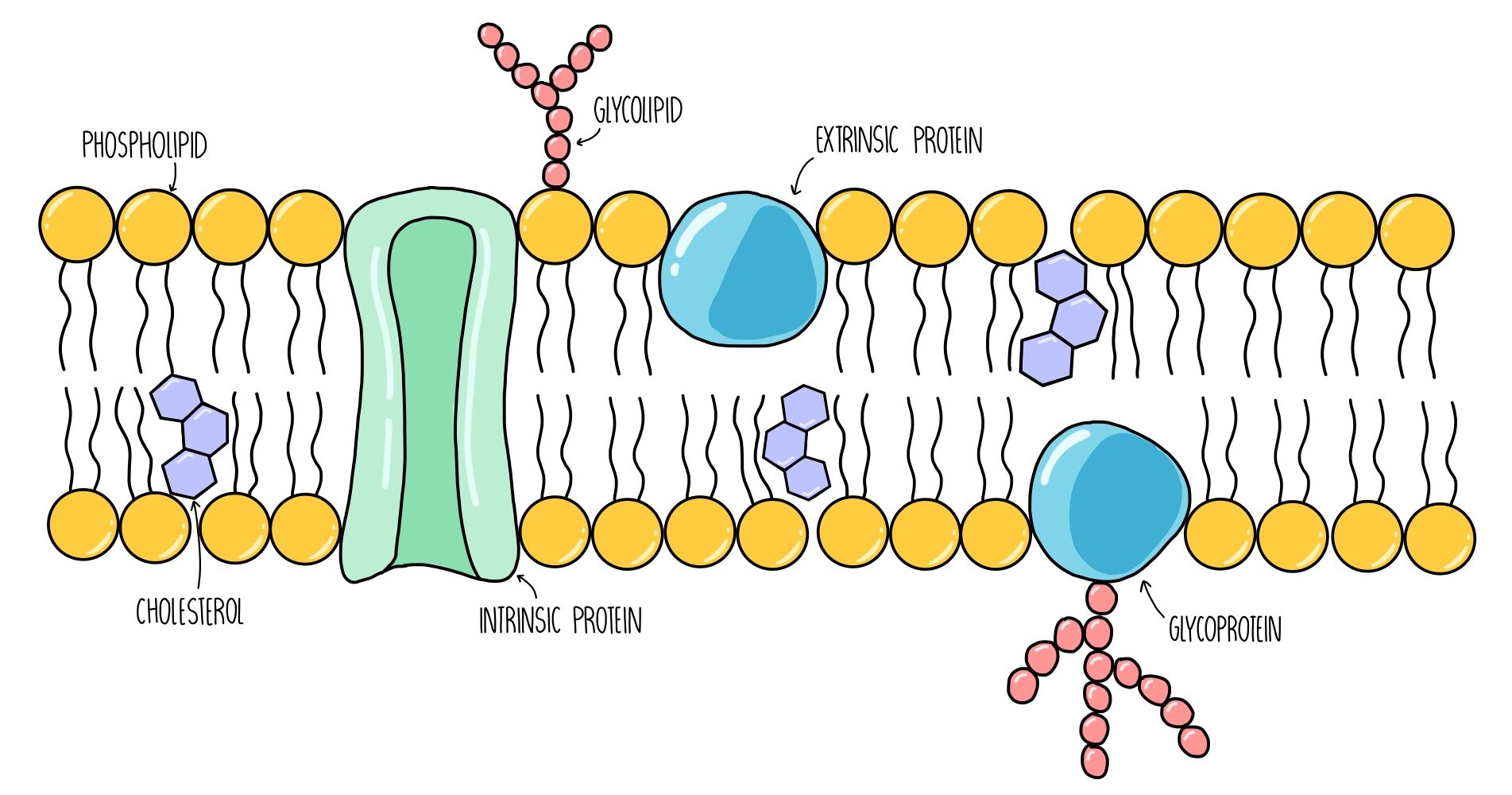
the structure is constantly moving
What can get into the cell?
lipid molecules
small nonpolar molecules- that way they can fit through
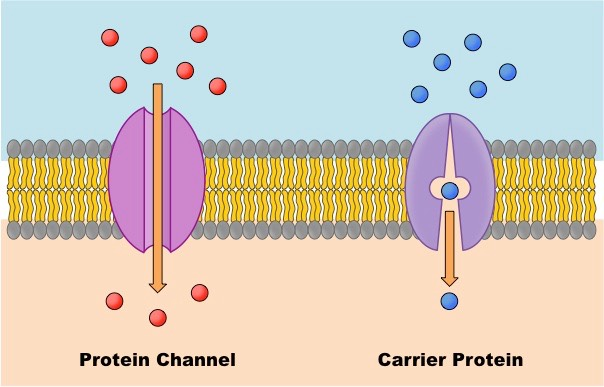
when the molecules trying to pass through are too big or are polar, they have to go through protein channels which allow more molecules in (passive transport)
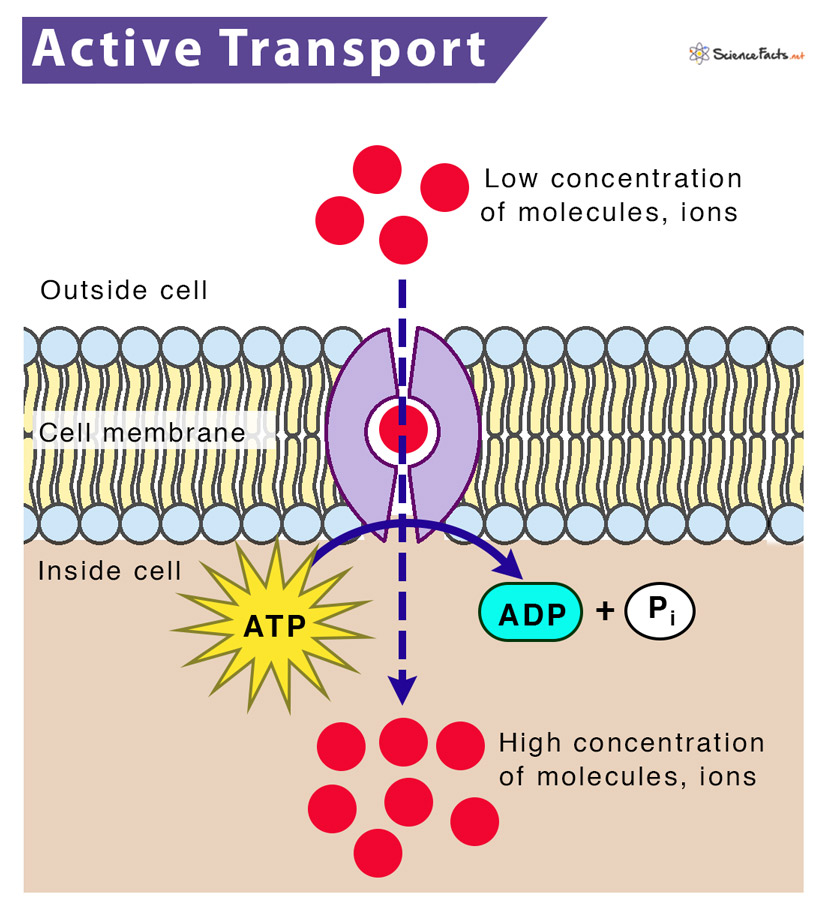
Active Transport: uses energy to pump things out of the cell
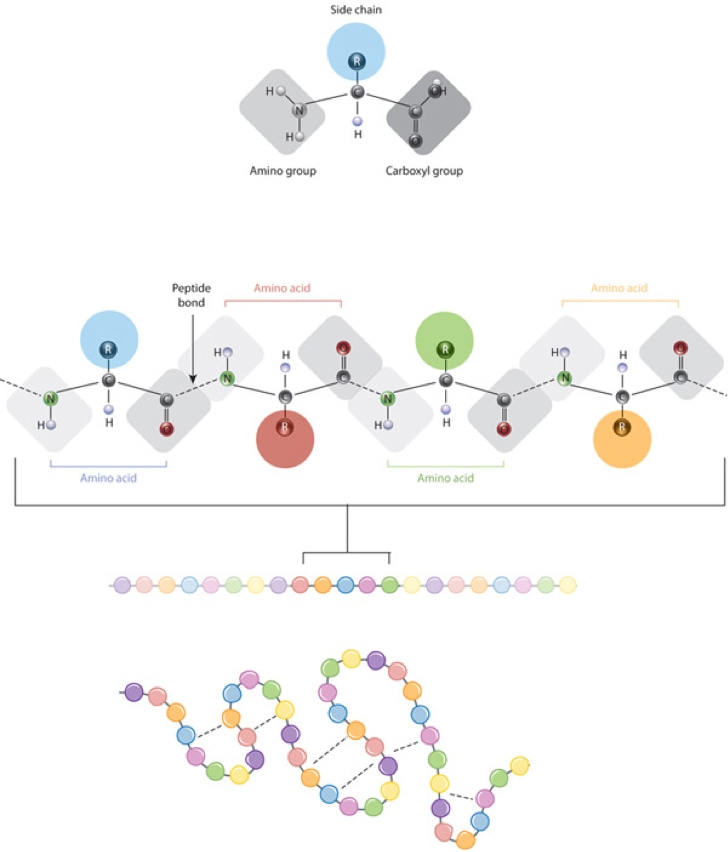
6. Amino Acid Structure
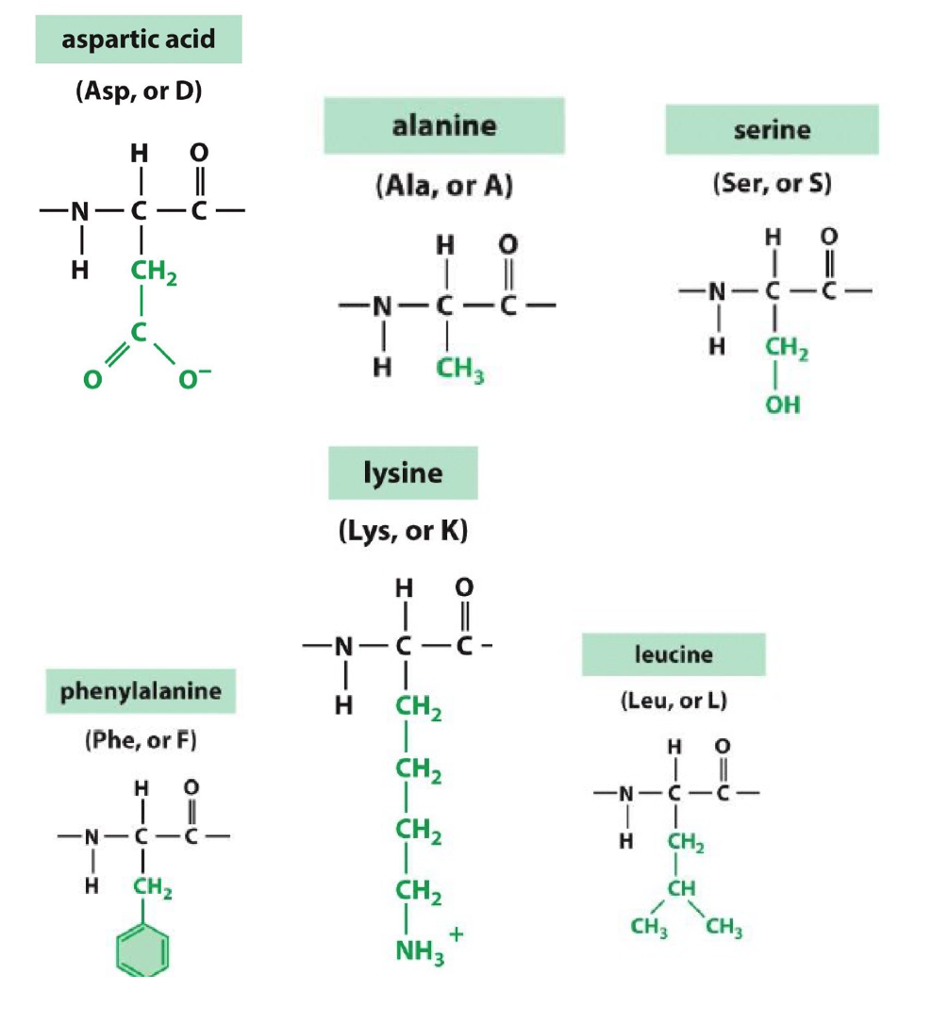
the side groups (R group) are in green in the picture above
How do you tell the properties of the side group?
you can tell based on the individual elements in the group and their electronegativity
polar and non-polar element
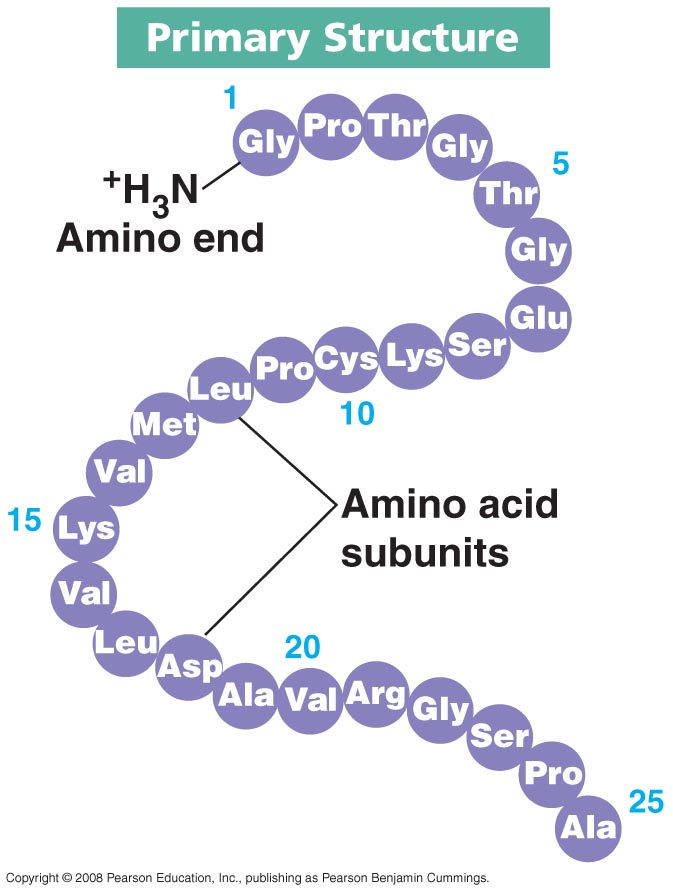
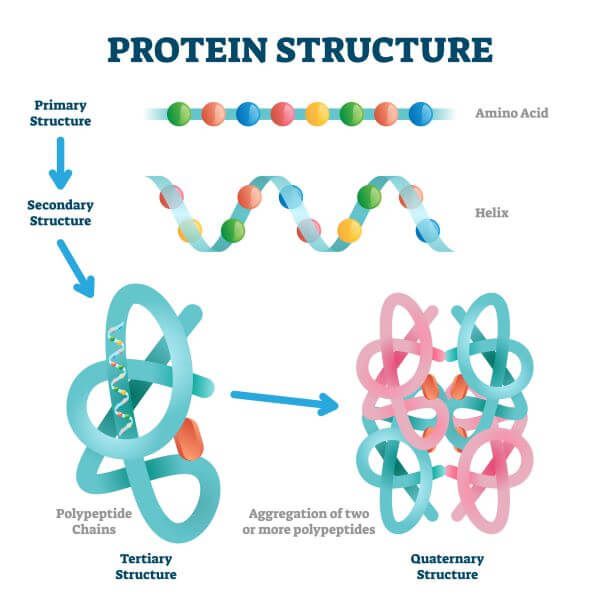
7. Four Types of Protein Levels
Primary Structure:
This is the 1st layer of the protein
it serves as the building block for the protein to form
the “sequence” of amino acids linked together to form the polypeptide chain in a linear sequence
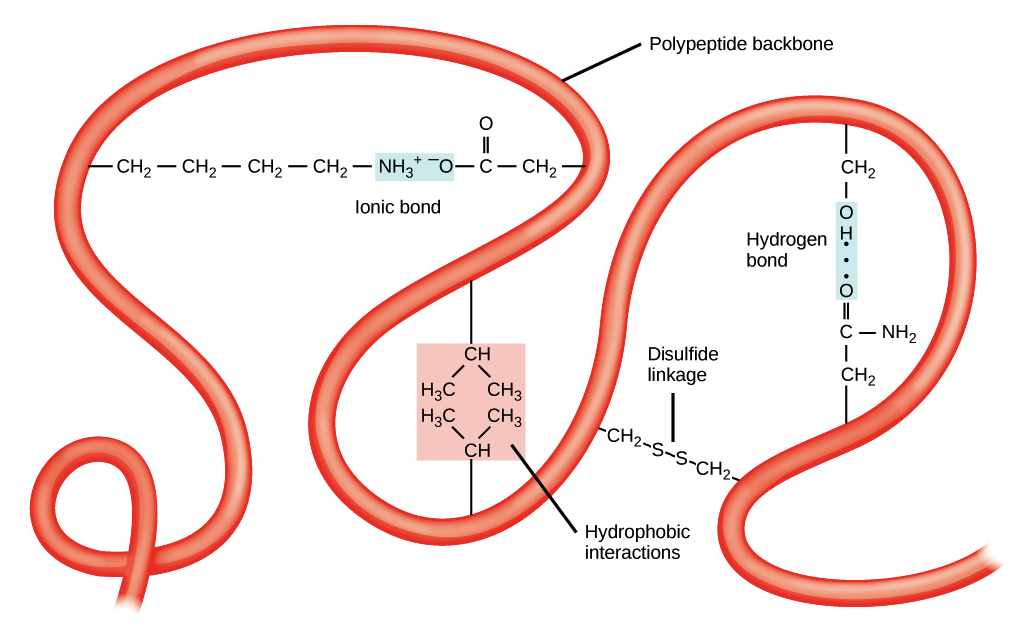
Tertiary Structure:
this is the overall 3-D structure of the polypeptide chain
it is stabilized by outside polar hydrophilic and hydrophobic and ionic bond interactions
Quaternary Structure
the association of several protein chains in a closely packed unit
What happens when one of the amino acids in the sequence is removed?
The structure has to fold in a new way because of the properties of the amino acids. Some of them don’t like being next to each other and have to fold in a way so that they are not next to each other.
hydrophobic, hydrophilic, acid, and base
What if you change one of the amino acids for the same one?
nothing changes
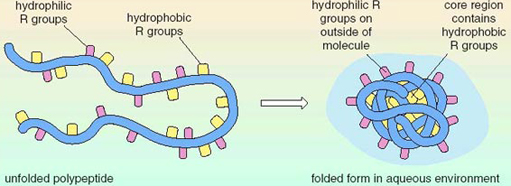
8. Water Interacting with Amino Acids
main idea: it creates the tertiary structure of the protein structure
location in the protein: in the center because they are hydrophobic
cysteine chains from covalent bonds with each other when exposed to oxygen
9. Primary Level is Responsible for Tertiary Level
each side chain has amino acids in a specific order in the primary level of protein and ordered in a certain way
depending on the order of the amino acids, the rules for each amino acid still apply, so the chain has to fold in a different way to meet the requirements for amino acids
everything will change the protein structure unless you take out the same exact amino acid and replace it with the same one
10. Enzymes and How They Work
what is an enzyme?
a biological catalyst
speeds up the rate of a specific chemical reaction in a cell
is not destroyed in the reaction and can be used over and over again
they function best at a specific temperature, pH, and salt concentration- if it is not perfect, they won’t work
What happens when you don’t have enzymes?
activation energy goes up because the enzyme is not there to speed up the process so it has to work harder to do the same thing
11. Enzyme Processes
Induced Fit Model
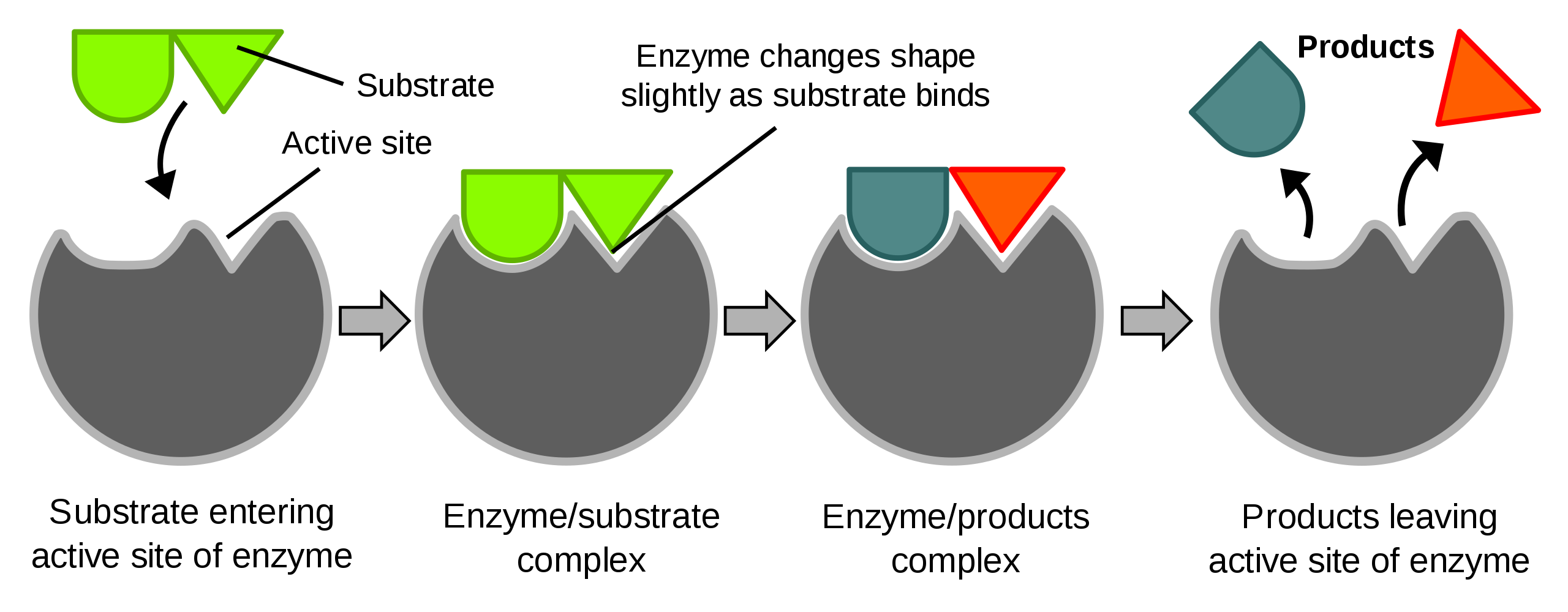
The substrate binds to the active site which is where everything happens and slightly alters the shape of the active site. The enzyme puts strain on the substrate causing it to break which creates the product. Everything in the cell happens rapidly.
Passive Transport:
no energy is being used
high to low concentration
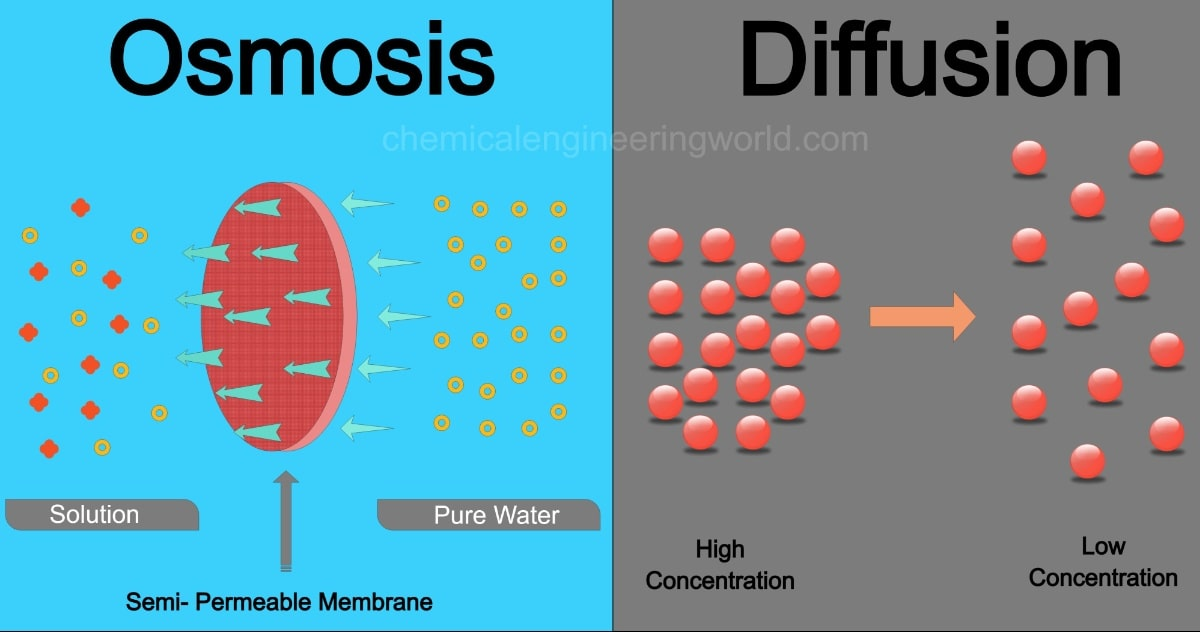
Facilitated Diffusion
When a molecule is too big to pass through the membrane, it can pass through a protein channel
type of passive transport
Active Transport: (Audie’s Favorite type of transport)
uses energy with protein channels to get things through the membrane of a cell
12. What Affects Enzymes in a Cell?
enzymes are picky (just like Audie) ♥️so they only like a specific environment
they like to have a specific pH, temperature, and concentration
enzymes bind to the reactant molecules and change their shape
lowers the activation energy 👍🏼
🤓
What happens when you don’t have enzymes?
the reaction in cells would not occur or run too slowly to keep organisms alive
Why do enzymes work at the rate they do?
If enzymes worked too quickly, too much heat energy is created making the process inefficient
when it occurs slowly and carefully, it can do its specific job better and more efficiently
13. Competitive and Noncompetitive Inhibition and Feedback Inhibition
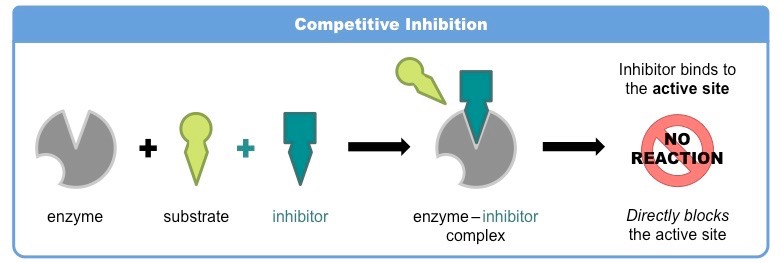
Competitive:
the inhibitor resembles the substrate, taking its place and binding to the active site of an enzyme
example: caffeine; it doesn’t give you energy just makes you not know that you are tired
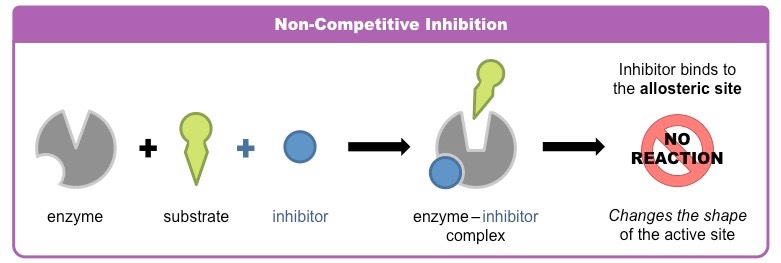
Noncompetitive (Allosteric)
inhibitor molecule binds to the enzyme in a location other than the active site known as the allosteric site
prevents the substrate to bind to the active site
changes the shape of the active site reduces the enzyme activity
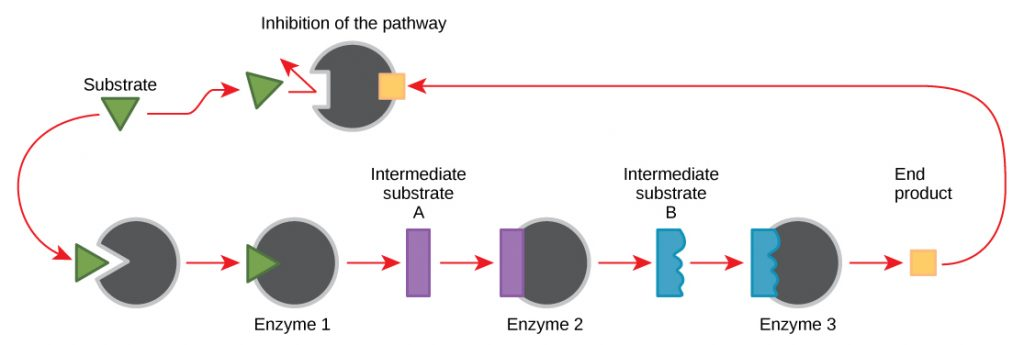
Feedback Inhibition:
occurs when the end product of a reaction interferes with the enzyme that helped produce it. The inhibitor does this by binding to a second active binding site that's different from the one attached to the initial reactant. The enzyme then changes its shape and can't catalyze the reaction anymore.
Other Random Questions:
Where does matter and energy come from and where do they go?
all living organisms require energy
if something has energy, it can cause change
energy is never created or destroyed instead it is transferred and transformed