
31: Movement of Elements in Ecosystems
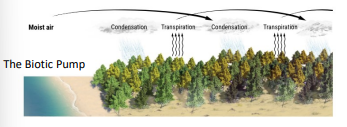
the movement of water through ecosystems and atmosphere
Major water pools (in 10³ km³)
Major water fluxes (in 10³km³yr^-1)
The Biotic Pump
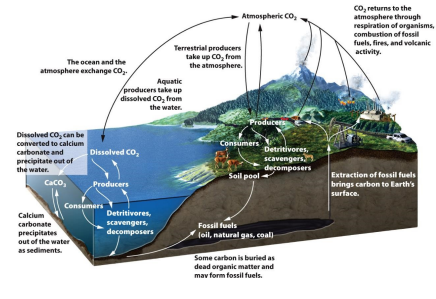
Six main transformations:
photosynthesis
respiration
exchange
mineralization
sedimentation/burial
combustion
Methane production:
Ch4
A greenhouse gas
Produced under anaerobic conditions
Concepts
Nitrogen fixation: the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms producers can use
Nitrification: the final process in the nitrogen cycle, which converts ammonium to nitrite (NO2-) and then from nitrite to nitrate (NOe-)
Mineralization: the process of breaking down organic compounds into organic compounds
Denitrification: the process of converting nitrates into nitrogen gas
Mostly in the soil
Eutrophication: an increase in the productivity of aquatic ecosystems
Weathering
in terrestrial systems, nutrients are mostly in the soil
main source of P
Breakdown of organic matter
Decomposition
Aquatic: Sediments and nutrients
nutrients tend to sink to deep waters or sediments
Allochthonous inputs
Rio Piedras, Puerto Rico
leaf litter decomposition rates decrease with increasing urbanization
Important factors
channelization/substrate
Macroinvertebrates
the movement of water through ecosystems and atmosphere
Major water pools (in 10³ km³)
Major water fluxes (in 10³km³yr^-1)

The Biotic Pump

Six main transformations:
photosynthesis
respiration
exchange
mineralization
sedimentation/burial
combustion

Methane production:
Ch4
A greenhouse gas
Produced under anaerobic conditions
Concepts
Nitrogen fixation: the process of converting atmospheric nitrogen into forms producers can use
Nitrification: the final process in the nitrogen cycle, which converts ammonium to nitrite (NO2-) and then from nitrite to nitrate (NOe-)
Mineralization: the process of breaking down organic compounds into organic compounds
Denitrification: the process of converting nitrates into nitrogen gas
Mostly in the soil
Eutrophication: an increase in the productivity of aquatic ecosystems
Weathering
in terrestrial systems, nutrients are mostly in the soil
main source of P
Breakdown of organic matter
Decomposition
Aquatic: Sediments and nutrients
nutrients tend to sink to deep waters or sediments
Allochthonous inputs
Rio Piedras, Puerto Rico
leaf litter decomposition rates decrease with increasing urbanization
Important factors
channelization/substrate
Macroinvertebrates