FINAL HISTORY STUDY GUIDE
UNIT 1: COLONIAL FOUNDATIONS
AGE OF EXPLORATION:
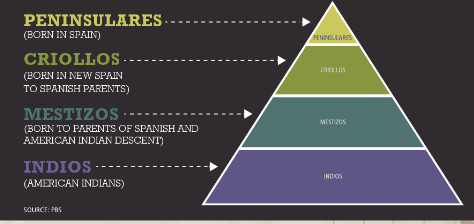
SPANISH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
acquire wealth
spread Catholicism
create a land empire
LOCATION
Columbus first lands in the Bahamas
Columbus continued to Hispaniola
Cortes conquers the Aztecs
METHOD
2 Vice-royalties: Peru and New Spain
Ruled by a Viceroy: King Appointed official
No elected officials
Racial Hierarchy:
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE PEOPLE
Columbus brutally captured and killed natives on Hispaniola after they attacked his men
conquistadors —> conquerors who brutally enslaved natives
enslaved native americans on encomiendas (large, Spanish owned plantations)
missionaries —> those sent to the Americans to forcibly convert natives to Catholicism
FRENCH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
trade intended with Asia —> ended up trading with the natives to acquire wealth
spread Catholicism
create a land empire
LOCATION
Caribbean
While searching for NW Passage, landed in Newfoundland (Canada) via the St. Lawrence River
Explorer Robert De Salle explored the Mississippi River
Landed in Louisiana → Founded New Orleans
METHODS
Jesuit Catholic missionaries converted some Huron Indians of the Great Lakes
Intendant: Military governor general appointed by the monarch
No representation in government
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE AMERICANS
Traded (beaver) furs for metal tools like arrowheads, axes, knives, etc.
Competition → Conflict between Native groups
Adopted some Native cultures and marriages between groups
Alliances with Algonquian language speaker nations in the Great Lakes region
Fewer French immigrants → Claimed less territory → Lessened conflict
ENGLISH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
acquire wealth initially believed gold —> became cash crops
spread Christianity and religious freedom
create a land empire
LOCATION
Caribbean
attempt in Roanoke → failed
Jamestown
METHODS
Headright System: VA company granted 50 Acres of land to anyone that a settler paid to bring over
Indentured Servants: 7-10 years of service in exchange for transportation & eventual freedom
Representative Government seen in the House of Burgess and Mayflower Compact
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE PEOPLE
Some positive relationships - EX. New England & Thanksgiving
Disease killed many Indigenous
Conflict arose as more territory was claimed by settlers
DUTCH EXPLORATION
MAIN GOAL
acquire wealth
spread Christianity
create a land empire
LOCATION
Caribbean
Hudson river and in modern day New York
Connecticut and New Jersey
METHODS
encouraged emigration with patroonship system
stockholders of dutch west India company would receive 50 emigrants to work on their land
reflected feudal system in medieval Europe
unsuccessful - most who had emigrated worked on their own land
second Anglo-dutch war (1664-1667)
the dutch ceded all their american colonies to great Britain
RELATIONSHIP WITH NATIVE PEOPLE
purchased land from local Indians
leasing vs owning
refrained from learning culture and inter-tribal conflict
dutch setters disrupt traditional way of life and encroached on ancestral land
THE YEAR 1619
CREATION OF THE HOUSE OF BURGESS
first popularly elected legislature in the american colonies
todays virginia general assembly
had to obey the king and governor
SLAVES INTRODUCED TO THE VIRGINIA COLONY
mercantilism —> gaining wealth and power by developing countries
cash crops
english emigration began to decrease
REGIONS OF THE COLONIES
NORTH
CLIMATE
cold winters with short growing seasons
small farms for own use
rocky soil
corns, beans, squash
ECONOMY
depended largely on the ocean
efficient in:
fishing
trapping
ship-building
logging
manufacturing
GOVERNMENT/RELIGION
predominately puritans
strict religious lives
the clergy devoted to the study of the scripture and the natural science
MIDDLE
CLIMATE
mild climate with warm summers
better for farming
deep rich soil
longer growing season
ECONOMY
fur trading
farming
fertile soil—> grain. corn, wheat exports (breadbasket of the colonies)
GOVERNMENT/RELIGION
religiously tolerant and diverse
welcomed people of all religious background
run by authoritarian governors
SOUTH
CLIMATE
fertile soil
warm climate, mild winters
good for agriculture
cash crops
tobacco, cotton, indigo, rice
ECONOMY
lots of plantations —> slavery
indentured servants
lots of cash crops
agriculture
GOVERNMENT/RELIGION
not religiously tolerant
Catholics
slaves
debtors/criminals
house of Burgess
Jamestown - 1st representative government
IMPORTANT PEOPLE/EVENTS OF COLONIAL AMERICA
Sir Walter Raleigh
English explorer
tried to create permanent solutions 2x
tried to establish Roanoke
John Smith
leading role in establishing Jamestown
established the first permanent English settlement in north america
John Rolfe
credited with introducing marketable tobacco to Virginia
planted the first tobacco seeds
helped turn Jamestown into a profitable venture
Powhatan
powerful leader and principal contact for English colonists from 1607-1618
united dozens of tribes into a single powerful alliance
led his people through the early years of colonial invasion
Pocahontas
Powhatan’s daughter
encouraged interest in Virginia and the company
Cash crops/tobacco
crop that is grown for the purpose of selling
fueled the transatlantic slave trade
boosted the economy
the great awakening
a religious movement in the north American countries that emphasized individual salvation and high standards of personal mortality
challenged traditional beliefs and practices
new sense of American identity
Bacon’s rebellion
1676
protests against the governor
governor prevented war against Native Americans
high taxes benefiting the wealthy
governor is removed
taxes reduced
showed that population will not be ruled by wealth elites
individuals can find own salvation
challenged authority of the church
Indentured servitude vs. slavery
Indentured Servitude
Slavery
someone who chose to immigrate
originally captured native Americans
contract of 5-7 years
forced to migrate against their will
kidnapped/sold
freedom were given
clothes
food
small plot of land
hard labor
no pay
children were also condemned to slavery
not considered property
considered property
UNIT 2: THE REVOLUTIONARY WAR
IDEAS OF THE ENLIGHTENMENT
natural rights
all people are born with them
life
liberty
property
social contract
people give the power to the government but can take it away
it led to the revolutionaries to break free of Britain
consent of the governed
the government’s power is only legitimate when it it determined by those who are being governed
GROUPS DURING THE REVOLUTIONARY WAR
patriots
2/5 of colonists
wanted a new government based on merit, not inherited privilege
opposed taxes
emphasized Locke’s natural rights
fought the British
Loyalists
1/5 of colonists
believed that the British government was more legitimate and disliked violent protest
opposed taxes but wanted to follow the law
feared destruction/chaos
fought with the British
appealed to British natives and slaves
neutralists
the people who didn’t choose a side in the war
remained neutral
Native Americans
most native Americans thought colonists were more dangerous than the British
6 Iroquois tribes
4/6 fought with the British
2/6 fought with colonists
enslaved African Americans
England promises freedom to slaves that fought for the loyalist cause
most African Americans assigned to non-combat positions
were initially prohibited from the joining the continental army
later allowed due to labor shortages
ADVANTAGES AND DISADVANTAGES OF EACH SIDE
advantages of the patriots | advantages of the british |
|---|---|
|
|
disadvantages of the patriots | disadvantages of the British |
|
|
IMPORTANT PEOPLE/TERMS OF THE REVOLUTIONARY WAR
great awakening
challenging traditional authority
reshaped ideas about government
creation of unique american identity
french and Indian war
caused by increasing hostilities between the french and the Indians at the american frontiers over territory
war is expensive → British gets the colonies to pay for the share
increases taxes, cracking down on smuggling, end of salutary neglect
anger and resentment towards the British
proclamation of 1763
prohibited colonists from moving west of the Appalachian mountains
increased anger and resentment to the British policy
Paine’s common sense
1776
pamphlet
colonies would be better off as an independent country
circulated throughout the colonies
widespread audience
George Washington
leader of the continental army
became the first president of the US
sugar act
lowered duty (tax) on foreign molasses (sugar) coming to the colonies
actually prosecuted smugglers
stamp act
march 1765
required colonists to pay a tax on almost all printed materials
first direct tax that wasn’t a duty (tax)
Boston massacre
march 1770
colonists insulted stationed British soldiers and threw rocks on them
soldier shot into the crowd
5 colonists killed
first and second continental congress
the first continental congress announces the boycott of all British goods
fall 1774
second continental congress agrees to send troops to support New England
may 1775
Boston tea party
1773
colonists are upset with the tea act → dumped tea into the Boston harbor out of protest
declaration of independence
written and published on July 4th, 1776
written primarily by Thomas Jefferson
explains to the world why the 13th colonies regarded themselves as independent
battle of Saratoga
Sept. 19, 1777 → Oct. 7, 1777
British general john Burgoyne → ambitious plan to capture New York
allow the British to cut off northern colonies from southern colonies
persuaded the french to recognize american independence and provide military support
battle of Yorktown
Sept. 28, 1781 → Oct. 19, 1781
Yorktown, VA
the american forces under the command of George Washington surrounded the British army
Cornwallis (leader of the British army) surrendered his army after a siege that lasted 20 days
last major battle
articles of capitulation signed
UNIT 3: EARLY FEDERAL PERIOD
ENLIGHTENMENT CONCEPTS:
natural rights
rights given to all individuals by the natural law
life
liberty
property
consent of the governed
the authority of the government should depend on the consent of the people
social contract
people give the power to the government but can take it away
ordered liberty
a system of laws and order
separation of church and state
government/religious leaders are different
separation of powers
different branches of government with different functions
FOUNDING DOCS
VA declaration of rights
George Mason
1776
documents that listed rights that were granted to all men
inspired the bill of rights
VA statute for religious freedom
Thomas Jefferson
1786
document that said the government should not force a certain religion on to its people
articles of confederation
constitutional convention in 1777
original constitution
established national government
loosely tied the states together
US constitution
James Madison
1788
document that outlines supreme law of the US
outlines role/function of government
bill of rights
James Madison
1791
first 10 amendments to the constitution
guarantee individual liberties to American citizen
IMPORTANT PEOPLE/EVENTS OF THE EARLY FEDERAL PERIOD
George Washington
first president
creation of the national bank
whiskey rebellion
John Adams
XYZ affair
alien and sedition acts
Kentucky and VA resolutions
James Madison
federalists
wanted to have close relations
favored strong central government
seen as an elitist
Thomas Jefferson
democratic-republican
disliked taxes imported during Adam’s presidency
denounced alien and sedition acts
accessible to the people
federalists vs anti-federalists
federalists
anti-federalists
believed in strong, central government
didn’t think a bill of rights was necessary
believed in a weaker government
wanted power to be kept in the states
wanted a bill of rights to ensure liberties
federalist paper
essays that urged the ratification of the new constitution
convinced votes to support the constitution
convinced votes that the articles of confederation needed revisions
democratic-republicans
strict interpretation of the constitution
no national bank
loved the French revolution
the great compromise
proved for a bicameral federal legislature that used a dual system of representation
upper house → equal representation from each side
lower → proportional representation based on the states population
the 3/5 compromise
agreed to hold a national census every 10 years that would be used in determining the apportionment for the following 10 years
slaves would count as 3/5 of the population during the census
north and south would be both represented
UNIT 4: THE EARLY REPUBLIC
WESTWARD EXPANSION
Louisiana purchase
1803
Jefferson purchased the land from the France
expands US territory for $15 million
allowed for later addition of new states
seen as an overstep of the government power
led to Lewis and Clark expedition
Indian removal act
may 1830
signed by Andrew Jackson
native Americans would be required to exchange their territory for land west of the Mississippi
the trail of tears
1838-1839
movement of Cherokee native Americans to reservations in present-day Oklahoma
forced to walk the distance between Florida and Oklahoma
Mexican-american war
conflict over the Texas-mexico border
US wins
border reaffirmed at the Rio grande
southwest boundaries expand
Monroe doctrine
part of the annual message to Congress that included a warning to European powers to not interfere in the affairs of the western hemisphere
manifest destiny
it is the cultural belief in the US that expansion was inevitable because of their god-given ability to spread liberty and democracy
GROUPS DURING THE WAR OF 1812
federalists
merchants and businessmen opposed war
relied on trade with Britain
anti-federalists
anti-British feelings grew in the south and west
demanded war against the British
wanted more land = push the British from Canada
wanted to restore national honor after impressment
British
occupied Washington DC
burned the public buildings
didn’t want Americans to supply food to enemies
a partial blockade
Andrew Jackson
became a hero at the battle of new Orleans
led his troops through enemy territory to victory
THE ROAD TO THE CIVIL WAR
Missouri compromise
1820
admitted Missouri as a slave state and Maine as a non-slave state at the same time
outlawed slavery about 36*30* latitude line in the remainder of the Louisiana territory
known as the 36th parallel
Nat Turner’s rebellion
1831
Nat Turner → enslaved laborer and preacher
led to the largest slave revolt in South Hampton VA
the fugitive slave law was put into place
required slaves go be returned to their owners even if they were in a free state
Tariff of 1832
brought imported taxes back down to 35%
shrunk English demand for southern raw cotton and increased the final cost of finished goods to American buyers
nullification crisis
South Carolina nullified a federal tariff that favored northern manufacturing over southern agriculture
compromise of 1850
California enters union as a free state
strengthened fugitive slave laws
banned the slave trade in DC
proto-government for new mexico territory →but could be set up as free or slave once it was ready for statehood
proto-government for Utah territory → could be slave or free once it was ready for full statehood
Kansas Nebraska act
1854
repealed the Missouri compromise since both were north of the 36th parallel
established new territories of Kansas and Nebraska
said that these states would use popular sovereignty to determine if they would be slave or free
bleeding Kansas
1854 - 1859
series of violent conflicts in Kansas between pro-slavery and pro-abolition advocates
pro-slavery advocates rushed from Missouri to Kansas to pretend to be residents
wanted to use popular sovereignty to make Kansas a slave state
violence from both groups ensued for four years
UNIT 5: CIVIL WAR AND RECONSTRUCTION
MAIN IDEAS
advantages of the Union | advantages of the confederates |
|---|---|
|
|
leaders of the Union | leaders of the confederates |
|
|
IMPORTANT EVENTS OF THE CIVIL WAR
fort Sumter
April 12, 1861
marked the official beginning of the civil war
Charleston, South Carolina
forces from the confederates attacked the Union military Garrison
the fort surrendered 2 days later
Antietam
Sept. 17, 1862
one of the major turning points of the war
showed that the union could stand against the Confederate army
enabled Lincoln to issue the emancipation proclamation
emancipation proclamation
Jan. 1, 1863
issued by Lincoln
enslaved people in the southern states would be declared free
announced the acceptance of African Americans into the union and the navy
battle of Gettysburg
July 1-3, 1863
marked the turning point of the war
union victory
brought the war to an end
one of the bloodiest battles of the war
Gettysburg address
Nov. 19, 1863
Lincoln’s short but powerful speech
places civil war into the historical context of American fight for freedom
urges American to devote themselves to the task of preserving freedom for all Americans
Sherman’s March to the sea
Nov. 15, 1864 - Dec. 21, 1864
most destructive campaign against civilian population
purpose → frighten Georgia’s civilian population to abandon confederate cause
was a strike to the heart of the confederacy
Appomattox
Apr. 9, 1865
Robert E. lee surrendered his army to Ulysses S. Grant
brought an end to the civil war
UNIT 6: GILDED AGE AND PROGRESSIVE EAR REFORM
NATIVE AMERICAN RELATIONS AFTER THE CIVIL WAR
wounded knee massacre
dec. 29, 1890
US soldiers killed hundreds of Lakota men, women, and children in an attempt to suppress a religious movement
reservations
an area of land that is reserved for a tribe or tribes under the us government
able to better subdue them
homestead act of 1862
government encourages farming with free 160 acres if you farm it for 5 years
Carlisle industrial school
mission was to remove indigenous children from their families and communities to assimilate them
stop the spread of native cultures
wanted to strip away native identity and culture
THE GILDED AGE
captains of industry
a business leader whose means of personal fortunes contribute positively to the country in someway
laissez-faire capitalism
an economic philosophy that advocates for minimal government interference in the economy
political machines
political parties organization that wins voter loyalty and grants power to a small group of leaders often for political gain
often created loyal bases of immigration by offering housing or jobs
tenement housing
housing buildings with multiple units
run down, low quality, typically many families in a room
result of urbanization and immigration
TREATMENT OF MINORITIES
“new” vs. “old” immigration
“new” immigration | “old’ immigration |
|---|---|
|
|
Chinese exclusion act
congress passed it
suspended the immigration of all Chinese laborers for 10 years
required every Chinese person entering or leaving the country to carry paperwork
first law to broadly restrict immigration based on national origin
Jim crow laws
federal, state, and local laws that enforced racial segregation
buck v. bell
may 2, 1927
affirmed the constitutionality of Virginia’s law allowing state-enforced sterilization
social Darwinism
social economic and political philosophy emerged in late 19th and early 20th century
principles of natural selection and survival of the fittest should be applied to human societies
used to justify race and class distinctions
INDUSTRIES AND BUSINESS TYCOONS
John D. Rockefeller → standard oil
Andrew Carnegie → Carnegie steel company
J.P. Morgan → JP Morgan bank
UNIT 7: IMPERIALISM AND WWI
IMPERIALISM
CONFLICT | DATE | WHAT HAPPENED | SIGNIFICANCE |
|---|---|---|---|
Spanish-american war | April - Dec 1898 |
|
|
US-Philippine war | Feb. 4, 1899 - July 2. 1902 |
|
|
annexation of hawaii | July 7, 1898 |
|
|
WWI
MAIN causes of WWI
M → militarism
A → alliances
I → imperialism
N → nationalism
the US got involved in April of 1917
Woodrow Wilson’s 14 points
no militarism/secret alliances
freedom of the seas
self determination
league of nations
Treaty of Versailles
lost territory in Germany
intense reparations to be paid by Germany
Germany was to be blamed for the entire war
mandate system established in the middle east
the terms of the treat punished Germany very harshly
Germans were angry and turned to Hitler
UNIT 8: INTERWAR YEARS
POPULAR CULTURE
Changes in media → transform entertainment
Listening to the radio
Able to listen to new music & hear about distant events
Going to the movies
Silent movies featuring Charlie Chaplin
Newspapers/Magazines
THE NEW DEAL
FDR’s domestic programs
Involved the 3Rs in the different programs
Split into 2 eras
First New Deal: 1933-1934
Second New Deal (1935-1938)
IMPORTANT TERMS
Harlem Renaissance
A new wave of African American culture centered around, but not limited to, Harlem, NY
prohibition
18th Amendment: nationwide ban on the sale and import of alcoholic beverages
Led to the rise of Organized Crime
Al Capone & other gangsters made their fortunes from the illegal distillation and sale of alcohol
women’s suffrage
19th amendment gave women the right to vote
National American Woman Suffrage Association
Lobbied and petitioned to pass state suffrage amendments that would lead to a national amendment
National Association of Colored Women
Promoted progress of women of color through suffrage and education
National Woman’s Party
Used more intense methods to enfranchise women
hunger strikes, marching with picket signs in front of the White House
scopes trial
Tennessee passed a law saying that teachers in public schools could NOT teach evolution
John Scopes: Biology teacher, taught evolution
At the trial: Scopes was convicted and had to pay a fine
Nationwide story - highlighting the fundamentalist vs. modernist argument
black Tuesday
October 29, 1929
More than 16 million shares were sold as the stock market collapsed in the Great Crash
bank runs
when a large number of depositors try and withdraw at the same time
Few banks could handle this number of withdrawals → led to banks closing
Banking system collapses
protective tariffs
Tariffs: Taxes on imported goods
Hawley Smoot Act: Increased tariff by 20% → Other countries placed tariffs on the U.S. in response
→ Global trade plummeted
→ no one to sell American goods to
Franklin D. Roosevelt
wanted the federal government to take charge of the economy
bonus army: sent his wife Eleanor Roosevelt to talk with the troop
she empathized with them
utilized the 3 Rs to end the depression and prevent another from returning
social security act
Created the Social Security Administration
Created the pension system for retirees
Established unemployment insurance for those who lost their jobs
Created insurance for victims of work related incidents
Continues to still provide basic economic security to millions of Americans
FDIC/SEC
FDIC
insure bank customers against the loss of up to $5,000 their deposits if their bank should fail
reform
SEC
a federal "watchdog" administrative agency to protect public and private investors from stock market fraud, deception and insider manipulation on Wall Street
reform
works progress administration
Created new jobs in road construction, harbor creation, etc.
Provided jobs for displaced artists, writers, actors, etc.
AAA/CCC/PWA
AAA
paid farmers for not planting crops in order to reduce surpluses
And increase prices
recovery act
CCC
unmarried men aged 18-25 from relief rolls and sent them into the woods and fields to plant trees, build parks/roads/fight erosion (BRP)
relief act
PWA
construction projects including public buildings, highways, bridges (e.g., San Francisco's Golden Gate Bridge), and dams for water and power.
relief and recovery act
UNIT 9: US INVOLVEMENT IN WWII
THE US’S NEUTRALITY
Neutrality Acts of 1935-1937
Embargo on arms - Made it illegal for Americans to sell or transport arms or other war materials to any nations at war (belligerent nations)
This was supported by isolationists
Neutrality Act of 1939
Allowed belligerent nations to buy goods and arms in the U.S. if they paid cash and carried their own merch on their own ships
British Navy controlled seas → benefited them
Many criticized and said this violated American neutrality
Lend Lease Act (1941)
allow the United States to lend or lease war supplies to any nation deemed "vital to the defense of the United States
ENTRANCE OF THE US INTO THE WAR
The US joins the war after the bombing of pearl harbor
declares war on Germany and Japan
IMPORTANT TERMS
island hopping
American strategy in the Pacific
battle of Midway
June 1942
Utilized knowledge of Japanese plans
Americans sunk 4 Japanese aircraft carriers &
Japanese only sunk 1 American aircraft carrier
Turning point in the war → Japanese now on the defensive
Hiroshima and Nagasaki
the two places where the US dropped the atomic bomb
ended the war
Japanese internment
Executive Order 9066
1942
forced removal of all persons deemed a threat to national security from the West Coast to "relocation centers" further inland – resulting in the incarceration of Japanese Americans.
defeat Hitler first
focus on finishing the war in Europe before trying to end war in Asia
d-day
Allies land in Normandy, France (June-August 1944)
Months of preparation led up to the largest military assault in history, the Allied landings at Normandy in Northern France
Led by Dwight D. Eisenhower, over 200,000 British, American, and Canadian forces landed at beaches named Gold, Juno, Sword, Utah, and Omaha.
The worst fighting was on Omaha beach, where Americans were killed as they stepped off their landing crafts.
Eventually, the Allies established a beachhead and pushed inland.
With landings behind German lines in the form of paratrooper support, the push to Paris was underway.
The French capital fell two months later.
battle of the bulge
begins in Belgium (December 1944-January 1945)
In late 1944, during the wake of the Allied forces' successful D-Day invasion of Normandy, France, it seemed as if the Second World War was all but over.
On Dec. 16, with the onset of winter, the German army launched a counteroffensive that was intended to cut through the Allied forces in a manner that would turn the tide of the war in Hitler's favor. The battle that ensued is known historically as the Battle of the Bulge.
Within days, Patton's Third Army had relieved Bastogne, and to the north, the 2nd U.S. Armored Division stopped enemy tanks short of the Meuse River on Christmas.
Through January, American troops, often wading through deep snow drifts, attacked the sides of the shrinking bulge until they had restored the front and set the stage for the final drive to victory
Never again would Hitler be able to launch an offensive in the west on such a scale. the Battle of the Bulge is arguably the greatest battle in American military history
holocaust
the systematic state-sponsored killing of six million Jewish men, women, and children and millions of others by Nazi Germany and its collaborators
Tuskegee airmen
1578 combat missions
Highly successful bomber missions
Awarded more than 850 medals
nisei regiments
Japanese Americans earned a high number of decorations while fighting predominantly in Europe
Fought discrimination at home
rationing
Supplies such as gasoline, butter, sugar and canned milk were rationed because they needed to be diverted to the war effort.
women join labor force
More women in labor force
More of these older and married
Different from WWI
Drawn into previously male-dominant jobs (heavy industry, mechanics)
Most women still in service sector jobs
More jobs in government
Not as politicians, but pink-collar workers (secretaries, receptionists, phone operators)
UNIT 10: THE COLD WAR AND THE CIVIL RIGHTS MOVEMENT
DIFFERENT VALUES OF THE US & THE USSR
the US values
capitalist
democracy
goal: temporary division of Germany, eventually reunited, and to spread democracy throughout war torn Europe
USSR values
communist
goal: Germany stays divided and remains weak, spread communism throughout war torn Europe
US INVOLVEMENT IN THE KOREAN WAR
June 27, 1950
the United States officially entered the Korean War.
The U.S. supported the Republic of Korea (commonly called South Korea), in repelling an invasion from the Democratic People's Republic of Korea (commonly called North Korea)
THE VIETNAM WAR
In December 1960, the National Liberation Front, commonly called the Viet Cong, emerged to challenge the South Vietnamese government.
A civil war erupted for control of South Vietnam, while Hanoi sought to unite the country under its own communist leadership.
The Second Indochina War began in earnest with the US commitment to prevent the communists from overrunning South Vietnam.
In spring 1961, the administration of John F. Kennedy expanded US support for the South Vietnamese government, including an increase in US military advisers, the doubling of military assistance, and authorization of the use of napalm, herbicides, and defoliants.
was the first televised war and was highly unpopular in the states
IMPORTANT TERMS
Truman Doctrine
President Truman’s pledge to help nations struggling against communist movements
Marshall Plan
Foreign policy plan that offered aid to Western Europe after WWII
NATO
Collective security group of the US and its allies
Created to protect from potential threats from the Soviet Union
Warshaw pact
Collective security group of the Soviet Union and its satellite states
Satellite states: independent nations controlled by a more powerful nation
Included all communist states of Eastern Europe except Yugoslavia
Desegregation of armed forces
Executive Order issued by President Harry S. Truman.
Abolished racial discrimination in the United States Armed Forces.
Civil disobedience
a public, nonviolent, conscientious, yet political act, contrary to law, usually done with the aim of bringing about change in the law or policies of the government
“McCarthyism”
Senator Joe McCarthy claimed he knew 205 top officials who were communists
Made baseless claims and accusations
His accusations → jobs lost
Went too far → attacked the U.S. army & held harsh televised hearings
Censured for his accusations
John F. Kennedy
Democrat
Youngest and first Catholic President
Ran against Richard Nixon
Televised Debates helped Kennedy win
Cuban Missile Crisis
In 1962 the Soviet Union began to secretly install missiles in Cuba to launch attacks on U.S. cities.
The confrontation that followed, known as the Cuban missile crisis, brought the two superpowers to the brink of war before an agreement was reached to withdraw the missiles.
closest the two superpowers came to nuclear war
final agreement was that the US would remove their missiles from turkey and then the USSR would remove theirs from Cuba
Lyndon B. Johnson
Vice President Lyndon B. Johnson became president after, finishing the last year of JFK’s term.
President Johnson was faced with a deteriorating situation in Vietnam. Pressured by advisers predicting “disastrous defeat,” intent on proving his and America’s “credibility,” fearful of drawing China and the Soviet Union into the conflict, and passionate about maintaining focus on his “Great Society” initiative,
he planned a course of gradual escalation he hoped would avoid public scrutiny and, hopefully, avoid another Korea.
Even after the Gulf of Tonkin Resolution, Johnson claimed America’s role would continue to be support for South Vietnam mainly through material and advice, which was popular with the American public.
doesn’t run for reelection
Immigration Act of 1965
eliminated the quota system for people from all countries to immigrate to the United States.
Brown v. Board of Education
Said separate is inherently unequal
Public facilities HAD to desegregate
Massive Resistance
movement by southern states to avoid desegregation
School attendance was NOT mandatory
Shut down schools that integrated
Civil Rights Act of 1964
Johnson’s most notable piece of legislation
prohibited discrimination in public places
provided for the integration of schools
made employment discrimination illegal
Faced LOT’s of opposition but was passed!
Voting Rights Act of 1965
prohibited the poll tax, federal government can intervene in state elections to prevent discrimination
UNIT 11: THE MODERN ERA
END OF VIETNAM WAR
Vietnamization
Nixon’s plan to achieve “peace with honor” in Vietnam
gradually turning the responsibility of fighting the war over to the South Vietnamese army.
He started phased withdrawals of US troops and ended the draft in 1973.
in 1973 they signed the Paris Peace Accords, and a cease-fire was called during which American combat support ended.
END OF THE COLD WAR
During 1989 and 1990, the Berlin Wall came down, borders opened, and free elections ousted Communist regimes everywhere in eastern Europe.
In late 1991 the Soviet Union itself dissolved into its component republics. With stunning speed, the Iron Curtain was lifted and the Cold War came to an end.
IMPORTANT TERMS
Nixon
Elected in 1968
Republican
Vietnamization
resigns from the presidency before impeachment about Watergate scandal
Ford
Became president after Nixon stepped down
Pardoned Nixon → Made him seem suspicious
Vietnam falls and Cambodia turns to brutal communist leader
Tried to fix an economic downturn but failed → did not get reelected
Carter
Democrat
Elected because he was an “outsider to Washington”
Had a humanitarian focus in his foreign policy
hostage crisis
Reagan
D.A.R.E. programs to fight war on drugs
Slashed Welfare programs , Environmental protection, and business regulations programs
Failure to respond to AIDS Epidemic → called the “gay plague” by Moral Majority supporters
SDI/ “Star Wars” - massive spending on anti-missile defense
Iran-Contra - sold weapons to Iran and then diverted funds to Contra’s in Nicaragua
“Mr. Gorbachev, tear down this wall!”
Pressure on the USSR
H.W. Bush
Persian gulf war
republican
Clinton
President (1992-2000) impeached in office due to lying under oath (perjury) and obstruction of justice - Monica Lewinsky Scandal
Bush
Vice President to Reagan, he took over from 1988-1992 and continued many of the conservative reforms being pushed.
Obama
democrat
President that promised "Hope and Change”
was elected in 2008
signed the Affordable Care Act.
Sandra Day O’Connor
first female Supreme Court Justice
appointed by Reagan
Clarence Thomas
appointed by H.W. bush
controversial because of sexual harassment claims
SALT
First attempt to reduce tensions with the USSR
agreement between the US and the USSR to remove their ballistic missiles
Detente
the relaxation of strained relations
Nixon pursued this policy to relations with the Soviet Union
Fall of the Berlin Wall
symbolized the end of the cold war
9 November 1989
helped with the reunification of Germany
Watergate
Scandal where documents were trying to be stolen from the Democratic National Convention that led to Nixon stepping down
Impeachment (Clinton)
Bill Clinton was impeached by the House of Representatives on two charges, one of perjury and one of obstruction of justice, on December 19, 1998.
Iran Hostage Crisis
Resenting America for helping the Shah of Iran and backing Israel, Iranian students seized the staff at the US Embassy (1979)in Tehran, Iran and held them hostage for more than a year (444 days)
No Child Left Behind
requiring schools to demonstrate their success in terms of the academic achievement of every student
Moral Majority
sought to mobilize conservative Americans to become politically active on issues they thought were important.
Reaganomics
INCREASE defense spending; tax cuts & supply side economics
Disability Rights Movement
The Rehabilitation Act of 1973 prohibits discrimination on the basis of disability in federal programs and by recipients of federal financial assistance.
Took until 1990’s to prohibit discrimination based on disability and ensure that children with disabilities received an equal education
Roe v. Wade
Texas woman challenged a law that made abortion illegal except by a doctor’s orders to save a woman’s life.
Went against her right of personal privacy
9/11
an Islamist extremist group named al-Qaeda, attacked on the morning of September 11, 2001.
their affect was killing 93 nations, 2,753 in New York, 184 at the Pentagon, and 40 people at Flight 93.
Al-Qaeda hijacked four commercial planes.
Two crashed into the Twin Towers, one into the Pentagon, and the passengers in Flight 93 fought back and crashed into an empty field. It was known to be headed to Washington DC.
War in Iraq
U.S. forces invaded this country because it was feared Saddam Hussein was hiding WMD’s