Copy of 10.3 The Hormones of the Pancreas.docx
The Hormones of the Pancreas
The pancreas has exocrine and endocrine functions.
Exocrine: secrete digestive enzymes that break down nutrients in the small intestine.
Endocrine:
- Insulin
- Glucagon
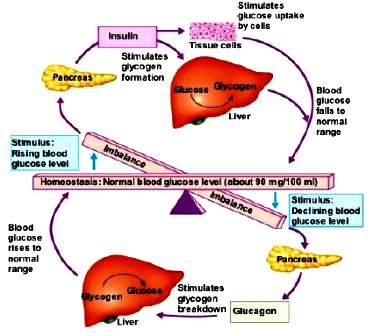
An increase in blood sugar will cause the beta cells (islets of Langerhans) to secrete insulin into the blood which stimulates glucose uptake from the blood into tissue cells and the conversion of glucose into glycogen in the liver.
When blood sugar levels are low, alpha cells stimulate the release of glucagon. Glucagon causes the liver to break down glycogen into glucose and release into the blood. Glucagon, cortisol, hGH, and epinephrine all contribute to increasing blood glucose levels.