quiz 1
photosynthesis converts light energy into chemical energy
solution w pH of 6 has ten times the [H+] as pH 7 solution
N TERMINUS TO C TERMINUS - naming
molar absorptivity, also known as the extinction coefficient of the sample. It is a unique physical constant of the chemistry of the sample that relates to the sample's ability to absorb light at a given wavelength.
aromatic AA: trp, tyr, and phe can absorb UV light
What limits the size of a functional cell?
Min based on number of necessary molecules, max based on rate of diffusion
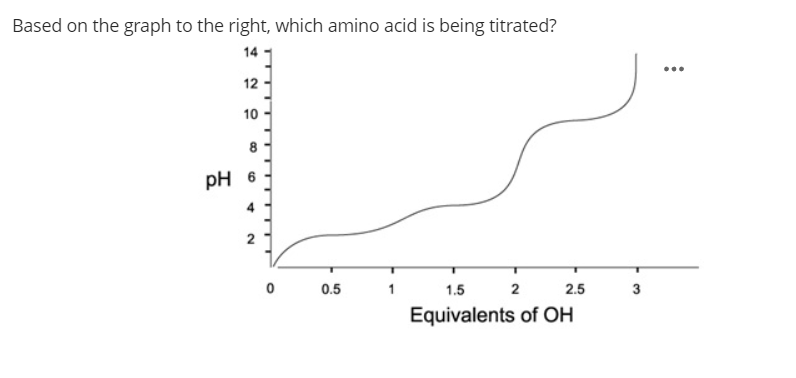
The first thing to notice here is that three equivalents of OH were added. We know that all amino acids will have one pKa around 2 and another around 9 from the carboxylic acid and amine groups on their backbone, so the fact that this one has three equivalents of OH added to overcome three plateaus in the pH curve shows that there's an additional acidic hydrogen on the side chain
The 2 and 9.5 are what we expect to see from the backbone, which leaves a pKa of 4 for the side chain.
Which of the following compounds are capable of hydrogen bonding with like molecules?
A molecule can form hydrogen bonds if it has a hydrogen atom directly bonded to a highly electronegative atom like oxygen (O), nitrogen (N), or fluorine (F); essentially, look for a molecule with an "O-H", "N-H", or "F-H" bond, which allows it to interact with lone pairs on another molecule containing O, N, or F atoms.
The function of mitochondria is to produce ATP through cellular respiration.
The central dogma of molecular biology describes the flow of genetic information in a cell. It states that DNA is transcribed into RNA, and RNA is translated into proteins.
quiz
q1
Calculate the pH of a buffer that is 0.225 M HA and 0.162 M A-. The Ka for HA is 1.8 × 10-5.
pKa=−log(Ka)
Ka=−log(1.8×10−5)≈4.74
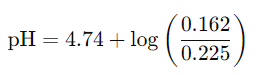
= 4.60
q2
Saline solution has an osmotic pressure of approximately 7.84 atm at 37ºC (310 K). This is considered to be isotonic compared to your red blood cells. If a potassium chloride solution has a concentration of 0.100 M, would this solution be isotonic, hypotonic, or hypertonic at 37ºC? What effect would you expect the solution to have on your red blood cells? R = 0.08206 L·atm/mol·K
Π=i⋅M⋅R⋅T
7.84 = 2 x M x 0.08206L·atm/mol·K x 310 K
M = 0.154 concentration (saline solution)
so the potassium chloride solution is less concentrated than the saline solution (which is isotonic to red blood cells), meaning that the red blood cells contain more particles so water would enter the cell
potassium chloride is hypotonic to red blood cells
Given the (rounded) pKa values for the amino acid histidine, estimate its net charge under the following conditions:
Histidine has three ionizable protons with approximate pKa values of 2, 6, and 9.
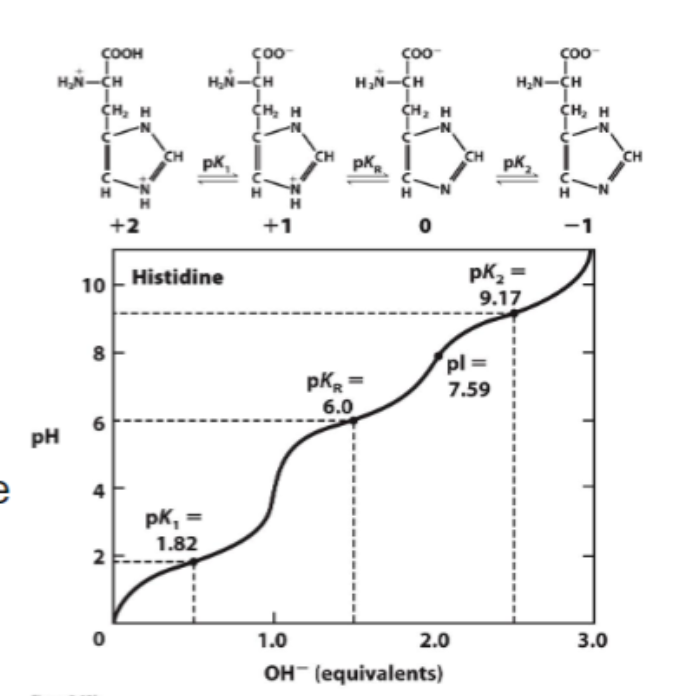
pH 0 :
pH 0:
Carboxyl group: neutral (0)
Imidazole group: positively charged (+1)
Amino group: positively charged (+1)
Net Charge = +2
pH 4:
Carboxyl group: negatively charged (–1)
Imidazole group: positively charged (+1) (still protonated)
Amino group: positively charged (+1)
Net Charge = +1
pH 7.5:
Carboxyl group: negatively charged (–1)
Imidazole group: neutral (0) (partially deprotonated)
Amino group: positively charged (+1)
Net Charge = 0
pH 11:
Carboxyl group: negatively charged (–1)
Imidazole group: neutral (0)
Amino group: neutral (0)
Net Charge = –1
Which of the following statements is FALSE regarding the structure of each of the example proteins?
Silk fibroin is composed almost exclusively of β-strands.
Collagen and α-keratin are both examples of coiled coils.
Myoglobin is used for oxygen storage.
Collagen makes up the hard structures in mammals, such as horns, nails, hair, and hooves.
Myoglobin is a soluble, globular protein.
A biochemist is interested in studying the dynamic movements of the three-dimensional structure of a protein in solution. Select from the experimental techniques that we discussed in class, the most suitable to gather such information and briefly explain your choice.
NMR spectroscopy