Cell Biology
Cell structure
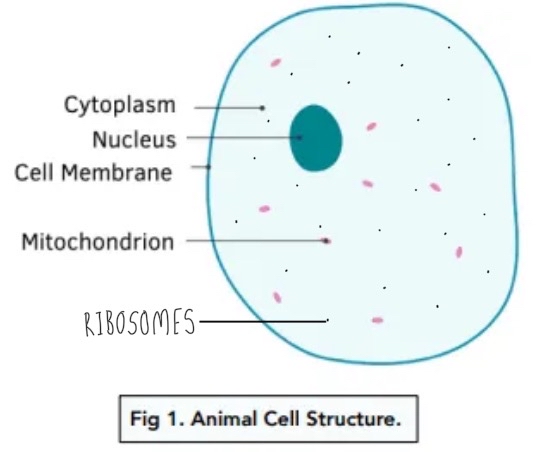
Animal cells:
Nucleus → contains genetic material
Mitochondria → releases energy
Ribosomes → protein synthesis (triple only)
Cell surface membrane → partially permeable to allow only certain substances to enter the cell
Cytoplasm → site of chemical reactions within the cell
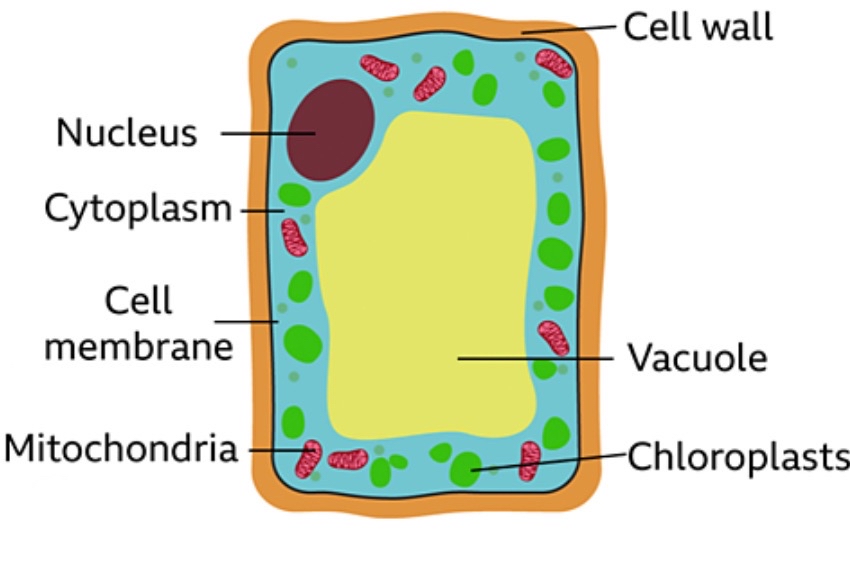
Plant cells :
Chloroplasts → contain chlorophyll which absorbs sunlight for use in respiration
Permanent vacuole → contains cell sap
Cell wall → strengthens the cell
Bacterial cells - Bacterial cells are known as prokaryotic cells unlike plant and animal cells which are both eukaryotic
Prokaryotic are much smaller than eukaryotic cells
Prokaryotic cells have fewer organelles, they typically have only cytoplasm and ribosomes
In prokaryotes DNA is free floating in the cytoplasm and additional DNA can be found in plasmids which are circular rings of DNA
Prokaryotic cells divide by binary fission
Magnification equation
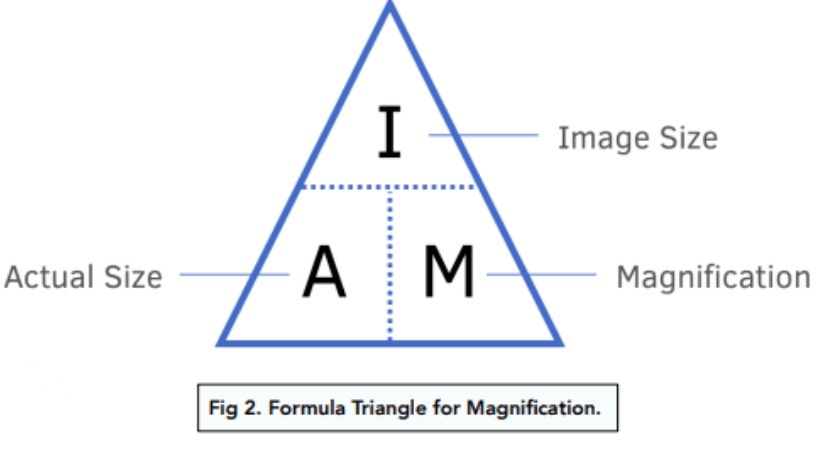
To manipulate the equation cover the section you are trying to find and multiply or divide the other two numbers
Magnification does not have units however image size and actual size will often be measured in either mm or micrometers and it is important to know how to convert between the two
Microscopes
What are the differences between light microscopes and electron microscopes?
Light microscope | Electron microscope |
|---|---|
Cheap and easy to use | Expensive |
Lower magnification | Higher magnification |
Lower resolution | Higher resolution |
Magnification → How many times bigger the specimen is
Resolution → Ability to distinguish between two separate
points
Specialisation and differentiation
What specialised cells do we have as humans
Type of cell | Where is it found/Function | How is it adapted? |
Red Blood Cell | Blood - moves oxygen around body | Biconcave shape, no nucleus |
Sperm cell | Testes - reproduction | Many mitochondria, tail, enzymes to digest membrane of egg cell |
Egg cell | Ovaries - reproduction | Nutrients for growth, haploid nucleus |
Nerve cell | Everywhere - send messages around body | Long and thin (can carry messages fast and far), branched connections at each end, fatty sheath surrounding them |
Ciliated cell | Airways - prevent infection | Tiny hairs which move mucus |
Villi | Intestines - better at diffusion | Large surface area, thin, good blood supply |
What types of specialised cells do plants have
Type of cell | Where is it found/Function | Adaptations |
Root hair cell | Roots of plants - absorb water and minerals | have tiny hairs that increase surface area |
Palisade cells | Leaves - site of photosynthesis | Top of leaves, lots of chloroplasts |
Xylem | Inside stem - carry water and mineral ions | Dead cells, thick cell walls |
Phloem | Inside stem - carry sugars | Living cells, companion cells (which have lots of mitochondria |
What is cell differentiation?
Cell division
The nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA, each chromosome is made from a single molecule of DNA . A section of a chromosome is called a gene.
Chromosomes are found in pairs
Humans have 23 pairs or 46 individual chromosomes, the 23rd pair of chromosomes are the sex chromosomes
Females have two X chromosomes
Males have one X and one Y chromosome
THE CELL CYCLE:
Cell grows
DNA synthesis
More growth and DNA is checked for errors
Mitosis
Cytoplasm separates and two cells are formed
What happens in mitosis?
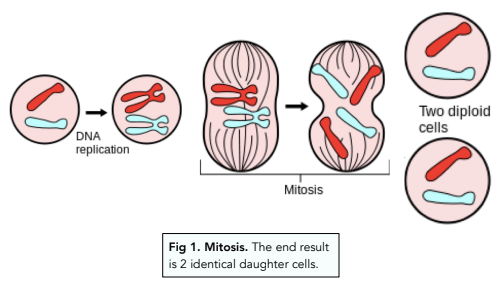
The DNA replicates and forms copies of the chromosomes
The chromosomes line up in the centre of the cell
Chromosomes are pulled to each end of the cell
Cell membrane divides forming two cells
In mitosis two daughter cells are produced, these cells are known as daughter cells and are identical to the parent cell
Stem cells
Stem cells are unspecialised cells otherwise known as cells that have not undergone differentiation, embryonic stem cells can be found in embryos and they can differentiate into any type of cell. Adult stem cells are limited and only found in certain areas of the body, adult stem cells can only differentiate into related cell types
Cell division in plants occurs in the meristem, cells in the meristem can produce all types of plant cell at any time during the life of the plant.
Meristems are located in roots and shoots of plants
Transport
for information on transport find other note on my account titled : transport