Hunger notes
Hunger and Thirst
Introduction
Fundamental Needs for Survival:
Hunger and thirst.
Israel Kamakawiwoʻole - ‘Izzy’
Career Overview: Iconic cover of ‘Somewhere Over the Rainbow’, reached #1 on the German singles chart in 2010.
Honors: Hawai'i State Flag flown at half-staff at his funeral, a unique honor for a private citizen.
Physical Struggles: Struggled with obesity, weighing up to 757 pounds.
Death: Passed away at age 38 from heart failure in 1997.

Homeostasis and Thirst Mechanisms
Negative Feedback Systems
Definition: Main mechanisms for homeostasis.
Behavioral Response: Actions like eating and drinking occur when deviating from a set point.
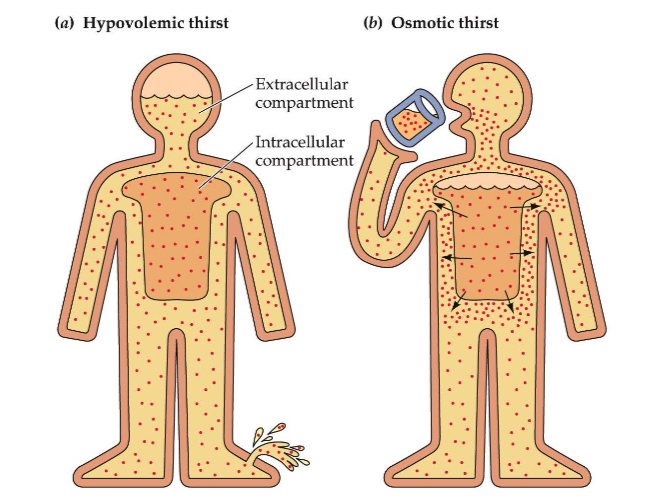
Thirst Types
Osmotic Thirst: Triggered by high extracellular solute concentration.
Hypovolemic Thirst: Triggered by low extracellular/intravascular volume.
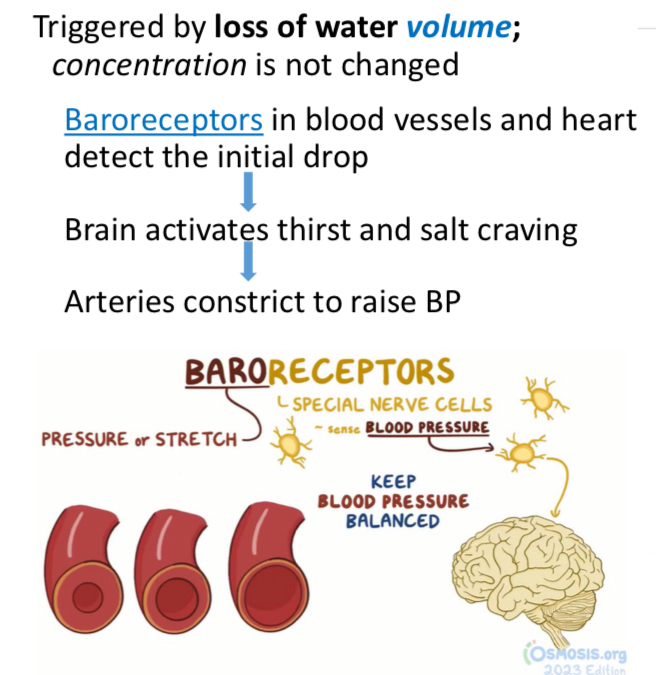
Mechanisms of Hypovolemic Thirst
Detection: Baroreceptors in blood vessels and heart sense decreased water volume.
Response: Brain activates thirst and salt craving; arteries constrict to elevate blood pressure.
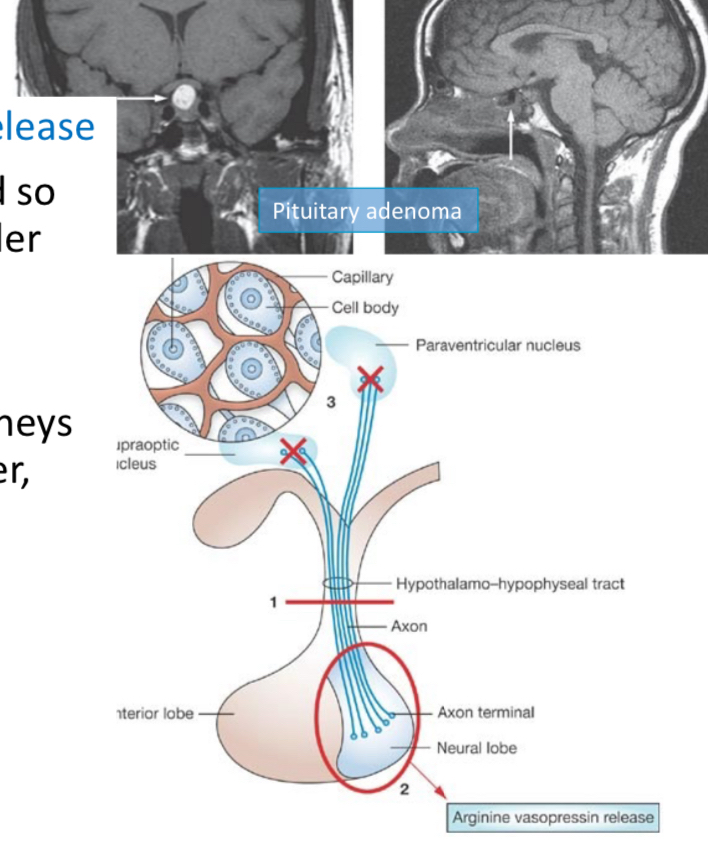
Hormonal Response
Vasopressin: Released during hypovolemia; constricts blood vessels and reduces urine output.
Angiotensin Cascade Process: Low blood volume triggers renin release from kidneys, producing angiotensin II, causing blood vessel constriction and stimulating drinking.
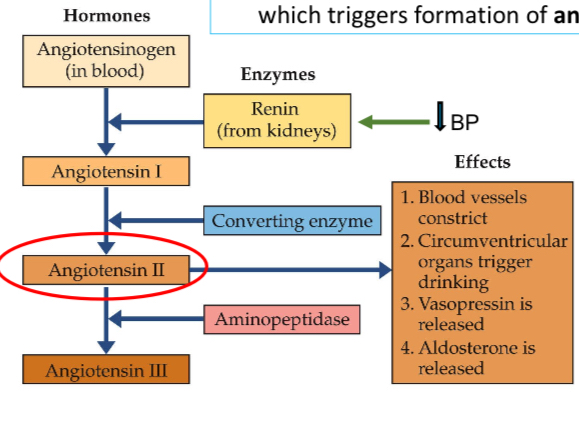
Brain Control of Drinking
Mechanism: Angiotensin II acts in the subfornical organ, signaling brain areas for drinking behavior.
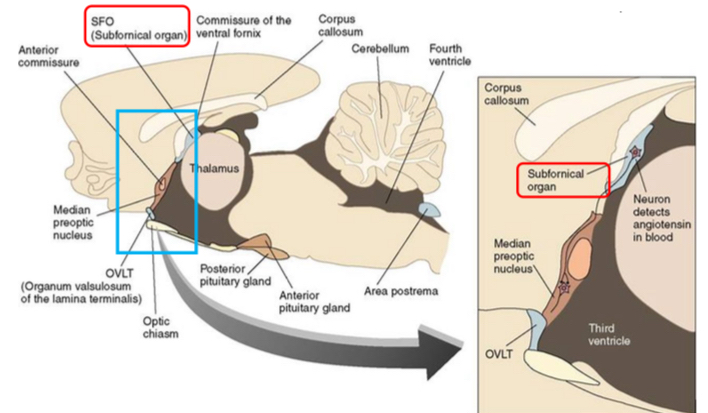
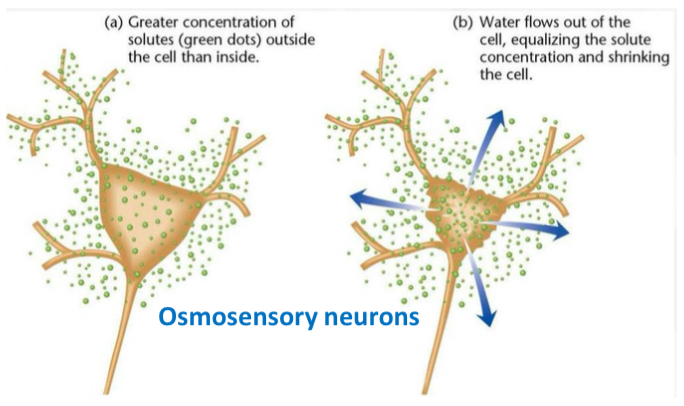
Osmotic Thirst Mechanism
Process: Osmosensory neurons in the anterior hypothalamus respond to increased blood osmotic pressure. Na+ channels open as membranes shrink; neurons activate pituitary to release ADH.
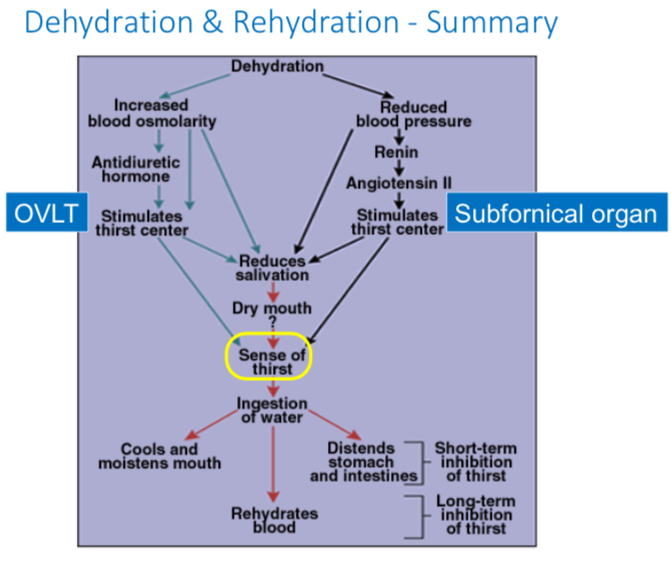
Dehydration & Rehydration Summary
Increased blood osmolarity prompts ADH release, leading to thirst and dry mouth. Drinking water rehydrates blood and reduces salivation.
Hunger Awareness
Cultural Quotations: Complexities of managing hunger.
Dieting Challenges
Metabolism Adjustment: Energy expenditure declines when dieting, reducing basal metabolic rate (BMR). Longevity studies show restricted food intake may benefit rats but are uncertain for humans.
Obesity and Metabolism
BMR: Energy needed for basic functions, comprising 75% of daily energy for sedentary students; genetics also play a role.
Energy Storage and Utilization
Primary Energy Source: Glucose; glycogen serves as short-term storage.
Metabolic Rate Insights: Peaks in infancy, slows in youth, stabilizes until age 60, then declines.
Food Intake Regulation
Neurotransmitter Influences: Brain signals (NPY, a-MSH) regulate hunger and satiety, influenced by hormones and nutritional status.
Leptin and Ghrelin
Leptin: Produced by fat cells; informs the brain about body fat. Resistance leads to obesity.
Ghrelin: An appetite stimulant, elevated during fasting, low post-eating; dysregulated in Prader-Willi syndrome.
Hypothalamus and Appetite Control
Dual Functionality: Two neuron types exist; one stimulates appetite (NPY/AgRP) and the other inhibits it (POMC/CART).
Obesity Effects on Brain
Consequences of Overeating: Leads to hypothalamic inflammation, inhibiting neurogenesis and resetting hunger signals.
Eating Disorders
Anorexia Nervosa
Criteria: Refusal to maintain body weight, intense fear of weight gain; highest mortality rate among psychiatric disorders.
Bulimia
Criteria: Characterized by recurrent binge eating and inappropriate behaviors to counter it.
Co-occurrence with Other Disorders
High anxiety and depression rates associated with anorexia and bulimia; significant suicide rates among afflicted individuals.
Children and Eating Disorders
Survey reveals concerning rates of dieting and disordered eating behaviors among students in grades 5 to 8.
Treatment of Obesity (Effective Strategies)
Eating Habits:
Creating a caloric deficit of 200 calories/day requires lifestyle changes and monitoring.
Exercise:
Engaging in more than 200 minutes of strenuous aerobic activity weekly is effective combined with dietary changes.
New Drug Treatments
GLP-1 receptor agonists: Drugs like Mounjaro and Ozempic show significant long-term weight loss effects by modulating appetite and metabolic responses.
 Knowt
Knowt