Unit 2: Organisation of the organism
Fundimentals of Bio
Cells are the building blocks of life
Cell is the common basic structural and functional unit of living beings.
Robert Hooke discovered cells in @@1665@@
Two Different Types of Cells :
| Multicellular | Unicellular |
|---|---|
| Many cells group together in a single body and assume different functions in it to form various body parts (Division of Labor). Example - fungi, plants and animals. | In unicellular organisms, all function are carried out by the single cell. Example - Chlamydomonas, paramecium bacteria. |
M.J. Schleiden and Theodore Schwen @@(1838-39)@@ first formed a theory “All plants and animals are composed of cells and cell is the basic unit of life”.
Later was changed in @@1885@@ R.Virchow changed it to “all cells arise from pre-existing cells”
Electron Microscope was discovered in @@1940@@
Different cells have different shapes depending on their functions
- Columnar - Epithelial cells
- Circular biconcave - RBCs
- Spindle shaped - Smooth muscle cells
- Oval - Ovum/egg cells
- Irregular - Ameba
- Branched - Nerve cells
- Spiral - Spirillum bacteria
- Rectangular - cells of spirogyra
- Rod shaped - Bacillus Bacteria
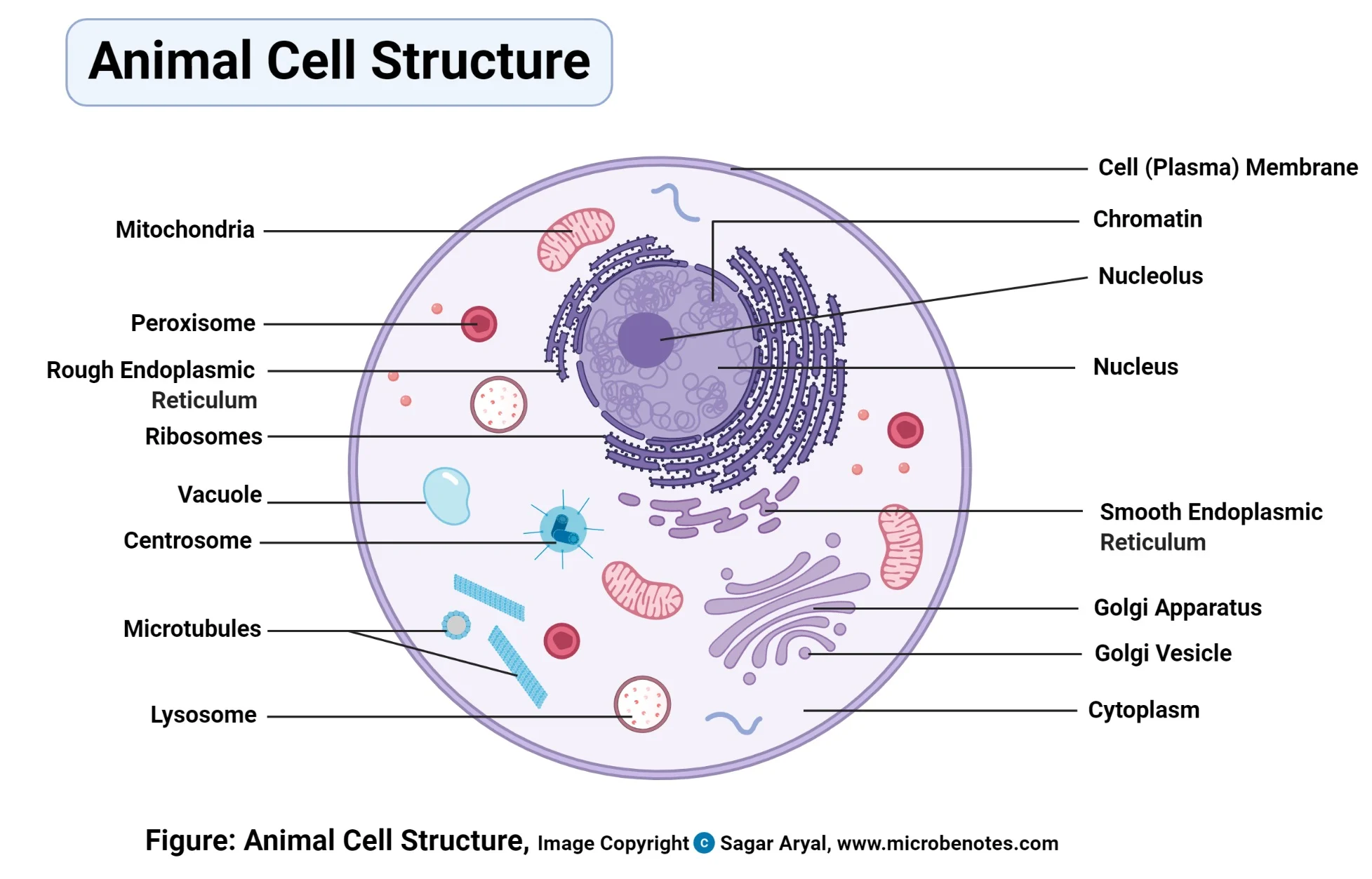
Cell Structure
Cell Walls (only in plants)
Plasma Membrane
Cytoplasm
Cell Organelles
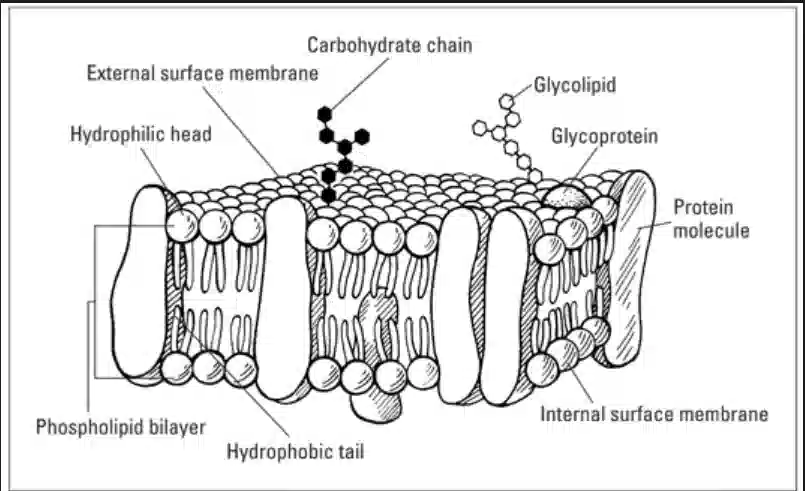
Cell Organelles: Plasma Membrane
- It is the thin outer covering of a cell.
- It separates the contents of the cell from external environment.
- The plasma membrane is flexible and is made up of organic molecules called lipids and proteins.
- The plasma membrane allows the entry and exit of some materials in and out of the cells
- It also prevents the movement of some other materials.
- Therefore, the @@plasma membrane is called as a selectively permeable membrane.@@
- [[For e.g. when the concentration of CO2 inside the cell increases, the CO2 moves outside of the cells by diffusion.[[
- [[Similarly when the concentration of O2 inside the cell decreases the O2 moves from the outside to inside of the cell.[[
- Plasma membrane also helps in the transport of water in out of cells.
Osmosis and diffusion in cells
Osmosis -
Movement of water from Higher concentration to lower concentration thru plasma membrane
It is a pure mechanical process (which doesn’t require energy)
Diffusion -
IS the net movement of molecules
Isotonic solution -
Medium surrounding the cell has same water concentration as that of the cells. NO EXCHANGES OF WATER. In this case there is neither entry of water in the cell nor exit. So the cell remains %%Flaccid%%. (flaccid - not hard or firm)
Hypotonic Solution -
Medium surrounding the cell has higher water concentration that that of the cell. I.E. outside solution is very dilute in this case water moves inside the cell.
Water enters → Inside cell → swells up
So cell become turgid.
(Turgid - Swollen)
Hypertonic Solution -
Medium surrounding the cell has lower water concentration than that of the cell. I.E. outside solution is very concentration so cell becomes plasmolysed
Water comes → outside cell → shrinks up (Plasmolysis)