SQL Guide: Getting Started
Query — a request for data or information from a database
Basic Structure of a SQL query
SELECT
[choose the column(s) you want] #2
FROM
[from the appropriate table] #1
WHERE
[a certain condition is met] #3
Numbers next to description is suggested order in which you would write your SQL queries.
SELECT — choose the columns you want to return
FROM — choose the tables where the columns you want are located
WHERE — filter for certain information
Example of a Query
SELECT first_name
FROM customer_data.customer_name
WHERE first_name = 'Tony'The above query uses three commands to locate the customers with the first name, Tony.
SELECT the column name first_name
FROM a table named customer_name (in a dataset named customer_data) (The dataset name is always followed by a dot, and then the table name.)
But only return the data WHERE the first_name is 'Tony'
Result:

Multiple Columns in a Query
If requesting multiple data fields from a table:
SELECT
ColumnA,
ColumnB,
ColumnC
FROM
Table where the data lives
WHERE
Certain condition is metExample of how it would appear:
SELECT
customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
FROM
customer_data.customer_name
WHERE
first_name = 'Tony'The above query uses three commands to locate customers with the first_name, 'Tony'.
SELECT the columns named customer_id, first_name, and last_name
FROM a table named customer_name (in a dataset named customer_data) (The dataset name is always followed by a dot, and then the table name.)
But only return the data WHERE the first_name is 'Tony'
Another example:
SELECT
ColumnA,
ColumnB,
ColumnC
FROM
Table where the data lives
WHERE
Condition 1
AND Condition 2
AND Condition 3Example of how it would appear:
SELECT
customer_id,
first_name,
last_name
FROM
customer_data.customer_name
WHERE
customer_id > 0
AND first_name = 'Tony'
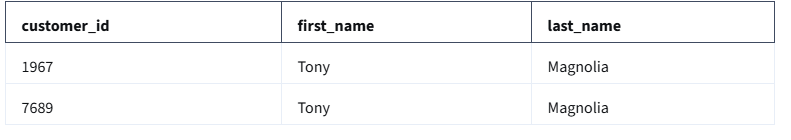
AND last_name = 'Magnolia'The above query uses three commands to locate customers with a valid (greater than 0), customer_id whose first_name is 'Tony' and last_name is 'Magnolia'.
SELECT the columns named customer_id, first_name, and last_name
FROM a table named customer_name (in a dataset named customer_data) (The dataset name is always followed by a dot, and then the table name.)
But only return the data WHERE customer_id is greater than 0, first_name is Tony, and last_name is Magnolia.
Results:
If only one customer is named Tony Magnolia, the results from the query could be:
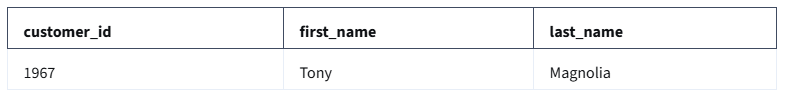
If more than one customer has the same name, the results from the query could be: