Ch.2
2.1- The Atomic Theory:
Democritus and other early Greek Philosophers described that the world is made up of tiny particles called atomos
Dalton Atomic Theory: created by John Dalton
Each element is composed of small particles called atoms
All the atoms of a particular element are the identical
- Atoms of one element are different from an atom of another element
Atoms of one element cannot be changed into atoms of a different element by chemical reactions
- Atoms are neither created nor destroyed in chemical reactions
Compounds are formed when atoms of one or more element combine
Dalton’s theory also explained several laws of chemical combustion:
- Law of constant composition: In a given compound, the relative numbers of kinds of atoms are constant.
- Put in simpler terms- in a particular chemical compound, all samples of that compound will have the same elements in ratio.
- Example: Water will always be h2O. Any water sample will always have two hydrogen atoms and one atom of oxygen in a 2:1 ratio.
- Law of conservation of mass: The total mass of materials present in a chemical reaction before and after a chemical reaction is always the same
- Mass is not lost
- Both sides of the equation should be balanced
- Law of multiple proportions: If two elements combine to form more than one compound, the masses of the two compounds are in the ratio of small whole numbers
- Put in simpler terms: If two elements such as hydrogen and oxygen combine to form more than one compound like h2O (water) and H2O2 (hydrogen peroxide). The ratio is 2:1 and 1:1. (The ratio is always in small whole numbers)
2.2- The Discovery of Atomic Structure:
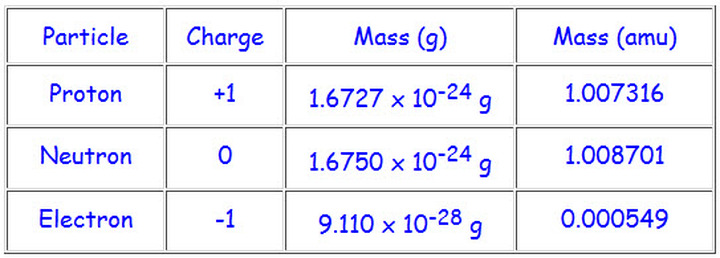
Atom is composed of subatomic particles
- Neutral- present in the nucleus- no charge
- Proton- present in the nucleus- 1+ charge
- Electron- present in the orbit- 1- charge
*Particles with the same chargers repel; particles with opposite charges attract*
Cathode Rays: radiation produced between electrodes when a high voltage is applied to electrodes in a glass tube
- cathode rays originate at the negative electrode and then travel to the positive electrode
- Scientist J.J Thompson described cathode rays as streams of negatively charged particles that we know call electrons.
- In simple terms cathode rays are streams of electrons
Electrode: element or semiconductor that emits or collects electrons
Radioactivity: spontaneous emission of radiation
Types of radiation:
- alpha (α)- consist of fast- moving electrically charged particles, positive charge (2+)
- beta (β)- consist of fast- moving electrically charged particles, high speed electrons that are radioactive, have a negative charge (1-)
- gamma (γ)- High energy electromagnetic radiation (similar to x rays), no charge and no particles
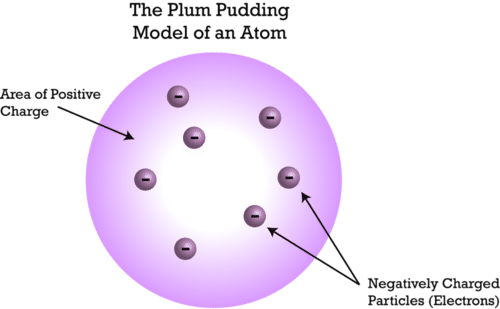
Thompson proposed that atom is an uniform sphere with evenly distributed mass and electrons embedded like seeds in a watermelon
- This was also called the plum pudding model
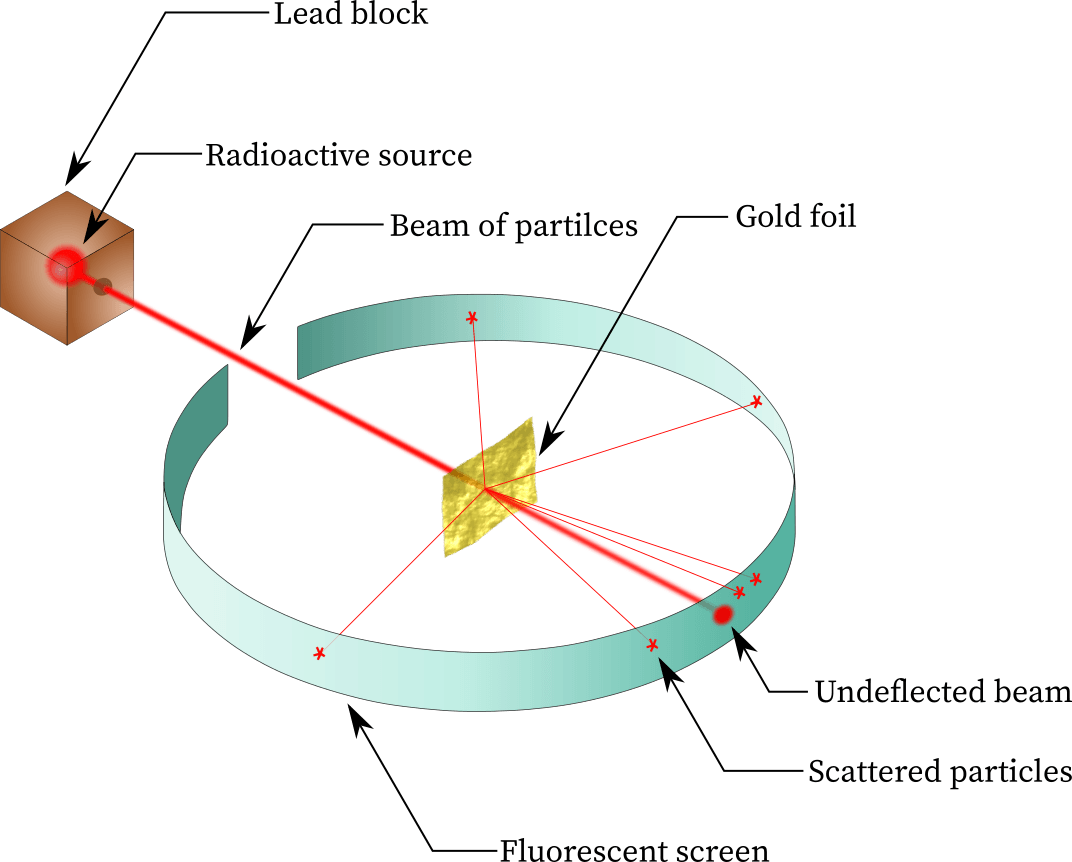
In 1910, Rutherford performed experiments by shooting a beam of α particles through a thin sheet of gold foil and recorded where the α particles hit. He concluded that the majority of the atom was empty space because almost all the particles shot straight through with out deflection
Rutherford explained the results of the experiment by creating the nuclear model of an atom: most of the mass and the positive charge of the atom lies in a dense region called the nucleus.
He also said that the electrons orbit around the nucleus
Further experiments lead to the discovery of protons(Rutherford) and neutrons(Chadwick)
2.3- The Modern View of Atomic Structure:
Electron Charge is -1.602 × 10^-19
Proton Charge is +1.602 × 10^-19
*Every atom has equal number of protons and electrons and therefore has no net electric charge*
atomic mass unit (amu): since atoms have such incredible small masses to make it easier for us to understand 1 amu = 1.66054 * 10^-24 g
 Protons determine which atom is which
Protons determine which atom is which
Each atom has a distinct number of protons
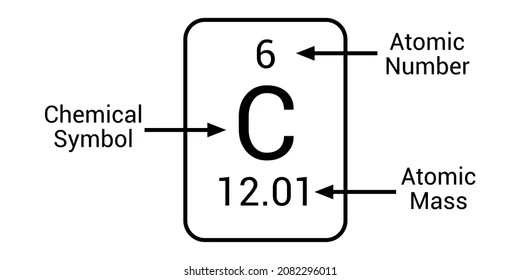
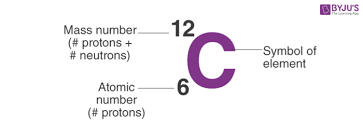
Number of protons determine the atomic number of an element.
- Since atom has no net charge, the number of protons = electrons in an atom
 Atoms in an element can differ in the number of neutrons forming an isotope
Atoms in an element can differ in the number of neutrons forming an isotopeFor example, the element carbon has 6 protons and 6 neutron having the atomic making the mass number(number of neutrons + protons) of 12
- Carbon-14 is an isotope of carbon with 6 protons and 8 neutrons and therefore has a mass number of 14
2.4: Atomic Weights:
Atomic weight is the average atomic mass of all the element’s isotope.
Example: naturally occurring carbon is composed of 98.93% carbon -12 and 1.07% carbon 13. The mass of carbon-12 is 12amu and the mass of carbon-13 is 13.00335amu
- The atomic weight of carbon is:
- (0.9893)(12) + (0.0107)(13.00335)=12.01amu
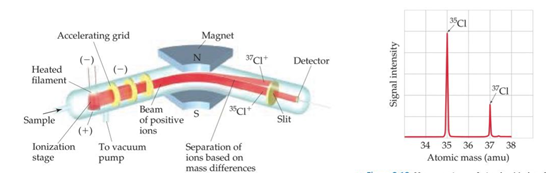
Mass spectrometer is used to accurately determine the atomic weight
- Steps for a mass spectrometer:
Get atoms or molecules in gas phase (by means such as heating)
Gas phase is converted to cations that are positively charged particles
Accelerated towards a negatively charged grid
Ions pass through the grid and encounter two slits which only allow narrow beam of ions to pass
The beam passes through between poles of a magnet causing the ion beam to curve
- the more massive the ion the less the deflection
Ions are separated by mass
The mass spectrum-- graph of the intensity of the detector signal vs. ion atomic mass
- mass spectrum shows the mass of ions as well as their relative abundance
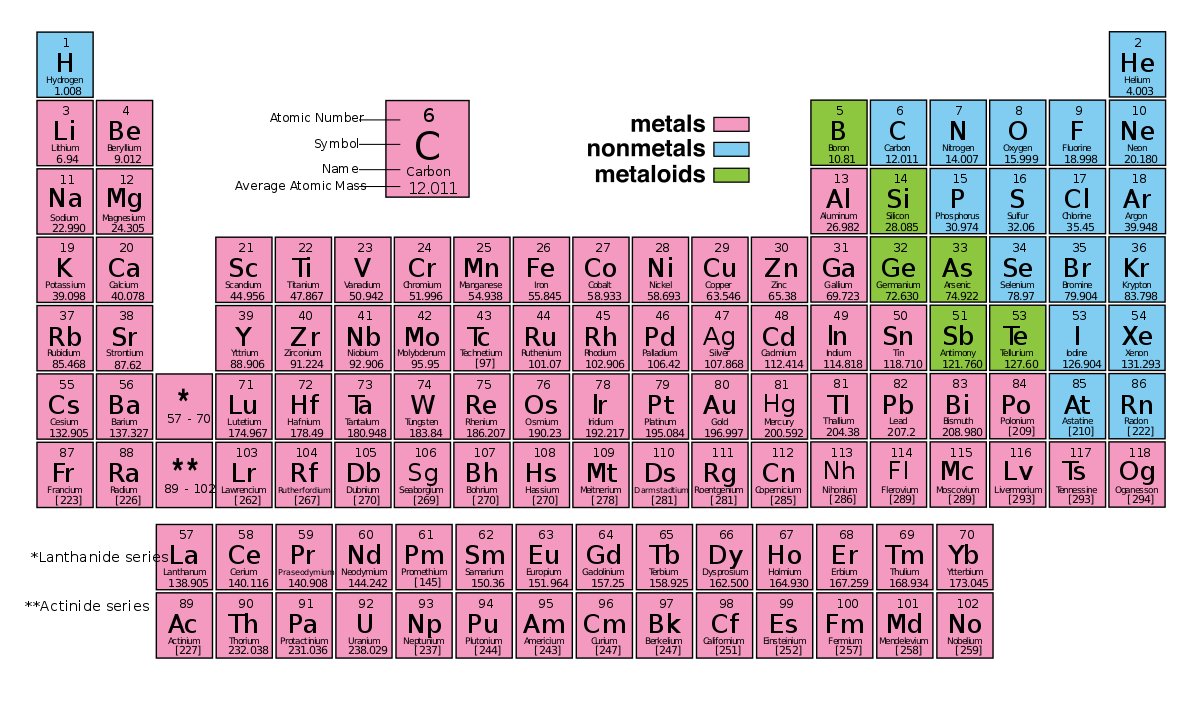
2.5: The Periodic Table
Shows patterns of repetition
- soft reactive metal comes immediately after one of the non- reactive metals.
Horizontal rows are called periods.
Vertical columns are groups
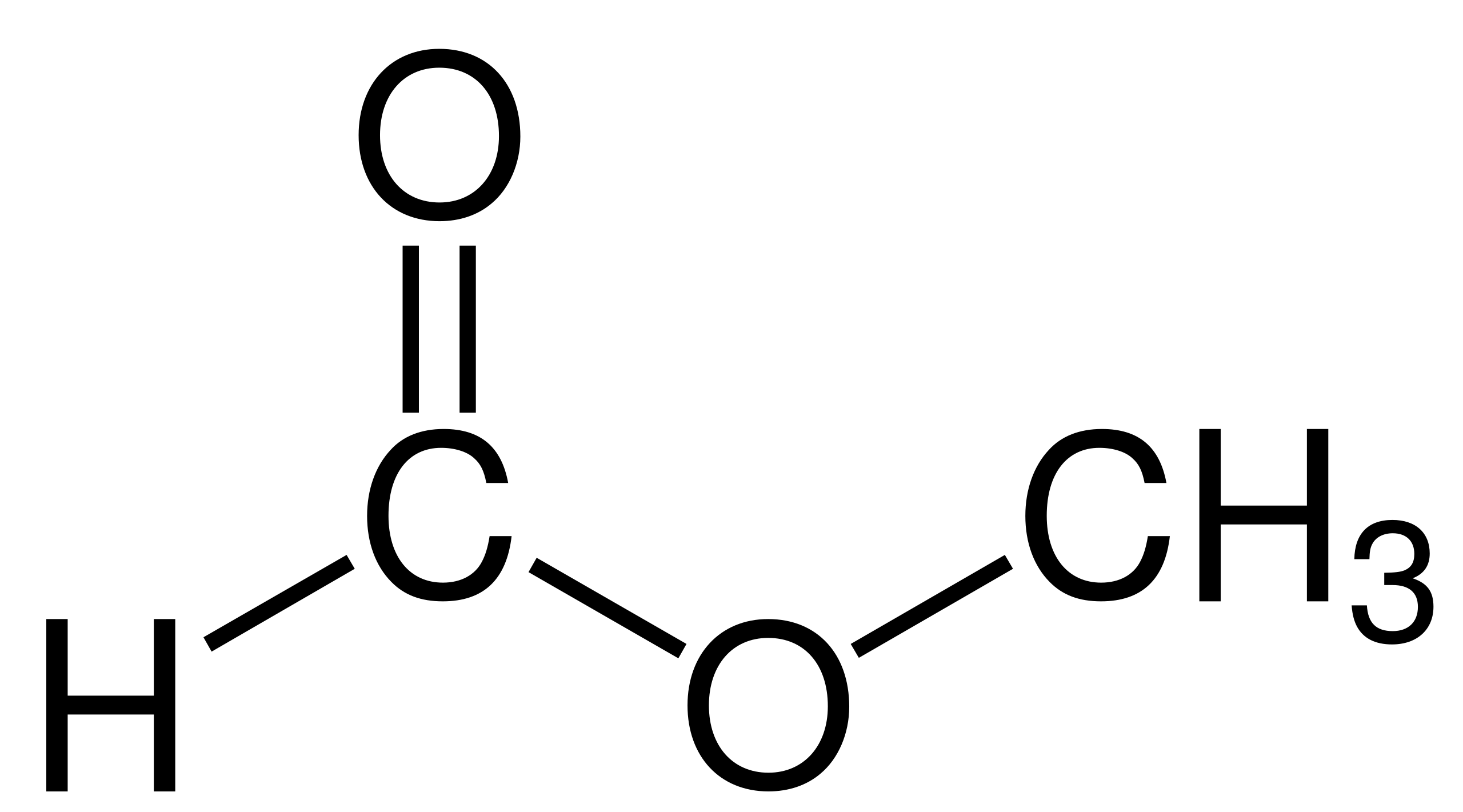
2.6: Molecules and Molecular Compounds
Chemical formula-- tells us how many of each atom is present
- Glucose= C6H12O6
Empirical formula-- give the relative number if atoms
- Glucose= CH2O
Molecular compounds are composed of molecules containing more than one type of atom
Structural formula-- shows how a substance’s atoms are joined together.
2.7: Ions and Ionic Compounds
If electrons are removed or added to an atom, the charged particle is called an ion
- The number of protons ALWAYS remains the same
- Ion with a positive charge (less electrons than protons; electrons were removed) are called cations
- Ion with a negative charge (more electrons than protons; electrons were added) are called anions