Marketing Exam 2
Key concepts to review include market segmentation, targeting strategies, and the marketing mix (4Ps).
Be prepared to analyze case studies and apply theoretical frameworks to real-world scenarios.
What is a Market?
Requirements of a Market
Must need or desire a particular product
Must have the ability to purchase the product
Must be willing to use their buying power to purchase the product
Must have the authority to buy the product
Segmentation
Taking a heterogeneous market and breaking it down into smaller homogeneous markets
Targeting Strategies
Total Market Demand vs Segment Demand
LOOK AT SLIDES
You are able to look individually at the demand versus the whole demand of every product as one
Value of Segmenting and Targeting
Better understand needs, desires and motives of consumers
Better understand why they buy or do not buy
Ability to assess competitive strengths and weaknesses
Ability to identify the promotional message to use
Specialization vs Generalization
Vodka made in America is all the same due to regulations
Targeting
How much are you willing to pay for a good mattress?
$100 or $1000
Selecting a target market to serve
Differentiated Targeting Strategy
Demographic Segmentation
Describe the observable characteristics of individuals living in the culture
Include: physical traits such as gender, age, race; Occupational-related traits such as education; and location related traits
The Phoenix Suns
Segmentation Strategy
Geographic segmentation for ticket sales
Geodemographic Segmentation
Clusters based on zip Code areas and even neighborhoods
Psychographic, Behavioralistic & Benefit Segmentation
Psychographic => personality characteristics, motives, and lifestyle
Behavioralistic => heavy, moderate, light
Benefit Segmentation
Prioritizing Target Segments
Capabilities of the Organization
Size and Growth Potential of the segment
Competitive field
Market niche
Consumer Behavior
The complex process by which individuals acquire, use and dispose of products or services to satisfy their needs and desires
Involvement
Personal Relevance
Buying candy vs buying a house
High Involvement
Low Involvement
Consumer Decision-Making Processes
Central Route (High involvement processing)
Beliefs => Attitude => Behavior
Looking at high quality reasons
Research
Peripheral Route (Low-involvement)
Beliefs => Behavior => Attitude
Shallow reasons
Not a lot of research
BEHAVIOR IS BUYING IT
Five Stage Process
Problem (need) Recognition
Search
Alternative Evaluation
Choice
Post purchase Evaluation
Information Search
Internal Information
What you already know
External Information
Research
Talk to others
Evaluation of Alternatives
Consideration set
All brands that you would consider buying
Cost in time and money
What is it going to cost me to find/buy
Information already available
Do you have that in your internal search
Perceived risk
Number of risk
Functional vs Emotional Benefits
Functional
Derive from objective performance characteristics
Emotional
(Subjective) ex/ love, belonging, prestige, etc.
Purchase & Post purchase Behavior
Satisfaction / Dissatisfaction
Satis - meaning enough
Meets expectations
Delight is higher
WOM (Word of Mouth)
If its good you tell 3 people
If its bad you tell everyone
Cognitive Dissonance
When you get home and wish you bought the other one
Situational Influences
Result from circumstances, time, and location ….affect the consumer buying decision process
Reactance Theory
Freedom
Taken Away
Want it more
Psychological Influences
Perception
Exposure
Attention
Selective Attention
Act of focusing on a product while ignoring something else
Closure
We want closure
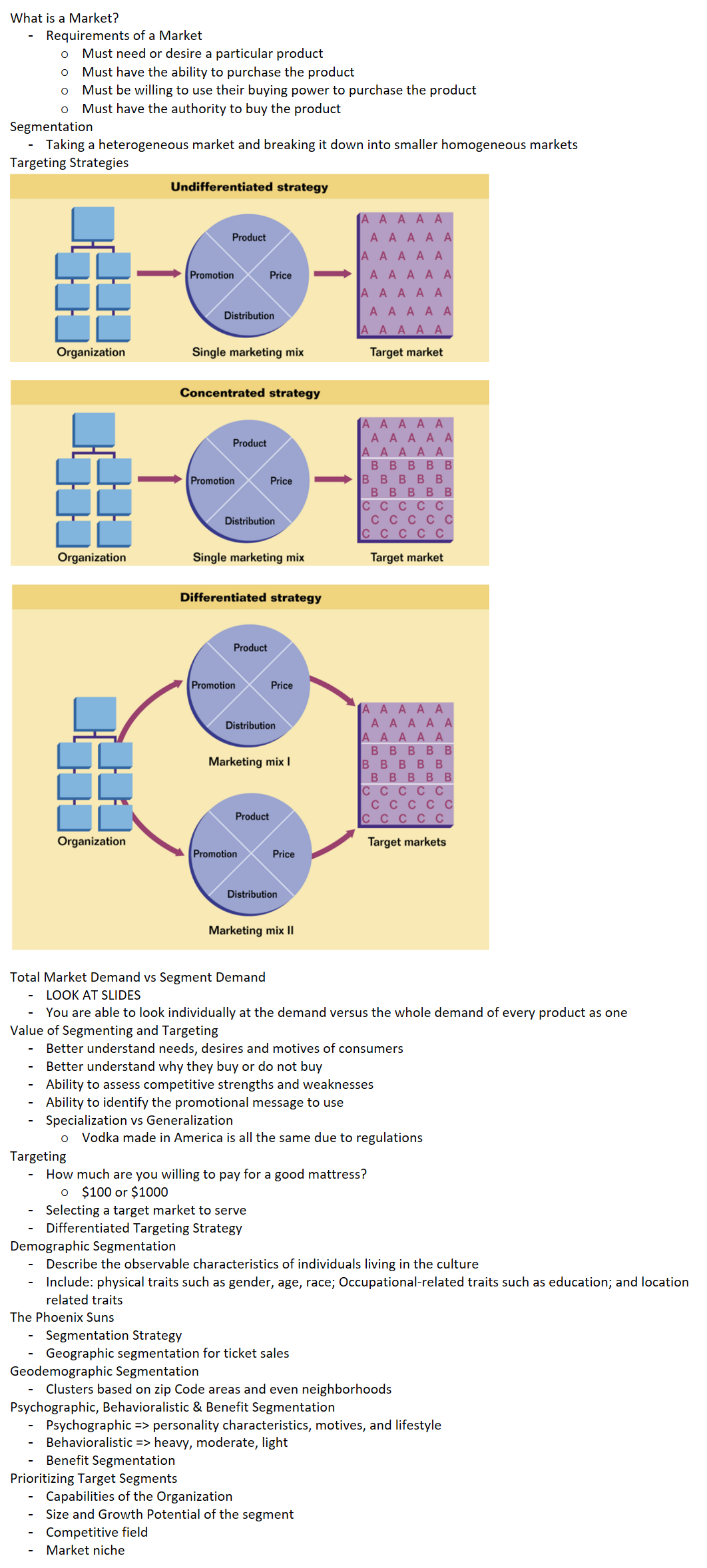
Motives - Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs
Maslow believed that people seek to fulfill five categories of needs
Behavioral Learning
Classical Conditioning
Response is learned as a result of the pairing of two stimuli
Operant Conditioning
Response is learned or strengthened because it has been associated with certain consequences
Do something and then you get rewarded or punished
Observational Learning
Learning from observing other behavior
Attitudes
An enduring disposition, favorable or unfavorable, toward an idea, person, thing or situation
The amount of affect or feeling for or against a stimulus. (Thurstone)
Three components of Attitudes
Cognitive (head)
Affective (heart)
Most powerful component
Behavioral (hand)
Multiattribute Model (Fishbein Model)
A=BiEi
A= attitude toward object
B = Strength of belief
E = goodness or badness (importance)
Personality and Self Concept
Internal Traits
Openness
Creative side
Conscientiousness
How thorough and precise you are
Extraversion
Agreeability
Neuroticism (Stability)
Degree of moodiness
Material needs
How materialistic you are
Arousal needs
Physical Needs
Personality and Need for Affiliation
Marketing Personality
Agreeability
Most agreeable of all categories
Openness
Highest openness
Materialistic
Highest on Materialism
Social Influences
Roles
Family Influences (identification with brand)
Reference Group
Membership
Aspirational
Dissociative
Social Class
Culture and Subculture
What is a Product?
Good, Service or Idea
Augmented
Don’t remember
Psychological
Status
Feel good
Social Affects
Sports Fans and attire
Classifying Consumer Goods
Convenience
You don't do much research on
Toothpaste, soda, milk, gasoline
Shopping
Lots of comparing
Appliances and shoes
Specialty
No substitutes
Lots of research
Buying a Painting
Unsought
Forced
Car breaks down
Bought / Unused
Gym equipment
Product Line and Product Mix
Product Line
Typically prices the same
Lawn equipment
John Deere
Product Mix
The total group of products that an organization makes available to customers
Yamaha has odd product mix
Width of Product Mix
The number of product lines a company offers
Depth of Product Mix
The number of different products in each product line
Product Life Cycle
The progression of a product through four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline
Introduction
The first people to buy a product are the innovators
You are going after these people
Willing to pay a premium
Pricing Strategies
Skimming
Start with high price and then slowly go down until you find equilibrium
Penetration Pricing
Profits at the end of intro
Growth
Competition appears dramatically
Profits maximize at the end of this stage
Maturity
Profits are declining
Specific Groups
Decline
Kjkj
Product Adopter Categories
Innovators 2.5%
Tech people
Early Adopters 13.5%
Early Majority 34%
Late Majority 34%
Laggards 16%
Skepitcal
Brand
A name, term, design, symbol, or other feature that identifies a seller's products and differentiates them from competitor's products
"The art of marketing is the art of brand building. If you are not a brand, you are a commodity," (Philip Kotler)
Branding
Value of branding
Brand Loyalty
Brand recognition
Aware of the brand
Brand Preference
Stronger loyalty
You prefer…
Brand Insistence
Only want this brand
You insist…
Major Elements of Brand Equity
Brand name awareness
Brand loyalty
Brand associations
Perceived brand quality
ALL GO INTO BRAND EQUITY
Brand Personality
Sincerity
Excitement
Apple
Competence
Sophistication
Ruggedness
Tough, outdoorsy
Selecting a Brand Name
The name should
Be easy to say, spell and recall
IMPORTANT
Indicate the product's major benefits
Suggest the products major uses
Be distinctive
IMPORTANT
Be compatible with all products in line
Designed for use and recognition in all types of media
Brand Extension
Using an existing brand to create a new one
Co-Branding and Licensing
Using two or more brands on one product to capitalize on the brand equity (customer confidence and trust) of multiple brands
Agreement to use brand on other products for a fee
Harley Davidson F-150
Packaging / Labeling
Color, design, shape, texture
MJ water bottle and UNC shorts

Key Marketing Concepts
Market Definition and Requirements
A market is defined by the need or desire for a particular product, the ability to purchase it, the willingness to utilize buying power for this purchase, and the authority to buy the product.
Segmentation and Targeting Strategies
Segmentation involves breaking down a heterogeneous market into smaller, homogeneous segments. Understanding Total Market Demand versus Segment Demand can reveal insights into demand for individual products compared to overall demand. The value of segmenting and targeting lies in better understanding consumer needs, desires, and motives, which aids in assessing competitive strengths and weaknesses. This enables the identification of effective promotional messages. Key strategies in targeting include differentiated targeting strategy, and demographic segmentation which describes observable characteristics of individuals, including gender, age, race, occupation, and location.
Specific Examples and Strategies
For instance, the Phoenix Suns employ geographic segmentation for ticket sales. Other segmentation strategies involve geodemographic clustering based on zip codes, psychographic characteristics related to personality and lifestyle, behavioral segmentation based on consumption levels, and benefit segmentation that prioritizes segments based on consumer needs.
Consumer Behavior
Consumer behavior pertains to the complex processes that individuals go through to acquire, utilize, and dispose of products to satisfy their needs and desires. It encompasses concepts like involvement which differentiates between high (e.g., purchasing a house) and low (e.g., buying candy) involvement decisions. The consumer decision-making process includes five stages: problem recognition, search, alternative evaluation, choice, and post-purchase evaluation.
Information Search and Evaluation of Alternatives
Information can be sourced internally from previous knowledge or externally through research and discussions with others. Evaluation of alternatives includes forming a consideration set of brands and considering costs in time and money. Perceived risk and benefits, both functional and emotional, influence these decisions.
Purchase and Post-Purchase Behavior
Post-purchase behavior can lead to satisfaction or dissatisfaction, which further influences word-of-mouth, or WOM. Cognitive dissonance may occur when consumers wish they had made a different choice. Situational influences, such as circumstances, time, and location, also affect purchasing decisions.
Psychological and Social Influences
Psychological influences include perception and motives that drive consumer decisions, such as Maslow's Hierarchy of Needs. Social influences come from family, reference groups, social class, culture, and subcultures that shape consumer attitudes toward brands and products.
Product Definition and Classification
A product can be a good, service, or idea and often carries psychological and social implications. The classification of consumer goods includes convenience goods for impulse buys, shopping goods requiring comparison, specialty goods with unique attributes, and unsought goods needed unexpectedly.
Product Life Cycle and Pricing Strategies
The product life cycle consists of four stages: introduction, growth, maturity, and decline. During the introduction phase, innovators are targeted, often at a premium price. Skimming and penetration pricing strategies are used to maximize profits as products move through the life cycle phases.
Branding
Branding is crucial in distinguishing a seller’s products from competitors and includes elements like brand name awareness, loyalty, associations, and perceived quality. Strong branding fosters brand loyalty categorized into recognition, preference, and insistence. Effective brand names should be easy to recall, indicate major benefits, be distinctive, and fit within the product line.
Brand Extension and Co-Branding
Brand extension leverages existing brands to create new products, while co-branding and licensing involve collaboration between brands to enhance credibility. Finally, product packaging and labeling can significantly affect consumer perception and purchasing behavior.