1) Current and Circuit symbols:
1. Basics of Current and Charge Flow
Current: Flow of electrical charge (electrons).
Condition: Only flows in a closed circuit with potential difference (p.d.).
Unit of Current: Ampere (A).
2. Potential Difference and Resistance
Potential Difference (Voltage): Drives the charge around the circuit.
Unit: Volt (V).
Resistance: Opposes the flow of current.
Unit: Ohm (Ω).
3. Circuit Behaviour
In a single, closed loop, the current is the same throughout.
Formula: Q=I×tQ=I×t
Q = Charge (Coulombs, C)
I = Current (A)
t = Time (seconds, s)
4. Current and Resistance Relationship
Higher Resistance = Lower Current (for a fixed p.d.).
Example Calculation:
If a current of 2 A flows for 2.5 hours, charge Q=2×(2.5×3600)=18000Q=2×(2.5×3600)=18000 C.
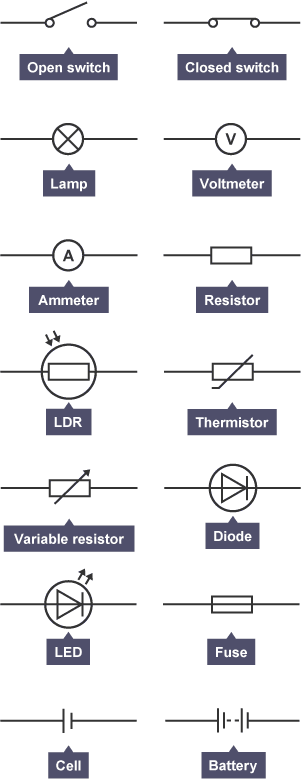
Circuit Symbols:
Symbol | Symbol Component: |
Battery | Power source |
Switch (Open) | Controls circuit |
Switch (Closed) | Completes circuit |
Filament Lamp | Produces light |
LED | Diode emitting light |
Fuse | Safety device |
Resistor | Opposes current |
Variable Resistor | Adjusts resistance |
Ammeter | Measures current |
Voltmeter | Measures voltage |
Diode | Allows one-way current |
Thermistor | Temp.-dependent resistor |
LDR | Light-dependent resistor |