Chapter 13: Coordination and Response: I The nervous System in Mammals
%%Sensitivity%% is the ability to respond to a stimulus (change)
Nervous System of Mammals:
comprises:
- %%Central Nervous System (CNS)%% - brain and spinal cord.
- %%Peripheral Nervous System (PNS)%% - cranial nerves, spinal nerves from spinal cord and sense organs.
- %%Receptors%% are sense organs that receive stimuli.
- %%Effectors%% are muscles.
Neurones:
- %%Sensory neurons%% - transmit impulses from sense organs to CNS.
- %%Relay neurons%% - transmit nerve impulses from sensory neurons to motor neurons - found in CNS.
- %%Motor neurons%% - transmit nerve impulses from CNS to the effector.
- %%Synapse%% is the junction b/w two neurons.
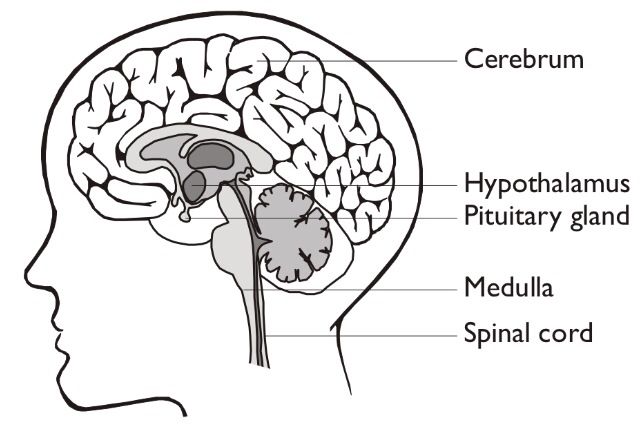
Human Brain:
%%Forebrain%%
- @@Cerebrum@@
- Concerned with intelligence, memory, learning and overall control of voluntary actions.
- @@Hypothalamus@@
- Concerned with body temperature and blood osmotic pressure, appetite, sleep and emotions.
- Produces ADH
%%Midbrain%%
- Concerned with visual reflexes e.g movement of eyeball.
%%Hindbrain%%
- @@Cerebellum@@
- Concerned with muscular coordination and maintaining body balance.
- @@Medulla@@
- Concerned with involuntary actions such as heartbeat, peristalsis, rate of respiratory movements and contraction.
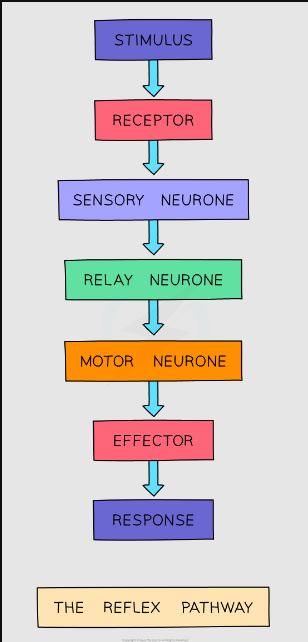
Reflex Actions:
Is an immediate ^^response^^ to a ^^specific stimulus without conscious control.^^
Spinal and Cranial Reflexes:
- ^^spinal^^ - controlled by the spinal cord.
- ^^cranial^^ - controlled by brain.
Reflex Arc
consists of:
- a receptor or sense organ
- receptor neuron
- reflex centre
- an effector neuron
- an effector (muscle or gland)
Conditioned Reflex:
Is a ^^reflex action^^ acquired ^^from past experience or learning^^ with a stimulus which is originally ineffective in producing the response.