Lab Midterm Review Guide
Midterm Test Study Outline
This is just a reference to help guide your studying but does not mean only what is on here will be on the midterm
Covers:
● Lab Safety
Microscopy lab ppt
Calculating total objective = (Ocular lens magnification * objective lens magnification) Ocular lens is always 10x
The image you see is reversed
If you move the specimen to the right, it moves left in your lens
If you move the specimen up, it moves down in your lens
As objective magnification increases, the incoming light decreases
Microbial world lab ppt
Prokaryotes
Diverse
Classified based on:
Shape (Bacilli → rod, Cocci → spheres, Spirili → spiral)
Locomotion (paramecium → cilia, amoeba → pseudopods, euglena → flagellum)
Gram staining (Gram - pink, Gram + purple)
In 1977 they were divided into Archaea and Bacteria
Trichonympha in termites exhibit a mutualistic relationship where Trichonympha convert cellulose in wood into starches and sugars that the termite can use as nutrients. This fuels a continuous supply of energy-rich cellulose and a suitable environment in which to live.
Green revolution lab ppt
Non-vascular plants:
Found in damp and moist areas
Lack specialized vascular tissues so they are low to the ground because of insufficient water and nutrient transport.
Vascular plants:
Found anywhere on land
Contain lignified vascular tissue for transporting water and nutrients.
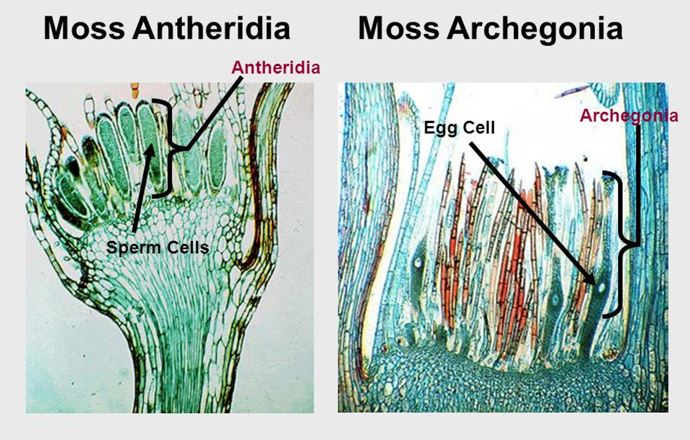
Antheridia (male sex organs) vs. Archegonia (female sex organs)
Seeds
Gymnosperm seeds: Seeds mature on the outside of the cone; naked seeds
Angiosperm seeds: Seeds mature on the inside of the cone.
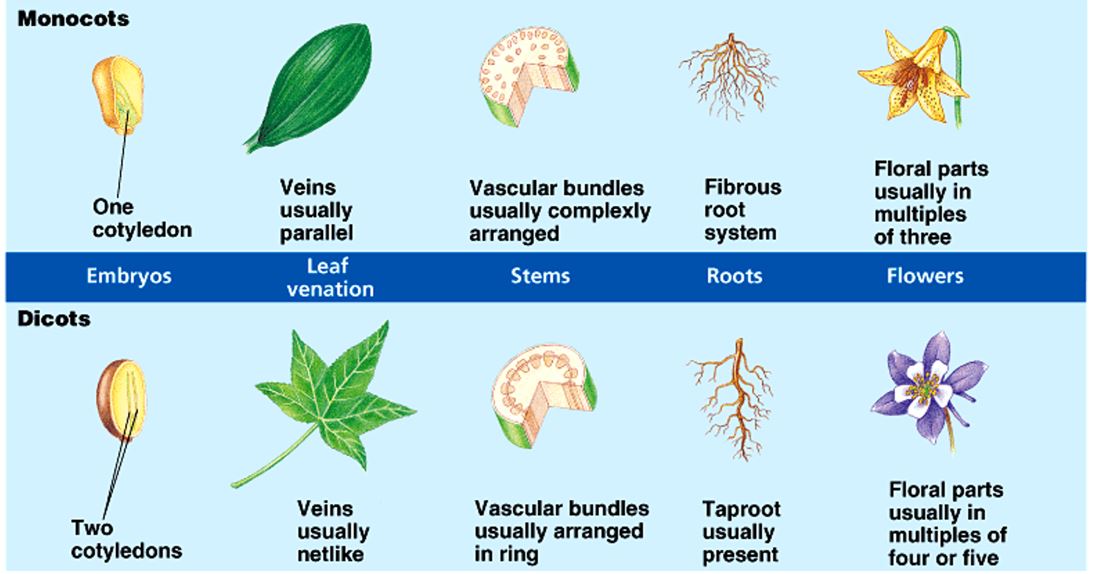
Monocots vs. Dicots
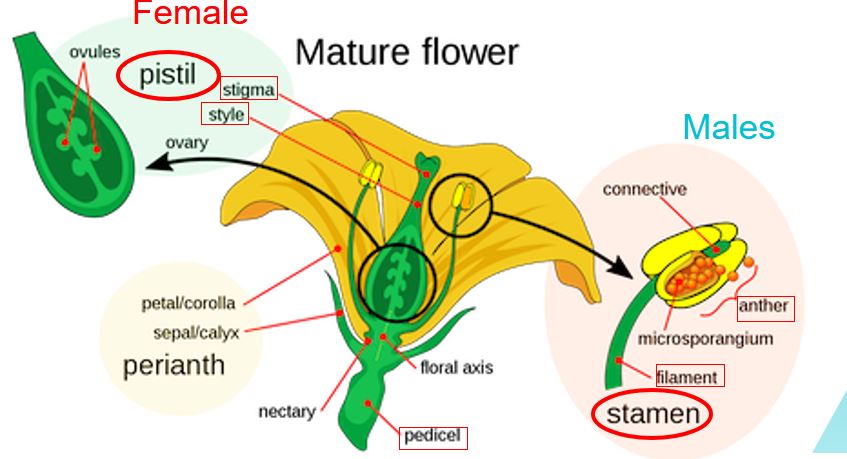
The perfect flower:
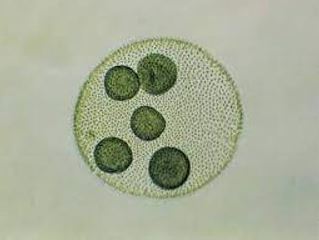
Volvox
Freshwater green algae with eyespots all around the outside
Brine shrimp lab ppt
● Pre and post lab quizzes on Tophat
Topics to understand
What is considered proper lab safety?
Hair tied up
Lab coat
Closed-toe shoes
Proper PPE
Review safety protocols for all chemicals and specimens
No food or drink in the lab
Follow instructions
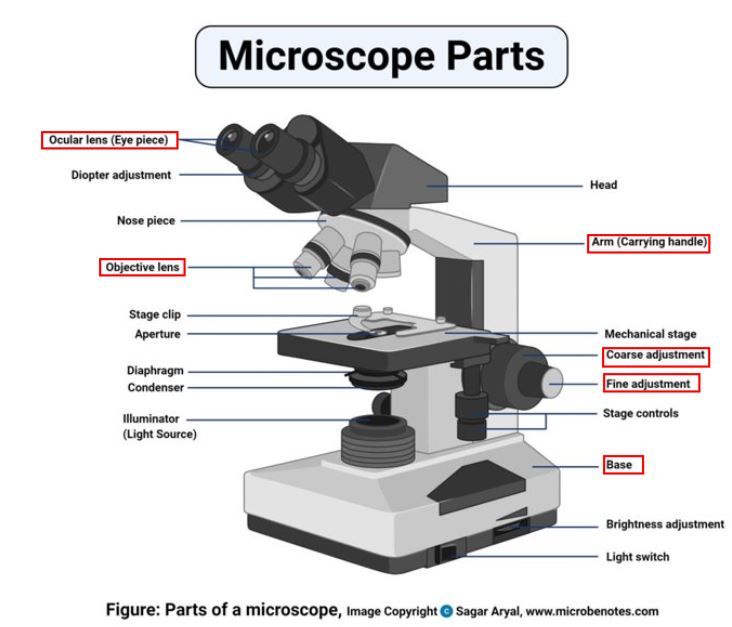
What are the different parts of a microscope and what do they do?
Objectives: Provide magnfication, can be changed to go up or down in magnification using the nosepiece
Oculars/Eyepieces: Where you look into
Stage: Where you place the prepared slides
Coarse focus adjustment knob: Focuses the slide at a greater margin
Fine focus adjustment knob: Focuses the slide at a smaller margin
Arm: Supports the eyepiece and the stage
Base: Supports the whole microscope
Condenser: Controls the focus of light entering the microscope
Iris diaphragm: Controls the amount of light entering the microscope.
Difference between degree of magnification and total magnification.
Degree of magnification → the degree to which the objective lens can magnify something (ex: 4x, 10x, etc)
Total magnification → calculated by doing ocular * objective
What are the different shapes of bacteria?
Bacilli: Rods
Cocci: Spherical
Spirillia: Spiral
Why do you use staining and what does color signify?
Gram staining allows us to distinguish between gram + and - bacteria which differ in their cell wall structure.
Gram (-): Thin peptidoglycan layer surrounded by two membrane, outer membrane made of lipopolysaccharides and proteins
Gram (+): One thick peptidoglycan layer.
This allows us to pinpoint whether or not someone has a bacterial infection and how we can go about treating it.
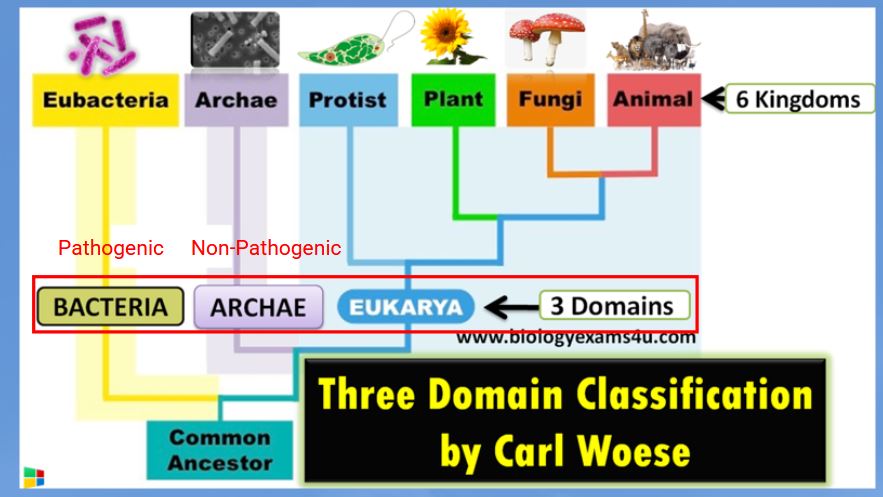
What are the three domains of life and what characteristics make them different from one another?
Bacteria, Archaea, Eukarya
Bacteria are pathogenic, archaea are non-pathogenic, Eukarya are eukaryotic.
Characteristics of Paramecium, Amoeba and Euglena
They are all eukaryotes, they differ in their method of locomotion
Paramecium → cilia
Amoeba → pseudopods
Euglena → flagellum
What organism lives within termites and what relationship does it have?
Trichonympha; a symbiotic relationship with termites.
Difference between vascular and nonvascular plants?
Vascular plants have lignfied vascular tissues which allow them to transport water and nutrients across larger distances. This allows them to grow taller and have a more rigid structure
Non-vascular plants do not have lignfied vascular tissue which force them to live close to the ground in shady, moist areas.
Volvox and its characteristics.
Freshwater green algae that has eyespots all around it’s perimeter
Moss Antheridia vs Moss Archegonia.
Moss antheridia is the male sex organs of a plant
Moss archegonia is the female sex organs of a plant
Gymnosperms vs Angiosperms.
Angiosperms are more diverse than gymnosperms
Gymnosperm seeds mature on the outside of the cone; naked seeds
Angiosperm seeds mature on the inside of the cone; fruit
What does the perfect flower have?
Male and female sex organs. Stamen and Pistil
Characteristics of Fruit.
Encase the seed
Allow for better seed dispersal and provide nutrients to the seed
review pre and post lab quizzes
Mr