World History Sem 2 Key Concepts
Note: Study what is necessary, some things are extra info
Dynasties of China
Dynasties (in order)
- Sui - Sorry
- Tang - To
- Song - Say
- Yuan - You’re
- Ming - My
- Qing - Queen
- Republic
- Mao Zedong (communist party)
Geography (also see East Asia Map in your INB.)
- Mongolia shares the longest border with China.
- Multiple geographic barriers
- Himalayas, Gobi Desert, Seas surrounding, Taklimakan Desert
- Important Rivers
- Huang He (Yellow) River
- Yangtze (Changjiang) River
- Xi River
End of the Han
- No single ruler so kingdoms fought amongst themselves and nomads invaded from the north
- Floods, droughts, and food shortages
Sui, Tang & Song Dynasties
Emperors
Wendi
- Restored old political traditions
- Allowed religious freedom
- Started public works projects
- Rebuilt Great Wall
- Started building Grand Canal
- Made a civil service exam that you needed to pass in order to become government official
- Peoed on Confuciaple get job based on merit
- Basn ideas (see Religion)
Yangdi
- Son of Wendi, liked luxury and built palaces
- Extended projects
- Rebuilt more of the Great Wall
- Built state granaries (storage for food and other things)
- Finished Grand Canal which connected the Huang He and Yangtze Rivers (see Geography)
- Launched expensive and unsuccessful wars against Korea
- Assassinated for heavy taxes on people (to pay for wars and public works projects)
Taizong
- Helped father Gaozu found the Tang Dynasty in 618 A.D
- Took throne by killing his two brothers and their sons
- People considered him fair leader as he did not overburden peasants and helped the poor with land and taxes
Wu Zhao (Wu Zetian)
- Declared herself first and only female emperor of China in 690 A.D
- Reconquest of Korea led by her
- Promoted equality for women
Xuanzong
- Grandson of Wu Zhao
- Came to power in 712 A.D
- Literature and arts flourished
- Sculptures during his rule were highly valued in trade
- Usually sculptures of horses; especially favored by the Chinese
Advancements
Political
- Imperial = related to an empire
- Bureaucracy = a government divided into multi. departments
- Tang copied the tax system, local government and military models, and the Sui capital from the Sui
- Government was set up like this - local governments reported to a central bureaucracy which went to advisors then to the Emperor if it was deemed significant
- Tang law code was great as it listed all of the laws of China everywhere (same laws applied everywhere)
- Scholar-official = educated person with a government position
- Needed to pass civil service exam to become scholar-official
- Most came from upper class as you needed to be rich to pay for education
- Skill/ability used to determine if a person was educated was Calligraphy
- Song Dynasty improved civil service exam by creating more schools and changing exam to have more practical subjects
Travel and Trade
- Roads and waterways built and improved transportation
- Made moving people and goods more efficient
- Inns popped up
- Linked parts of China
- More roads = messengers could carry government mail
- Gigantic ships powered by oars and sails and magnetic compass helped with sea exploration and trade
Agriculture
- New species of rice appeared
- Ripened faster = farmers could raise more crops
- Built additional farmland using pumps and canals to drain water from marshes, and built terraces + more irrigation systems
- Increase in food supply allowed job specialization and more people worked in tradeCommerce
- First governments in the world to print paper money
- Most merchants lived in private cities and towns were trade took place
Literature and Art
- Tang artists produced mostly pottery
- Landscape painting was important during the Song
- Used black ink in different shades
Technology
- Paper was easier to write on, so was mass produced using silk
- Wood-block printing = form of printing where printers carved wooden blocks with enough characters to print an entire page
- Moveable type printing = a small block of ceramic or wood with a single raised character used for printing
- Better than wood-block printing as it could be used more than once and rearranged
- Goryeo kingdom would later develop moveable-type with metal
- Gutenberg would develop printing process in Europe
- Chinese were first to make printed books to record knowledge with these
Inventions (just get a general idea of these)
check your class period slides
Religion
Confucianism - symbol = water in chinese
- System of beliefs (philosophy, not religion) based on teachings of Confucius or Kong Fu Zi
- Focused on proper conduct, hard work, respect for elders, education , and government service; he felt this would create a peaceful, stable society
- Believed in the right relationships to produced social order
- i.e ruler and subject, parent and child, husband and wife, sibling and sibling, friend and friend
- Believed these relationships would be harmonious if the people were loyal, obedient, and honest
Daoism (Taoism) - Symbol = yin and yang, known as “the way”
- Religion based on the teachings of Laozi, aka “the way”
- Taught that the goal of life was to achieve oneness with the Dao, a universal force connected to nature; it can only be experienced
- Teaches that humans shoulds see themselves as part of nature
- The best way to live is to live simply in harmony with nature
- Nothing in nature strives for fame, power, or knowledge
- Things in nature move without effort because they follow the Dao
- Daoists do not believe in strong government but happiness and peace by having a balanced life instead of following laws and rules
- Teaches that harmony comes from balancing yin and yang (symbol of Daoism
Buddhism - Symbol = Eight Spoked Wheel, known as “The Middle Way”
- Religion based on the life and teachings of Siddhartha Gautama (Truly Humble Under Gautama….) known as the Buddha or “enlightened one”
- Summed up in the Four Noble Truths
- all life is suffering
- all suffering is caused by desire for wealth, pleasure, fame, and power
- to end suffering one must overcome desire
- to overcome desire you must follow the Middle Way (or eightfold path)
- Preaches reincarnation
- Teaches that the first goal in life is to reach nirvana, or enlightenment, the condition of desiring nothing.
- When one reaches nirvana the cycle of reincarnation ends
- Final goal for Buddhists is to devote their lives to bringing others to enlightenment
Yuan Dynasty (Mongols)
Emperors
- Genghis Khan - original name was Temujin
- Became a tribal leader and took the name Genghis Khan or “universal ruler”
- Organized all the Mongols into a strong military and began conquest throughout Asia
- Kublai Khan
- Genghis Khan’s grandson who took power in China
- Defeated the Song in 1279 and controlled all of China
- Kept many aspects of Chinese rule but removed civil service exam
- This was to keep Chinese out of government
- Gave government positions to trusted foreigners and Mongols
- Opened up China to Europe and other lands through the Silk Road
- Since total control over Silk Road = made it safer and more efficient
- Aka “Great Khan”
Politics & Conquest
- Expanded empire through military conquest and strong leadership
- Moved quickly (nomadic) and looked for weak spots
- Conquered Central Asia, China, Lower Russia, Korea, Persia, and Eastern Europe
- Government = strong central state built around a bureaucracy with Confucian ideas i.e rituals and ceremonies
- Maintained control by keeping Chinese out of high government positions
- Chinese only given minor positions
Trade
- Made Silk Road safer as they controlled all of Central Asia
- Mongol Ascendancy - period of Mongol rule over Central Asia which made overland travel safe which increased trade
- Used foreigners to advertise Chinese products
- Marco Polo - Venetian trader who stayed in China for 17 years and worked for Kublai Khan
- Had experts that would determine the value of goods
Ming & Qing Dynasties
Ming Dynasty
Formation
- Hongwu emerged as a leader during a rebellion and brought an end to Mongol rule, declaring himself emperor
Emperors
Hongwu
- Overthrew Mongols
- Encouraged Confucianism
- Public Works
- Built roads and canals
- Rebuilt and extended Great Wall
- Agriculture
- Rebuilt agricultural system
- Gave farmers land
- Trade
- Supported growth of manufacturing
- Maritime - related to the sea or ocean
- Politics
- Cut government spendings and made more efficient taxation
- Brought back and strengthened civil service exams
- Took direct control of govt. and set up a secret service to spy on others and killed people for treason
- Yongle
- 3rd emperor of the Ming dynasty, Ming reached height of its power
- Sponsored sea expeditions and great literary works
- Encouraged governments to build schools for commoners
- Enlarged capital city of Beijing and part of it became the Forbidden City, made it the imperial capital
Extra
- Forbidden City’s architecture made it the perfect place for the emperor to fulfill his role as a connection between the will of heaven and practical rule of Earth
- Emperor rules with a mandate of heaven
- Forbidden City = imperial family’s walled palaces in Beijing
- foreigners and commoners were not allowed to enter
- Increased amount of sea exploration under Ming
- Sought foreign contact by Zheng He’s voyages
- Wanted to glorify Yongle by controlling trade routes
- Wanted to extend Chinese influence and win tribute/token allegiance
- Tribute - payment made by one country to another as a sign of respect
Isolationism
- No more voyages as they were claimed to be expensive and brought dangerous foreign ideas
- Ended maritime voyages and banned building of seagoing ships
- Foreign contact and influences rejected; foreigners and their ideas were banned
- Banned foreign trade and tried to get rid of all foreign influences
- Economy geared towards self-sufficiency
Qing Dynasty
Formation
- The Manchus, a tribe from Northern China, took control of the confusion during a rebellion and founded the Qing Dynasty
- Manchus - people from Manchuria who conquered the Ming dynasty in 1644 and founded the Qing Dynasty
Opium Wars
- Europe wanted to have easy access to Chinese goods, so they smuggled in opium (a drug) which led to many people getting addicted
- China weakened internally and internationally
- Europeans seized Chinese territories and took control of the economy
Zheng He (he gets his own section!!!)
Background
- Got his name from the honorific Zheng given to him by the emperor and was also Grand Eunuch
- Led 7 naval expeditions
- Motivation of first three expeditions was to gain tribute and token allegiance from the Indian Empires
Ships and Navigation
- Treasure Ship - ship loaded with precious goods and gifs for rulers to exchant for exotic products of the Indian Ocean
- Ships were large and slow moving, also heavily reinforced.
- Good for deep-sea sailing, but bad in shallow waters
- Chinese navigators found latitude using stars and stellar charts
Expeditions
- Ma Huan, a Muslim Chinese translator, recorded the final four expeditions
- He called Mecca “The country of the Heavenly Square”
- Recorded the political, military, religious, and economic background of each port
- Also ethnographic information and list of trade goods
- Chinese were ignorant and thought everyone was their subject, Yemen found this amusing after giving them gifts that they thought was tribute
- Ming expeditions established long-lasting relationship with Malacca
- Private Chinese merchants/enterprise took control of trade after the Chinese government stopped funding the expeditions (Hung-hsi emperor put an end to it
- Pepper was used as currency for years since a lot of it was found in Zheng He’s ships
Kingdoms of Korea
All Kingdoms
Acronym: Good Kings Practiced Good Style By Kicking Jayden
Gojoseon: the ancient Joseon
Koguryo
Paekche
Gaya
Silla
Balhae
Koryo
Joseon
The Myth of Tangun:
God’s son came down to earth onto a mountain where a tree lay. At this place he brought holy items and the wind, sky, and rain where his advisors. A bear and tiger wanted to be human and to do this they had to eat raw garlic and Mugboard for twenty days. The tiger gave up and the bear transformed into a woman. She had a child with the God’s Son who would rule over the Gojoseon Kingdom for 1,500 years
Fighting Periods
- The Three Kingdoms period:
Silla
Goguryeo
Baekje
These three kingdoms fought for control over the Korean peninsula during this period and they had many similarities as well as differences.
- North South States Period
Balhae in the North
Taken over by Khitan and the people and King moved
Silla in the South
Kingdom of Koryo
- During Song, Yuan, Ming of China
- Founded by Wang Geon
- Last dynasty controlled by buddhism
- Strong confucianism
- Known for celadon and moveable type printing in metal
- Where the name “Korea” Originated from
- Lacquerware with Mother of pearl inlay
(started during Silla but was made popular in Koryo by nobility who also gave them as gifts to foreigners.)
Kingdom of Joseon (Last)
- Land of the morning calm
- Seoul as capital city
- Was known as “Hermit Kingdom” because of its isolation from foreigners
- King/Emperor Sunjong=last king and emperor
- Mom was Queen Min who was assassinated by the japanese
- Dad was Gojung- forced to abdicate by the Japanese
Geography
- Peninsula in East Asia bordered by China & Japan
- Features mountains, seas & fertile coast plains
Korean Culture
- Ceramic Art
- Type of pottery made with a unique blue-green color called celadon
- Woodblock Printing
- Spent years carrying buddhists teachings called Tripitaka Koreana
- Moveable Type Printing
- Made Jikji, world’s oldest book printed with moveable type printing
- Reusable metal flexible characters
- Heating System
- Created ondol, hot air from fireplace is moved around a house by passageways, beneath the floors and rooms above
- Science from the Silla
- Cheomseongdae
- Means star-gazing tower in Korean
- Is the oldest surviving astronomical observatory in Asia, and possibly even in the world
- It was constructed in the 7th century
- Music from the Gayageum
- Similar to the Qin music from China, Guqin, and the Koto from China
Feudal Japan
Timeline
- Jomon - between as early as 10850 BC - 300 BC
- Yayoi - about 200 BC - 300 AD
- Tomb Culture (other names, see Early Cultures) - 250 AD - 550 AD
- Soga Clan/Prince Shotoku - 593 - 622 AD
- Kyoto Court & Fujiwara - when capital was moved to Kyoto in 794 AD, power from 858 AD - 1185 AD
- Kamakura Shogunate - 1185 AD - 1333 AD
- Ashikaga Shogunate - 1336 - 1573 AD
- Warring States Period (Sengoku Jidai) - around 1500s to 1603
- Tokugawa Shogunate - 1603 - 1867 AD
Geography (also see Political and Physical Map of Japan on pg. 38 of INB)
- Mt. Hiddaka is located on Hokkaido
- Mt. Fuji was located on Honshu
- Sea of Japan was west of Japan
- Japan = archipelago of over 3000 islands
- Four main islands :Honshu (largest & main main island)
- Kyushu
- Hokkaido
- Shikoku
- + 5th Ryukyu Islands at the southern end of Japan
- Seas & Pacific Ocean caused Japan to be isolated for long periods of time
- Also provided benefits
- Overseas Transportation & Trade
- Food & Protection
- Electrical Power
- Natural disasters very common
- Earthquakes (over 1500 yearly) = Tsunamis and floods
- Volcanoes (60 out of 150 are active volcanoes)
- Typhoons
- Biggest problem is lack of land/space due to mountainous land
- Height of the land = Altitude
- Only 16% of Japan’s land is good for living and farming
- High population density (# of people per square mile) so crowded cities
- Adaptation techniques include adding more land and capsule hotels
- Capital = Tokyo (known previously as Edo)
Early Cultures
Jomon
- First recorded culture of Japan
- Were fishermen and hunter-gatherers
- Evidence of this are accumulations of shells, fish hooks, and harpoon points found
- Also known as “Tree Culture” because of their use of trees in construction, daily implementation, and ceremonial ornaments
- Named after its cord patterned pottery
Yayoi
- Settled in Honshu and replaced Jomon culture
- Introduced growing rice in water & irrigation
- First culture in Japan to use metal tools, wove cloth textiles, and made pottery on wheels
- Shelter was sedentary farming villages made of wood and stone
- Wealth was from land ownership and grain
- Distinct social classes
Tomb Culture
- Also known as :
- Tumulus
- Kofun Period
- Great Burial Period/The Great Burial
- Named after big keyhole shaped tombs surrounded by moats
- Rulers from warrior class
- Clay figurines found in tombs
- Had metal works
- Found bronze mirrors and crowns in tombs
Religion
Shinto
- Taught that the world is filled with divine spirits called kami
- Highest ranking kami is the Sun Goddess
- associated with the emperor
- Religion started in Japan and mainly based on nature (not brought in like christianity or Buddhism)
Buddhism
- gets its own section later on
Taika Reforms & Prince Shotoku and the Soga Clan
Taika Reforms (changes in land ownership and government policies)
- All land in provinces is now owned by the emperor
- Land was split up into small plots
- Clan leaders governed them
- Government had more control over clans so the clans had less power
- No effects on the lives of the peasants
- (except they had to pay their taxes to the emperor instead of the clan leaders)
- Similar to the Tang
Soga Clan and Prince Shotoku
- Prince Shotoku :
- Regent (see definitions) of Japan who was part of the Soga Clan from 593 - 622 AD
- Liked Chinese culture so introduced things like Chinese art, Buddhism, and Confucianism to Japan
- Japanese eventually accepted Buddhism and it was mixed with Shinto
- Capital of Soga Clan = Nara
- Based of the Chinese city Chang'an
- Had intersecting streets
- Imperial palace in the north
- Bureaucratic system was used to rank advisors
- Exams had to do with a person’s genealogy/family
Chinese Influences
Religious/Cultural Influences
- Japanese monk named Dogen modified Chan/Chen Buddhism to Zen Buddhism
- Emphasis on meditation and concentration which made it appealing to samurai
- Many Shinto gods became Buddhist gods
- Shrines and temples began to merge
- Confucianism led to these in Japan :
- Emphasizing close family ties, the group over the individual, filial respect, respect for elders, honor (samurai followed greatly), connection between learning and “rightful living”, and worshiping ancestors
- Women married for political reasons for their family
- Merchants were the lowest in the social pyramid because it was based on learning/education
Architecture
- Buildings were made flexible using Chinese techniques to withstand earthquakes
- Multiple roofs symbolized different levels of awakening in Buddhism
- Pagodas (Buildings used to represent Buddhism) that had multiple roofs
- Gardens and courtyards were just as important as the buildings
- Japanese cities didn’t use all of the features of Chinese architecture because of lack of space
Writing, Music, & Art
- Writing
- Kanji was from Chinese and harder to use
- Men were expected to learn this
- Some women knew it (ex. Murasaki Skikibu)
- Hiragana was developed in Japan
- Phonetic, each symbol represents a syllable
- Women often learned this style
- Katakana was developed for foreign words
- Japan uses a hybrid script of the three now
- Art
- Often painted watercolor images of nature
- Zen monks used black ink and few brush strokes (Chan Chinese style)
Yamato (new painting style) was also developed
- Used gold and jade colors
- Fictional and narrative scenes of battle and still life
- Music
- Composed music on paper using symbols
- Many Chinese inspired instruments
- Koto is similar to the Chinese chin and the Korean gayageum
- Sho is similar to the Chinese sheng (mouthpiece)
- Biwa is similar to the Chinese pipa (lute)
- Court music (gagaku) was adopted from other countries such as Buddhist chants, Indian, Korean, and native Japanese music
Dress
- Upper class fashion was :
- Brightly coloured silk clothing with many layers (different sleeve sizes so you could see the different colors)
- Fans and parasols
- Women would blacken their teeth, lighten their skin, and shave and redraw their eyebrows to show beauty
- Farmer/working class’ clothes were made of hemp, linen, and cotton
- Kimono developed during the Ashikaga period
Kyoto Court
Capital was moved to Kyoto in 794 AD
- Power of the government was overwhelmed by the Buddhist clergy who tried to interfere with politics in Nara
Moved to Kyoto because Buddhist influences were limited there
Power
- Fujiwara Clan held most of the power
- Were related to the emperor by marriage
- Fujiwara women married imperial princes
- Fujiwara members also served as regents
- Emperor ended up becoming a religious symbol more than a political leader
Religion
- Courtiers liked Shingon Buddhism
- Had elaborate ceremonies
- Stressed learning and art
Literature
- Poetry
- Favorite form of writing of the courtiers
- Poetry contests were held often
- Wrote about beauty in nature
- Sadness of the death of beauty was aware
- Diaries
- Another popular form of writing
- Diary of Murasaki Shikibu told about the roles of women
- Murasaki was from the Fujiwara clan
- Learned kanji from watching her brothers
- Tales
- Short fictional stories
- Tale of Genji by Murasaki was considered to be the first tale; was a long account of the fictional life of a prince
Clothing
- Clothes were embroidered with gold, silver, and colored thread
- Women often wore 12 or more silk robes with different sleeve lengths
- Long hair was considered beautiful
- Other things included light skin (which women powdered their skin white), black teeth (put charcoal on their teeth), and long eyebrows high on the forehead (shaved the eyebrows and redrew fake ones)
Writing System
- Used kanji
- If the Japanese wanted to express their own feelings in their own language they used hiragana (also easier than kanji)
- Symbols represent syllables so created more expressive poetry/literature
- Katakana also developed (foreign sounds/words)
Income & The Clans
- Courtiers afforded their lifestyle by :
- Their own private land
- Farmers that paid imperial tax
- Clans gained back land ownership because :
- Imperial government/Kyoto Court was too involved with court life (isolated in luxury/out of touch with reality) and ignored the provinces
- Because of this, were called “dwellers among the clouds”
- Clans took back land slowly
- Small landowners gave their land to the provincial nobles (see definitions)
- This was to avoid paying taxes and military service
- Would become tenant farmers, menial laborers, or carpenters (see definitions)
The Warring States Period
- Period from 1467 - 1590 where different provincial nobles started fighting for power among the provinces
- Samurai class created as a result
- Samurai = warriors who serve the Daimyo (More info in Samurai & Bushido)
As more fighting happened :
- Power within the provinces skyrocketed and power towards the kyoto courtiers and emperor shifted away.
- Oda Nobunaga captured ⅓ of Japan’s land and killed the last Ashikaga shogun, ending the Ashikaga rule in 1573.
- After Nobunaga’s death, Toyotomi Hideyoshi captured the rest of Japan.
- After Hideyoshi’s death in 1598, Tokugawa Ieyasu took over and started the Tokugawa Shogunate
Medieval Japan
A Warrior Government
- Shogun
- Military ruler of Japan, translates to Great General
- Ruled under the emperor but held the real power
- Daimyo
- Owned estates in the provinces and supported the shogun
- aka nobles/minor warlords
- Samurai
- “those who serve”
- Main job was to protect the Daimyo
- Had small pieces of land from the daimyo
- Often held positions as officials
- Cherry blossoms used as a symbol for the samurai
- A samurai’s time was often as short as the flowering of a cherry blossom
Kamakura Shogunate
- Started when the Minamoto clan took power in 1185
- Leader was Yoritomo
- Set up a warrior government and moved the headquarters to Kamakura
- In 1200s fought the Mongols (Yuan Dynasty under Kublai Khan)
- Mongols had crossbows that shoot farther than Japanese ones and flaming bomb catapults
- Great typhoon that Japanese called the kamikaze (divine wind) wiped out the Mongol fleet
- Japan won
- Lost power because economic troubles due to war didn’t allow them to pay their samurai
- Samurai burned the capital to the ground and the Ashikaga clan took over and started the Ashikaga Shogunate
Ashikaga Shogunate
- Capital was in Kyoto
- Warriors married into noble families and learned ways of the courtiers
- Learned about etiquette, literature, art, and music
- Court life caused the Ashikaga Shogunate to weaken and started the warring states period (Sengoku Jidai) (also above and not below ☠️)
Tokugawa Shogunate
Social System
- Consisted of 7 levels
- Emperor: The top of the social hierarchy, but had little real power.
- Shogun: The actual ruler of Japan who was operating behind the scenes.
- Daimyo: Wealthy landowners who swore allegiance to the emperor and spent every other year in Edo and served the Shogun.
- Their wives and eldest sons lived in Edo.
- Samurai: “Those who serve” No land, but were paid salaries by the Daimyos. Became educated administrators due to the government official positions.
- Ronin Samurai = Samurai without Daimyo masters
- Samurai = “Those who serve”
- Artisans: Thrived in towns and sold their products to others.
- Peasants: Majority of the population
- Forbidden to leave the land they worked and paid half of their crops as tax to the shogun.
- Merchants: Deemed as the lowest class of all due to their contradicting behaviors against Confucianism.
- Lived in towns, excluded from politics, not allowed to live lavishly or luxuriously
- HOWEVER: Controlled the economy later on and grew to be an extremely powerful class over time.
- Optional class: (Outcasts) Eta
- Ignored and shunned by all statuses due to their work.
- Very strict rules targeted toward these people
- Butchers, Leather tanners, leprosy sufferers, criminals, etc.
- The Ainu: (indigenous japanese people) excluded entirely from society and still are to this day.
- Strict social system to preserve traditional ways of Japan and strengthen the Shogun
- Membership in each class was hereditary
- Couldn't move up classes or marry between classes
- Harsh punishments and strict rules (ex. rules of dress that applied to everyone)
- Women
- Their class determined their role
- Women in the samurai class had to prepare their sons to become samurai and daughters to become housewives
- In the peasant class they had to work on the farm and raise children
- However had more freedom than upper class women
- Always seen as lower than men and could be divorced but could not divorce
Strengthening the Shogun and Isolation
- Each daimyo had to swear loyalty to the shogun and serve military service when needed
- Also had to spend part of every other year in Edo serving the shogun
- Forced to leave their wives and eldest son in Edo when they returned to their provinces
- A line of succession was set up to ensure that only the sons would become shogun
- Were isolated from the rest of the world
- feared that Europe’s political and religious wars might spread to Japan
- Also feared that if the daimyo became rich from foreign trade they would rebel
- Foreigners were seen as a threat
Culture
- Entertainment
- Theaters, teahouses, gambling, wrestling, and public baths
- Kabuki Theater
- Had plays that included a mix of music, dance, mime, staging, and bright costumes
- Topics were adventures of samurai to romance stories
- Haiku
- Poem with three lines and 17 syllables
- Intended to create a mood or bring about a sudden insight into human existence
Samurai & Bushido
Were around from 800s - 1870s since guns came from Portugal
Translations/meanings
- Samurai = those who serve
- Bushido = the way of the warrior
- Seppuku or Harakiri = ritual suicide
Social Status
- Were basically armored warriors
- Held positions as administrators/officials in the provinces
- Respected
- Within the samurai were different classes
- Ronin was the lowest (ronin had no masters)
- Also acted as police and collected taxes
- Despite all of this, they lived simple and thrifty lives
- Also had great social privilege (ex. they could kill a commoner who insulted them)
- Only class who could have swords
Battle
- Honour meant everything
- Dying in battle meant bringing honor
- Samurai would never retreat (would bring dishonor)
- Skilled in martial arts and in using the bow & arrow
- Could kill people with just their fists
- Also great horsemen
- Liked one-on-one battles because they allowed the samurai to process and think faster
- Cut off an opponent's head and brought it back to show victory
- Applied meditation and concentration to their combat
- Learned to anticipate attacks and plan
- Sword and samurai would become “one” in some cases; called “no mind”
- Would commit seppuku or ritual suicide if he was defeated but didn’t die
- Includes stabbin the belly and then cutting out the guts
- Then another samurai cuts off the head :(
☻__
/▌ /▌
/\ /\ ☻
Yasuke
- Samurai from Africa brought by the Portuguese
- Learned and spoke Japanese
- Served Oda Nobunaga during the Sengoku Jidai (Warring states)
- Was the first foreigner to become a samurai
- Was alongside Nobunaga when Nobunaga died
Bushido - “The way of the warrior”
- Code of honor/conduct for the samurai
- Had 7 principles (don't need to memorize all just have a good understanding of)
- gi - right decision
- yu - courage
- jin - mercy/compassion/benevolence
- rei - courtesy/manners
- makoto - truthfulness
- meiyo - glory & honor
- chugi - devotion & loyalty
Other facts
- Treated their swords with respect and honor
- Samurai are taught to keep the blade moving at all times
- Big slicing/slashing motions
- Also taught to make the first move
- Armor made of leather, iron, bamboo, and silk
- Was made for ease of movement
Contact with the West
Portuguese - arrived in mid 1500s
- Portuguese society was based on competition, the individual, and had a flexible social structure compared to Japan
- Japan’s society was based on honor, respect, the group, and had a strict social structure
- Portuguese religion included Christianity (which they wanted the Japanese to convert to) which was monotheistic (one god)
- Japanese believed in Shinto and the Confucian code of correct behavior and Buddhist self discipline (zen)
- Buddhism & Shinto were polytheistic
- Portuguese had religious and political problems
- Japanese wanted to keep their political/societal structure without western politics that might disturb society
Buddhism’s Denominations
Shingon
- Art and learning was important
- Elaborate ceremonies and rituals
- Courtiers liked it for these reasons
Pure Land/Amida
- Chanted the name of the Amida Buddha (spiritual Buddha that lived in the past)
- Amida was said to have created a paradise (hence “Pure Land”) beyond the sun setting
- Followers chanted his name during sunset
- Taught happiness in the afterlife rather than finding enlightenment during your present life
- Believers were said to be reborn in the paradise
- Caused it to be popular in the peasant class and in the upper class
Nichiren/Lotus Sutra
- Creator was called Nichiren
- Taught that the only truth was found in the Lotus Sutra which was Buddha’s last teaching
- Was different because it taught that all other denominations were false
- Said that Japan would fall if it kept on believing in the other “false” denominations
Zen
- Encouraged physical and mental exercise that would produce a sudden recognition of the nature of existence
- Also taught that spiritual and physical discipline was the path to enlightenment
- Enlightenment can only come by breaking away from logic
- Ex. “Why do you drive in a parkway but park in a driveway?”
- Focused concentration and meditation
- Said that the moment and the process was important
- Don’t hurry to get something done otherwise you will not experience the natural world fully
- Appealed to samurai (didn’t include writing or reading)
- Influenced Japanese arts
- Tea ceremony
- Noh drama
- Flower arranging (ikebana)
- Rock gardens
- Incense blending
- Paintings (landscape and those of nature)
Definitions
- Altitude/Elevation = height of the land
- Isolation = setting apart or staying away from
- Shinto = the religion of early Japan revolved around nature and divine spirits called kami
- Kami = divine spirits in Shinto
- Regent = people who exercise power in the emperor’s name
- Courtier = people who took part in the highly refined social life of the court
- Tenant Farmers = farmers that paid rent in crops for the privilege to farm in the land owned by nobles
- Provincial Nobles = leaders of each province who controlled the land
- Denominations = different religious groups of the same religion
- Meditation = continuous and deep contemplation or musing on a subject or series of subjects, like spiritual matters
- Noh Drama = a drama in which a masked dancer supported by minor players and a chorus, performs a slow-dance drama (combines dance and gestures)
- Rock Gardens = gardens of rock and sand raked into patterns to provide a place of meditation. Rocks are placed to suggest things in nature
Medieval Europe
Timeline
- Middle Ages - lasted from around 500 AD to 1450 AD in Europe
- Early part of the Middle Ages after Rome’s fall was called the dark ages
- Decline in learning and technology which caused trade to decline as well
- No political stability
- People were mostly trying to survive due to many wars (people wanted to claim the crown)
- Medieval = related to the Middle Ages
- Christian Church survived the fall of Rome (later splits into the Roman Catholic and Eastern orthodox
- Crowning of Charlemagne - 800 AD
- Schism of 1054 - 2024 AD to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807 AD
- The Crusades (4 main ones)
- First Crusade - 1096 to 1099 AD
- Second Crusade - 1147 to 1149 AD
- Third Crusade - 1189 to 1192 AD
- Fourth Crusade - 1202 - 1204 AD
- Reconquista - 718 to 1492 AD
- The Hundred Years War(s) - 1337 to 1453
- Black Plague - mid 1300s to 1400s (no exact dates but could probably find online)
Beginning of the Dark Ages
Geography
- Geographical borders of Europe include :
- Atlantic Ocean to the west
- Arctic Ocean to the north
- Mediterranean Sea in the south
- Ural Mountains in the east
- Rugged mountain ranges like the Alps and Apennines in Southern Europe
- Northern and Western Europe is filled with plains and farmland
- Many winding rivers
- Key role in communication and trade
- Longest river = Volga River
- Runs from Moscow to the Caspian Sea
- Climate in the North includes cold winters
- Hot and dry summers & mild winters in the south
- Europe gets plenty of rainfall → forests and farmland thrive
- Also allows agriculture to thrive
- Citrus fruits grown in the Mediterranean
- Crops & grain like wheat and barley in the west
- Favorable climate and topography allowed people to take and produce what they needed from the land
Changes in Culture, Learning, and Trade
- Roman Empire split into many Germanic kingdoms which brought cultural trade
- Multiple kingdoms instead of one central govt. under Romans
- Romans
- Had a highly organized govt.
- State over the individuals
- Written laws and lived together
- Germanic Kingdoms
- Little notion of a state
- Lived in small communities
- Maintained order through unwritten rules and traditions
- Didn’t develop large governments, trade systems, or emphasize learning
- Learning also declined
- Educated middle class almost disappeared completely
- Schools stopped being built and became inactive
- Caused few people to know how to read or write
- Europeans forgot about Greek & Roman achievements
- Trade disappeared as well (caused cities to disappear)
- City dwellers made a living by trading so instead they moved to the countryside and became farmers
Rise of Germanic Kingdoms
- Clovis, a 15 year old warrior, became king of the Franks in 481 and led them in wars for 30 years
- Expanded the Frankish Kingdom and led them into Christianity
- Church supported him to serve Frankish Christians
- Encouraged Clovis to spread Christianity after he became Christian
- Church of Rome provided stability after the fall of the WRE
- Still used Latin & Roman traditions
- Centre was in Rome
- The laws of many Christian rulers used Roman systems of land ownership & taxation
- Old Roman trade routes were still in use
- Monks formed monasteries (religious communities)
- Preserved ancient Roman & Greek ideas and church writings
Christianity Grows
- Christian church survived the fall of Rome
- German rulers and their subjects converted to Christianity
- Helped to spread Christianity in Europe
- Franks played a big role in strengthening Christianity in northern and western Europe
- Monks also spread Christianity through monasteries
- Monastery = religious structure where monks practiced lives of prayer and worship
- Did things like studying Christian works and preserving copies of the Bible
Charlemagne’s Empire
- Charlemagne helped Pope Leo III put down a rebellion in 800
- Pope Leo knew he needed Charlemagne’s protection so he crowned him Emperor of the HRE
- Was a direct challenge to the Byzantine Empire since only the head of the Byzantine empire could technically claim the title of emperor
- However Charlemagne was a good emperor (and bad in some ways)
- Charlemagne was a good emp because :
- Charlemagne dedicated himself to strengthening the church and bringing learning
- Made services uniform
- Educated monks and preserved manuscripts
- Got rid of corruption
- Charlemagne was a bad emperor because :
- Forced people to convert to Catholicism
- Charl (Charlemagne) knew how to read and write but had scholars
- His greatest scholar was Alcuin from England
- Most of Europe’s libraries were destroyed during war
- Charl’s scholars copied books to preserve for future ages
- Charl’s scholars also made sure that religious services were uniform across Europe
- Charl’s empire declined as he became older
- Magyars attacked from E, Muslims from S (N Africa and Spain), and Vikings from N
- Charl died in 814 at age 72
Unstability
- Charl’s three grandsons fought for control but eventually split the empire into three
- Empire became weak and unstable
- Vikings attacked coastal villages, Muslims raided southern France, and Magyars attacked town in central Europe
- Europe becomes a place of conflict and unstable
Feudalism Rises
- In this conflict feudalism emerged as a way for kings and nobles to hold onto their power
- Feudalism based on agreement b/n lords and vassals
- Lord = powerful noble who owned land, gave pieces of lands called fiefs to vassals (lesser nobles)
- Vassals = gave service to the lord in his court and army in exchange, often knights
- Also hired their own knights (if they weren’t knights)
- Had to pay taxes to the lord
- Serfs = worked on the land of a lord or vassal in return for shelter and protection
- Were like peasants
- Made up most of the social class
- Feudalism created new political structures of small kingdoms ruled by kings or nobles
Social Classes of Feudalism in Europe
Ordered from highest ranking to lowest ranking
Pope/Emperor/Patriarch
- Pope
- Religious leader of the Roman Catholic Church (after the East-West schism)
- Had authority over everyone (including kings and nobles)
- Could excommunicate people (banish them from any ties with the Church)
- Emperor
- Political leader of the Eastern Orthodox Church
- Was a political leader, so could not really give orders to the patriarch
- Sometimes had conflicts with the Pope
- Patriarch
- Religious leader of the Eastern Orthodox Church
- Gave kings, nobles, and others more freedom than the Pope
Kings
- Ruled over large areas of lands (kingdoms)
- Still had less authority than the Pope
- Would eventually form monarchies and gain power near the end of the Middle Ages
Nobles (same ranking as clergy)
- Often lords or vassals
- Lived in manors & controlled the estate
- Manor can sometimes refer to the entire estate or the large house in the center of the estate
- Noble and his family lived in the house in the center of the manor
- Much of the estate was farmland which serfs who served the noble worked on
- Land on a manor supplied the residents with most of the things they needed from farmwork to woodwork
- Few left the manor (whole estate)
- Basically self-sufficiency
- House was a castle or was fortified with thick walls
- Thick walls had narrow slits which archers could shoot out of but hard for arrows to get in
- House was also usually built atop a hill with a moat surrounding it
- Was also often very dirty, people slept in the main hall which was not comfortable
- Noblewomen were subject to their husbands or fathers
- They had little power and no say in who to marry
- Took care of cleaning, cooking, clothing, and medicinal care
- Ladies of the house also had little power but did have power over female servants
- They took over the manor & estate when their husbands were away at war
- Some noblewomen became abesses (head of an abbey or community of nuns) or ruled over their own fiefs
Clergy (same ranking as nobles)
- Owned land so had much power and wealth
- Influenced many parts of medieval life
- Ceremonies held by the church guided baptism, marriage, burials, and more
- Had the power to condemn or forgive sinners
- Also meant that the clergy has the most comfortable lives
- Had power over everyday activities
- Monastery = complex community of different buildings within itself
- Granaries, breweries, bakeries, wineries, abbey churches, libraries
- Monks inside the library copied manuscripts and made copies of the Bible
- Monks & nuns also taught children, fed the poor, cared for the sick, and provided shelter to travelers
- Clergy worked long hours for few rewards
- Their dedication to the Church was like a vassal to a lord
Knights/Vassals
- Knights were often lower vassals and fought on behalf of lords for :
- land, food, lodging, armor, and horse
- Training for a knight
- Starts as a page, then a squire, and then finally a knight
- Knights were skilled horse riders and fighters
- Some knights were younger sons of nobles who didn’t have land
- Knights lived by a code of honor called chivalry
- Had to demonstrate a strong religious faith and willingness to defend the Catholic Church
- Also expected to protect the weak and women
- Had to fight against injustice and show courage
Peasants/Serfs
- Worked in the land for nobles
- Serfs mainly :
- Had to get permission to leave the manor, marry, give or sell property, and change jobs
- If they escaped for a year and a day they were considered free
- Serfs were very poor
- They lived in small damp huts made of wood and mud
- Ate stale bread and vegetable stew
- Peasant men farmed the land, while peasant women farmed the land and made clothing & food
- The economic basis of the manor was based off of serfs farming the land
- Serfs gave up most of their crops to the lord
- Worked some days on their own farms rather than the lord’s
- Serfs (not free peasants) were “bound to the soil,” which meant that they were part of the property
- If a new lord came, they stayed on that property under the new lord
Guilds & Towns
Revival of Towns
- As lords became more powerful lands became stable and peaceful
- Merchants began to travel again and settled in places that would eventually become towns
- Towns became popular again
- Townspeople included : craftsmen, tradespeople, peasants, second sons of nobles, and freed serfs
- Towns also had guilds
Guilds
- Groups of people who practiced the same trade or occupation
- Tanners, blacksmiths, shoemakers, different craftspeople/artisans had their own guilds
- Guilds regulated trade and controlled who entered the guild
- To enter a guild there were multiple levels (like becoming a knight)
- First you were an apprentice, then became a journeyman through trade
- After you became a journeyman, you would become a master to finally join the guild
The Church and its Power
Hierarchy and their Roles
- Pope
- Political and religious leader of the church
- Also known as the Papacy
- Cardinals
- Helped the Pope run the church
- Bishops
- Ran dioceses
- Areas with several churches
- Priests
- Ran individual churches
- Administered sacraments to Catholics
- Monks & Nuns
- Lived in isolated communities called monasteries
- Learned to read Latin and translated and copied religious texts
- Grew their own food
Jobs of the Clergy
- European nobles and Church leaders had much in common
- Went to school together and nobles sometimes became church leaders
- ∴ Supported each other
- Clergy helped political leaders run their kingdoms
- Local priests kept records of births and deaths in their parish (area served by the church)
- Was important information to run the kingdom
- Church was very wealthy
- Got its income from the property it owned (the Church had a ton of property)
- Pope’s wealth was greater than that of any individual monarch; Pope’s authority was also greater than kings
- Pope was so powerful that many people wanted to cooperate with the Church
Conflict b/n Monarch and the Church
- Pope Gregory VII and Emperor Henry IV had a conflict in the late 1000s
- Henry gained power by appointing church officials
- Gregory changed this by saying that laypeople (people who are not clergy) could no longer appoint church officials
- Henry responded to this by bringing together the bishops that supported him and declaring Gregory’s election invalid and demanded that he step down
- Gregory further responded by excommunicating Henry from the Church and telling his subjects that he was no longer emperor so they didn’t have to obey him
- Conflict was resolved when Henry begged for forgiveness
- Henry spent 3 days in the snow in beggar clothes outside the Pope’s residence
Religious Orders
- Religious order = group of people who live by rules based on their order
- Monastic order contain monks and nuns
- Separated themselves from society to focus on service to God & prayer
- Friars were also a religious order
- Traveled to preach the word of God
- Were mendicants (lived off of begging)
- Franciscans were the most important Friar/mendicant order founded by Francis of Assisi
- Francis called upon his followers to live without property and serve as teachers, healers, and friends to all living things
Universities
- Schools were established at cathedrals and eventually expanded into universities as cities grew
- Were centers of power for bishops
- Nobles attended these universities
- Scholars studied classical philosophers & Muslim scholars & the Church preserved and interpreted Greek texts or Latin and religious texts
- Church scholars translated these texts into Latin to be available at the universities
An Age of Faith
- Middle Ages was also called an “Age of Faith”
- Commonpeople lived according to the church’s principles and sought salvation
- In order to find salvation people accepted the beliefs of the Church, lived a moral life, performed good works, and paid a tithe (10% of the produce from their land) to the Church
- Church also highly influenced the lives of the people
- Churches were the center of every village and town
- Church bells announced the time for work, meals, rest, mass, and worship service
- Church holidays made time for peasants to rest from their farm labor
- Christians celebrated events in the life of Jesus and remembered famous saints by attending mass
- They feasted, danced, and visited friends & family
- A shared faith of the people gave them a sense of community
Church Art and Architecture
- Art in the Middle ages portrayed events in the life of Jesus through paintings and sculptures
- Paintings were very stylized
- Two dimensional, had gold backgrounds, used rich, dark, colors, and had little detail and emotions on faces
- Gothic cathedrals were gigantic buildings with large interiors
- Designed to represent the power of God
- Used artistic elements such as sculptures of Jesus & the saints, paintings of the life of Jesus, and stained glass windows with stories of the Bible
- Cathedrals were also where the bishop’s throne was located to demonstrate his power
- Gothic architecture in general dominated Europe
- Ribbed arches emphasized pointed ceilings, and flying buttresses which supported the heavy structure of cathedrals
- The goal of most religious art and architecture was to serve as an office for religious leaders
- Also gave the experience of heaven on Earth and bring awe at the power of God
Schism of 1054 (East-West Schism)
Icons
- Nonrealistic, flat images of Jesus and the Saints meant to put the viewer in a spiritual frame of mind
- Used in Byzantine churches to worship or honor the religious figures they worshiped
- Some lit candles before them or carried them in religious practices
- Some didn’t like icons because they feared that people worshiped the icons themselves as gods
- Byzantine Emperor Leo III thought that the icons were being worshiped as gods
- Ordered for them to be destroyed
- Pope Gregory III thought that icons were important for honoring holy people of the past
- Also thought that they provided a way for people who couldn’t read to learn about their faith
- Favored icons & condemned Leo’s actions
Crowning of Charlemagne
- Gregory crowned Charl the true and only holy Roman emperor for Charl’s support
- Was a big deal because the Byzantines believed that the Byzantine emperor was the only rightful emperor
- The emperor should technically come from the Byzantine empire
- Was a direct challenge to the Byzantine emperor (& their empire)
The Schism
- Question of whether the western pope or the eastern patriarch was supreme reached its climax
- Also questioned who controlled the churches in S. Italy
- The Eastern Patriarch Cerularius lost the argument and closed churches in Constantinople
- Pope Leo IX excommunicated Cerularius, which then Cerularius of the East excommunicated Leo in return
- Caused the western and eastern churches to split into the Roman Catholic (Western) Church and the Eastern Orthodox (Eastern) Church
The Crusades (4 Main Crusades) & Reconquista
First Crusade
- Called for by Pope Urban II to reclaim the holy land of Jerusalem from the Seljuk Turks and unite the western and eastern Christians
- Wanted to make pilgrimage possible
- Also wanted to redirect knights to a holier cause (they were getting out of hand)
- Knights, princes, foot soldiers, archers, cooks, priests, and women went
- Knights & princes went because they saw success in warfare as a way of gaining power and land
- Peasants went because they wouldn’t have to pay rent to their lords and just for the adventure
- Anyone who died during the Crusades was promised salvation
- Crusader States
- Small outposts that were run similar to feudal kingdoms in Europe
- 4 main states were Edessa, Antioch, Jerusalem, and Tripoli
- Kings had no more power than a feudal lord of these states
- Crusaders claimed control over the holy land after this crusade
Second Crusade
- Called for because Muslim Turks began to take over the Crusader states
- Christians struggled because they fought amongst themselves (specifically the armies of Germany & France)
- Were also exhausted due to the long and hard journey
- Saladin = leader of the Muslim forces in the late 1100s against the Crusaders
- Was a Muslim political and military leader (who was very strong) that took supreme control over Syria & Egypt and recaptured Jerusalem
- Name means “honoring the faith”
- Signed a peace treaty with King Richard (he respected him)
- Saladin attacked Tiberias, a capital city of a crusader state
- Near Tiberias the Crusaders stopped to rest near the Horns of Hattin
- At night the Muslim force surrounded and outnumbered the Crusaders, and set fire to the dry grass around them
- Muslims attacked the Crusaders through the fire and won
- Most crusaders died or were enslaved
- Muslims controlled the holy land in the end
Third Crusade
- Called for to reclaim the holy land from the Muslims
- Aka “Crusade of Kings” because three kings assisted in recapturing Jerusalem
- Frederick I of Germany
- King Richard of England
- King Philip II of France
- King Richard had the nickname “the lion heart” and was a military genius famous for his courage in battle
- King Richard and Saladin fought many battles and were evenly matched
- They eventually got tired of fighting and signed a five-year treaty which allowed them to keep their cities and for pilgrims to freely visit the holy places
- Both respected each other
- Muslims & Saladin had control of the holy land in the end
Fourth Crusade
- Venetians said that they would bring the crusaders to the holy land by sea in return for ensuring their choice for the next Byzantine emperor
- Crusaders kept their promise however the people rebelled against the new emperor
- Crusaders had to seize Constantinople and pillage it in the Sack of Constantinople
- Crusaders burned libraries, destroyed churches, and stole valuable art, jewelry, and gold
- They did not make it to Jerusalem in the end
- The spirit of the Crusade has been lost to be replace with hunger for wealth
- People lost respect for the crusaders
- Muslims controlled the holy land in the end
Positive effects of the Crusades
- The expansion of trade
- Crusaders passing through Europe created a need for services
- They also brought luxury goods and negotiated treaties
- Venice, Pisa, and Genoa made treaties with Muslim rulers
- Battles during the crusades helped introduce gunpowder
- Also taught the Europeans more advanced weapons and tactics
- European poetry and music grew after hearing of Arabic love music and literature
- Chivalry developed “courtly love” which helped women to be not seen as inferior
- The Crusades also strengthened the Church’s desire to spread Christianity and take over the Muslim Empire
- Also discovered exploration as a way to spread Christianity around the world
- Feudal lords were killed and landowners went bankrupt
- Strengthened nation governments because the land would return to monarchs (kings & queens)
- Allowed europeans to see gain knowledge of life in the other parts of the work
- Developed new ways to do things better (military, goods)
The Reconquista
- Was the reconquest of the Iberian Peninsula by the Christians
- Completed in 1492 after King Ferdinand and Queen Isabella forced out all the Muslim and Jewish rulers & their followers
- Reunified Spain after Muslim unity over the peninsula died down
- As Muslim unity broke down, the Spanish and Portuguese kingdoms took advantage and defeated the Muslim forces
- Ferdinand and Isabella reunified Spain through religious and military authority
- They captured cities and Church officials would punish people who opposed Church teachings through the Inquisition
- Inquisition = a court that was used throughout Europe
- Tortured or executed many Muslims
- Was also used to unify Spain
Changes in Europe - End of the Middle Ages
The Plague
- Killed tens of millions of people in Europe, North Africa, and western Asia
- Wiped out ⅓(agreed by most historians) of Europe (could be much higher even up to 50%)
- Started in Asia in the mid 1300s and came to Europe through land & sea trade routes
- Disease first touched Italy in 1347
- Aka Black Death or Bubonic Plague
- Symptoms included :
- severe chills, fever, convulsions, vomiting, dark spots on skin, and swollen glands
- Those infected were usually dead within a few days
- Buboes
- Christians saw the plague as a punishment for sin
- Muslims saw it as testing their faith in God
- Wars stopped for a short period of time
- Landowners were ruined by shortage of labor
- However lack of labor also allowed workers to demand higher pay for their services and weakened feudalism
- Jews were scapegoats and accused of causing the plague by poisoning wells
- Were driven out of many German towns
- Plague killed around 20-30 million people by 1400
Rise of Central Governments
- Power shifted from nobles to kings from 1100s - 1300s
- ∴ kings attempted to form monarchies (strong central governments ruled by a king or queen)
- Kings & queens collected taxes, created large armies, & ruled their subjects through central governments
- Revolts from nobles against kings and battles between kings for territories, money, and power over the people caused large amounts of war
- Wars raged on constantly from 1300s - 1400s
- Longest war(s) (in general) was the Hundred Years War between England and France; made monarchies stronger
- Towns favored monarchies b/c they brought stability and made trade reliable
The Hundred Years War
- Was actually a series of wars from 1337 to 1453 between England and France
- Began when William, Duke of Normandy, claimed to be the rightful king of England and captured England
- Aka William the Conqueror of France
- The English king, Edward III, responded by claiming he was the rightful king of France and attacked France in 1337
- The English had several victories, and decided to attack Orleans
- A french peasant girl named Joan of Arc led the French to victory in the battle of Orleans and won many other battles
- By 1453 the French had driven out the English from France
- Became a turning point in medieval technology and made monarchies stronger
Improved Military Technology/Strategies
- Newly developed longbows shot armor piercing arrows and killed horse-mounted knights in heavy armor
- Europeans were able to learn about Greek, Roman, Indian, Chinese, and Muslim war technology from the Muslims during the Crusades
- Muslim armies used hand grenades and flamethrowers
- Chinese used gunpowder
- Guns & gunpowder were introduced in the 1320s and made a big impact on wars
- Cannons → smaller cannons → hand-held cannons → harquebuses (long handguns)
- Rulers began hiring professional soldiers for large armies
- Mercenaries = soldiers that you pay
Trade and Commerce Grow
- Large scale manufacturing and commercial activity was centered in towns
- Towns (especially those on trade routes) were prosperous with people buying and selling food & goods
- As towns grew trade grew
- Town society was made up of :
- merchants, shopkeepers, and artisans who were socially above the laboring class and below the nobility
- also included women
- Commercial class focused on achieving success and wealth rather than following the church’s teachings
- Prosperous towns in Europe were mostly in Italy because of its location between three continents
- Italian traders bought and sold fine woolens, colored cottons, and silk woven with gold & silver
- They traded furs, leather, jewels, ivory, metals, and spices
- Many goods were exchanged
- Wealthiest Italian merchants were bankers and money changers
- Antisemitism = hatred against the Jewish peoples
- International trade brought upper-class and the commercial class into contact with new ideas and exotic goods
- Individualism = the idea that each person should be free to develop and pursue his or her own goals & the lure of money and success
- Became an important value
- People began to see themselves as valuable and seek/demand better pay rather than just providing for their lords or family
Joan of Arc
- Grew up in a small French village known as Donremy and had never learned to read or write
- Left home at the age of 17 insisting that God had called her to help drive the English out of French territory
- To join the French army she was tested by Charles, heir to the throne, and had to find him in a room full of nobles dressed as him
- Joan passed this test and joined the French army after convincing him she had spoken the truth
- Charles gave Joan supplies and soldiers and sent her off to Orleans, where a bloody battle had erupted for months
- Joan wrote a letter to the English hoping they would surrender, but they declined
- She fought alongside her soldiers and defeated the English in four battles, but was eventually captured in 1340
- She was tried as a witch and heretic, someone who speaks beliefs different from the accepted church opinion
- She was sentenced to be burned at stake, and died at 19
King John & the Magna Carta
- After the death of William the Conqueror, feudal lord’s power grew with their wealth
- King John led England into losing many wars
- He lost all of his land in northern France which angered vassals who had land in that area
- Due to a disagreement with the pope, the Church stopped supporting him
- The nobles renounced allegiance to John and cornered him in a meadow outside London where they forced him to put the royal seal (approval) on a document called the Magna Carta (aka Great Charter)
- The Magna Carta acknowledged the rights of nobles and prevented a king from taking those rights away
- Also made sure that no free man should be imprisoned, dispossessed, banished, outlawed, destroyed, or sent upon except by trial
- The Magna Carta become the basis for future reforms such as the Bill of Rights and marked the beginning of feudalism’s decline
- This was due to ideas of personal freedom and liberty being firmly established
Renaissance
The Renaissance Begins
What was it?
- Cultural movement from the 1300s-1600s that started in Florence, Italy
- Led to advances & creativity in art, writing, intellectual thought, and economics → Revived Europe
- Stands for “Rebirth” - rebirth to Greek & Roman classical ideas
- Created new way of thinking called Humanism
- Way of thought that focused on human beings and their potential for achievement in not just one thing but as many things as possible.
- Goal was to create well-rounded people (good in every subject/aspect of life, i.e Da Vinci) and encourage human achievement
- Renaissance Man = man who excels in many aspects of life (i.e Da Vinci)
- Concept of Renaissance women didn’t exist but Queen Elizabeth I = example of a Renaissance women
- Humanism made people think for themselves and do good for the single person, not always for the group.
- Petrarch was a famous & impt. humanist leader.
- Stressed the classics & teachers of the classics like Cicero & Livy
- The classics are previous thinking methods of civilizations such as the Romans and the Greeks and what they thought abt the world.
- Similar to individualism in that it stressed the individual rather than the group
- Weakened power of the Church because people began to question the power and teachings of the Church and search for their own answers
- Thinking rather than just blindly following the Church
- Could still enjoy life and think for themselves while being good Christian
- Big cause of experimentation and new inventions in the Renaissance
How did it begin?
- Feudalism fell due to :
- Plague (caused peasants to stride away from manors and look for their own jobs)
- Hundred Years War
- New weapons, rise of central governments & monarchies
- Commerce & trade expands
- Trade expanded through :
- Less warfare
- Rise of towns (merchant class expanded as peasants looked for their own jobs)
- Reopening of the Silk Road
- Marco Polo’s journeys encourage more exploration and int. trade with Asia
- Brought new ideas → Learning flourished → Humanism prospers
Where it Began (The Renaissance in Italy)
- Italy = good location because located between 3 continents
- good for exchange of ideas, goods, and growth of cities
- Florence = Center of banking → was very wealthy so many people became leaders in Florence
- One wealthy ruler family = Medici Family
- Rulers became patrons (supported artists) which meant that artists could work full time on their art
- Gained fame & painters would paint portraits of patrons’ families
- Mostly benefited upper class
House of Medici
- Mainly controlled Florence & Tuscany
- Owned Medici Bank - largest bank in 1400s
- Had double entry bookkeeping system w/ debits & credits (like credit & debit today)
- Included 4 popes, 2 queens, & Dukes of Florence
- Machiavelli
- Florentine historian, politician, diplomat, philosopher, humanist, writer
- Founded modern political science
- “The ends justify the means”
- “Be strong as a lion & shrewd as a fox” (The Prince)
- Tricking enemies or manipulating people
- Wrote The Prince
- Leader’s job is to grow and expand the state rather than administer justice
- Focus on benefiting the state (doesn’t matter if its good or bad actions)
- Is it better to be loved or feared?
Life in the Renaissance
Social Classes
- Socioeconomic classes (based off of both social status & wealth)
- Top = patricians or nobles (like from Roman Empire)
- Businesspeople who owned major guilds
- Cloth manufacturers, bankers, doctors, lawyers
- Controlled govt. and wealth of cities
- Patrons
- Middle = Commercial Class
- Shopkeepers & artisans who worked for minor guilds
- Blacksmiths, leather tanners, carpenters, butchers
- Could move up but was difficult
- Some work long & hard but few change classes
- Bottom = Lower Class
- Laborers like boatmen, porters, peddlers
- Peasants
- Lowest of the lower class
- Made up ¾ of the population
- Wealthy didn’t allow them to have a say in the government.
Jews & Ghettos
- Jews worked mostly in finance (weren’t allowed in most occupations & owning land)
- Jews lived in a neighborhood called a ghetto
- Gated in behind walls & controlled
- Had their own community lives
- Markets, hospitals, courts, also had high level education
Women & Men
- Men (upper class young age)
- Learned about family business
- Completed school → sent to other countries to learn international business → returned to family business
- Strived to become Renaissance Men
- Men (upper class older age)
- Married to join social & political fortunes of families
- Women (Upper Class)
- Expected to take care of the house & children
- Could become Renaissance Women
- Some became artists & writers
- Learned to read & books opened their minds to new ways of thinking
- Women (Middle/Lower Class)
- Worked in trades
- Prospered w/ rise of the economy
Renaissance Art
What was it like?
- Focused on form, decoration(details), and subject matter.
- The types of art ranged from sculptures, murals, drawings, paintings.
- It showed the importance of people and nature, not just religion.
- Figures took the ideal human body’s form
- Active and moving
- Clothed or not
- Scenes of daily life
- Expressed emotion
- Colors often responded to the lighting of the area, lots of detail in paintings, and symmetrical paintings that had balanced content on both sides.
Techniques Used
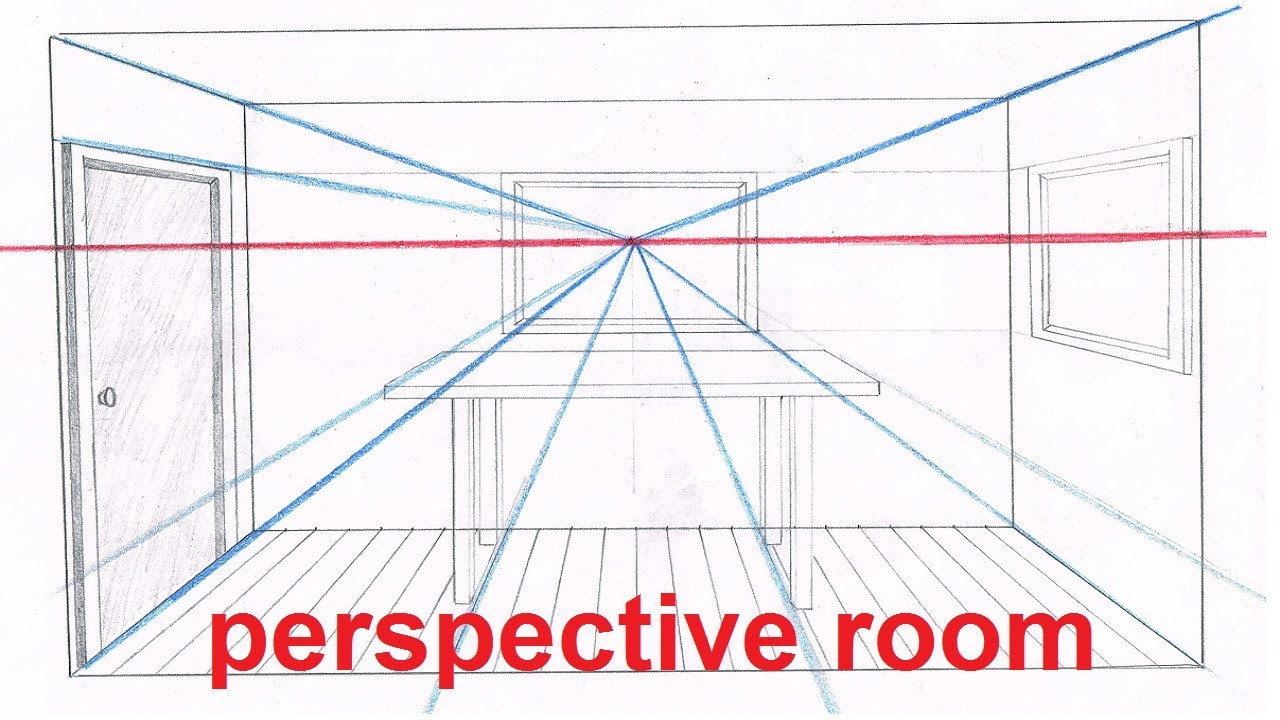
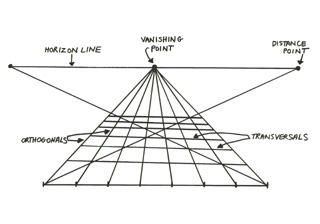
- Linear Perspective
- Used to show depth and distance in images
- Horizon line = line where the vanishing point is usually located, horizon = where ocean or land meets sky
- Vanishing point = Point at which the convergence lines meet
- Convergence lines = could be easy or hard to see, intersect at the vanishing point
- Atmospheric Perspective
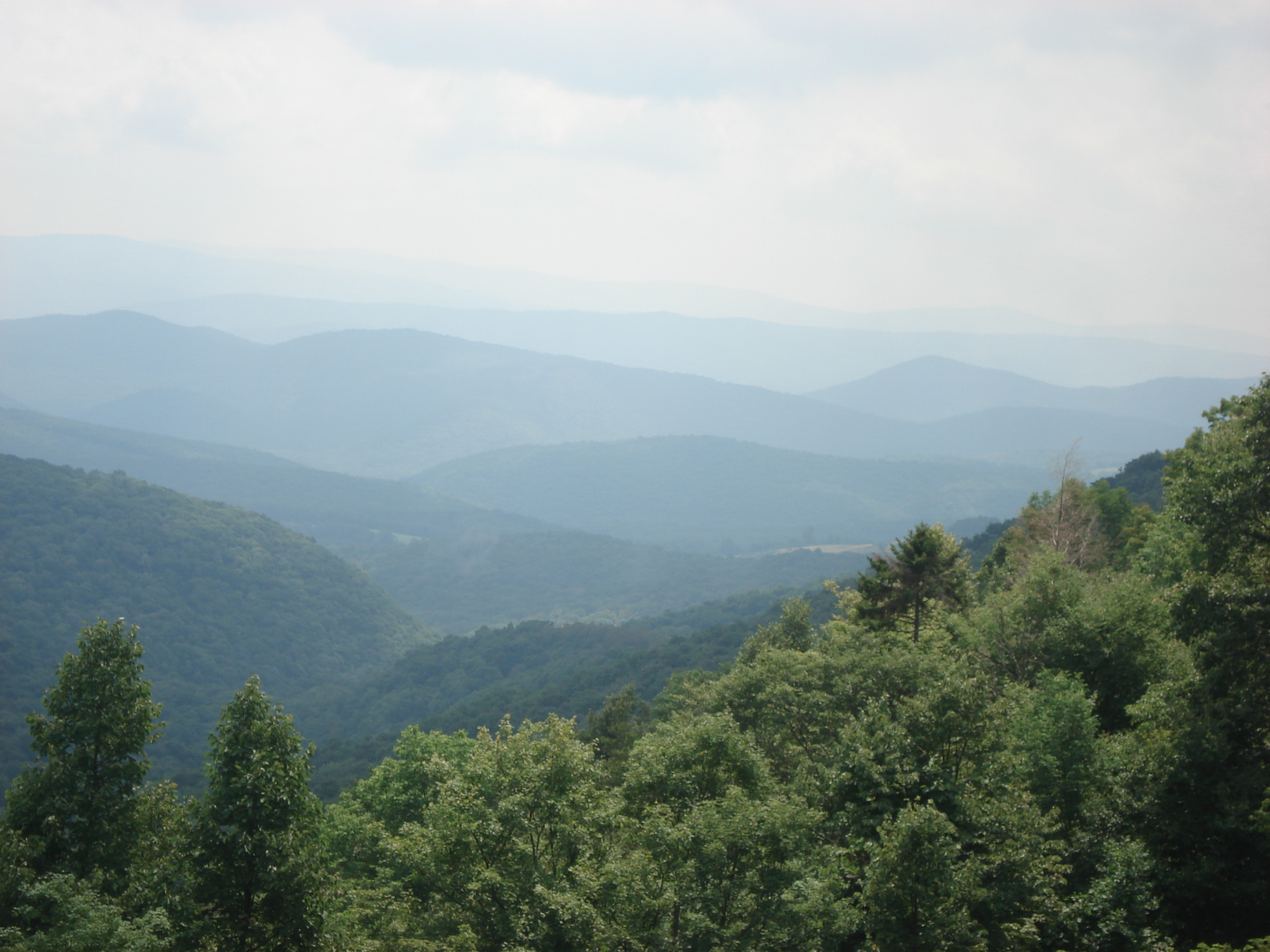
- Atmosphere on seeing depth
- Also another way to show distance/depth
- Creates contrast from the foreground & background
- Foreground is more detailed & less blurry to show more important details, background is more blurry & less detailed as details are less important
- Objects in the distance are blurry, pale, and less detailed
- Can be thought of as the “portrait” mode when taking an image on your phone

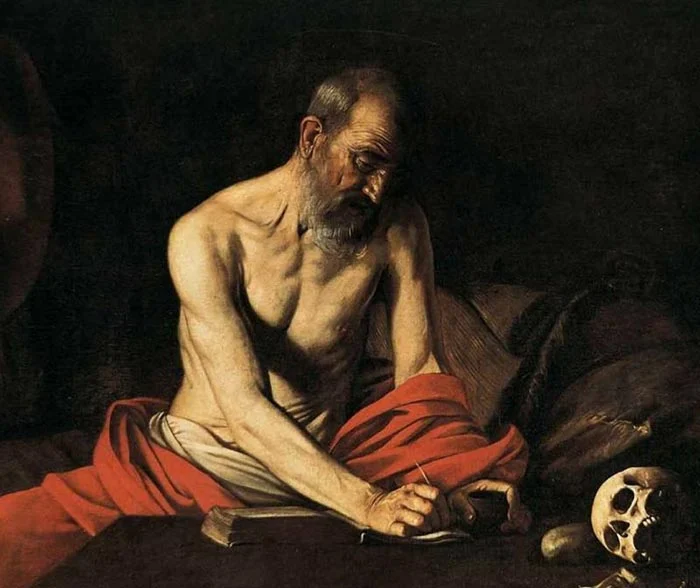
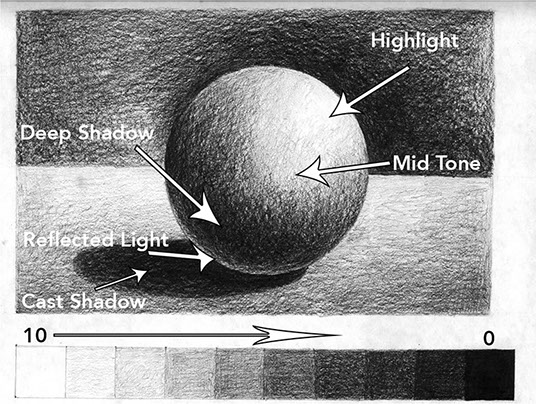
- Chiaroscuro (pronounced kee-ah-ruh-skyur-oh)
- “light-dark” in Italian
- Contrast between light and dark
- Plays with light and shadows to show volume
- Can also draw your attention to a certain part of the image by showing light on that specific area

- Realism
- Basically using studies of anatomy in art
- showing detail of the human body
- Measured proportions
- Wanted to create the ideal human figure
- Showed emotions
- Examples are muscles, blood vessels, wrinkles, tiny hair strands
- Mostly seen in sculptures

- Fresco
- Technique for murals where you would paint on a wall while the plaster was still wet
Famous Artists
- Michelangelo
- Famous for contending for the title of Renaissance Man
- Pieta, Moses, Sistine Chapel, David, Creation of Adam
- Leonardo Da Vinci
- Famous for being an example of the Renaissance Man
- Most diversely talented person to have ever lived
- Mona Lisa, The Last Supper, Self-Portrait
- Raphael
- Famous for perfection & grace of his paintings
- Saint Catherine of Alexandria, The Wedding of the Virgin, The School of Athens
- Titian
- Sandro Botticelli or Alessandro Filipepi
- Famous for his mastery of linear perspective (or perspective in general)
- Map of Hell, Primavera, Birth of Venus, Mars & Venus
Famous Architects
- Filippo Brunelleschi
- Il Duomo
- Famous for being an insanely large dome, was very hard to construct

Famous Writers
- Dante Alighieri
- The Divine Comedy (or Dante’s Divine Comedy)
- Cervantes
- Machiavelli
The Northern Renaissance (England, Germany, etc.)
Ideas from the North
- Rulers would sponsor artists from Italy, but artists would eventually move north due to war
- Northern artists move south
- Caused Renaissance technique to combine with Northern traditions
- Northern style was :
- Altar pieces & medieval manuscripts
- Detailed, factual, and had more realism
- Italian was ideal rather than real
- Renaissance Woman? = Queen Elizabeth 1
- Time when she lived was the Elizabethan Age (1558 - 1603)
- Promoted the Renaissance in England by speaking several languages, writing poetry, supporting artists & writers
Famous Artists From the North
- Jan Van Eyck
- Madonna of Chancellor Rolin, The Arnolfini Portrait, Annunciation
- Famous for perfecting (and maybe creating?) oil painting
- Used many layers of oil paint
- Variety of colors in clothing/jewelry, realism, personalities of subjects
- Pieter Bruegel (the Elder)
- The Peasant Dance
- Included realistic details
- Paintings depicted individuals in everyday life w/ lots of people
- Albrecht Durer
- The Four Horsemen of the Apocalypse woodcut
- Created paintings, etchings, woodcuts, drypoint, drawings
Famous Writer(s)
- William Shakespeare
- Had major talent in writing → was the most famous & popular writer
- His works showed that he had a strong understanding of human nature & life → works still performed today
- Romeo and Juliet, Hamlet, A Midsummer Night’s Dream
Advances
- Printing Press
- Created by Johan Gutenberg
- He printed the Gutenberg Bible & many other documents for the Renaissance & Reformation
- Machine that pressed paper against a full tray of inked moveable type
- Important because it allowed copies of books to be produced more efficiently
- Helped to spread ideas & encouraged people to become more literate
- Vernacular
- A person’s native language
- Allowed people to read books in their everyday language
- Was encouraged to by the printing press (writers/copiers didn’t have to write as much)
- Bible was translated into the Vernacular across Europe
- Allowed people to read the Bible for themselves and therefore interpret their own conclusions on religious teachings
- Examined the Church and their religious claims and interpretations more critically
- Math & Science
- Introduced letters to algebraic equations
- Developed theories about the universe
- Sun could be center of the solar-system
- Sun center = heliocentric, Earth center = geocentric
- Had better understanding of Earth’s surface
- Had more accurate maps in cartography
- Better understanding of the human body in anatomy
Reformation
Corruption of the Church & Beginning of the Reformation
Corruption
- Church was powerful, wealthy, and involved in political matter
- French are not happy with the Church
- French pope moved the capital to Avignon because Italy is unstable
- Other rulers think French is trying to control the Church
- Capital moves back to Italy where an Italian Pope is elected
- French don’t like the Pope & two popes get elected
- Clement VII of France & Urban VI of Italy
- Causes the Great Schism of 1378
- Ends in 1417 when both popes stepped down and a new single pope was installed
- Bishops begin to form councils (groups of church leaders) to decide matters of church law & faith
- Gained more power than the Pope & monarchs began to control them
- Church gained more interest in wealth & power than ruling for religious matter
- Sold indulgences (forgiveness), church positions (simony)
- Church positions being sold meant that unfit people would be in charge, caused decline of the Church
- Clergy lived luxurious but immoral lives by having mistresses & children, pursued power
Beginning of Reform
- Speaking out against the Church was dangerous & scary
- Labeled as heretics, could be excommunicated or executed
- Some brave people like John Wycliffe said that monarchs should rule churches in their own kingdoms
- Also translated the bible from Latin to English
- Was threatening Church’s power
- Spiritual movements like the Mystics begun
- More people questioned the Church’s power and its leaders
- People thought for themselves (Renaissance ideas of individualism & humanism)
- Paved the way for Martin Luther
Martin Luther & Protestantism
Martin Luther
- Started off as a lawyer, but when a great thunderstorm struck his town, he promised God that he would become a monk if he survived the storm.
- When Luther became a monk, he studied the Bible and found that the only path to true salvation was through faith alone.
- Luther believed that justification was not to be bought and the church had no right to sell justification
- Believed salvation was only given by God.
- Told many that the Bible was the only authority for Christians and the clergy weren’t the only people that could interpret the bible.
Beginnings of the Reformation
- In 1517, Luther nailed his 95 Theses to a church door in Germany for his ideas and beliefs to be debated about.
- The 95 Theses started a religious movement to reform the church.
- Hence it was called the Reformation
- Because of the way Luther and many others protested in this movement they were then called the Protestants
- These actions angered the Pope and he signed a bull, an official declaration, condemning Luther and banning his writings
- Luther then publicly burns this bull
- Pope Leo X then excommunicated Luther, and Charles V, the Holy Roman Emperor gives Luther a final chance to recant, or take back his actions.
- Luther refuses and he then becomes an outlaw
- In this time he hides in the Prince of Saxony’s castle through a fake kidnapping
- Luther writes more books, pamphlets, and translations of the bible of his native language.
95 Theses
- Vocab:
- Recant: to take back what one said.
- Remission: forgiveness
- Repent: to say that one is sorry, wrong, and that they won’t do it again.
- Purgatory: the place between heaven and hell where souls go to be good enough for heaven
- Mortification of the Flesh: to give up the desires of the flesh.
- Canonical: to be of church law
- Tribulation: trials, problems, hard times, difficulties to overcome
- Doctrine: beliefs held by a group of people
Spreading of Protestantism
- Many more people liked and followed Luther’s ideas because:
- People wanted a more simple and direct relationship with God
- Individualist and Nationalism ideas began to grow more popular
- The printing press kept on spreading Luther’s works through printing
- In fact, a war broke out in Germany against Protestant and Catholic princes, but was solved through the Peace of Augsburg
- Peace of Augsburg stated that if a Prince allowed Protestantism in a state it would be allowed, but if not it wouldn’t be.
Peasant Revolts
- Peasants began using Luther's ideas if individualism and individual freedom to justify revolts
- Believed they had God’s support to fight for better living conditions.
- Luther condemned the peasants for this unlawful matter surprising them.
- He also criticized the nobility for ignoring the peasants conditions
- He lost many followers both nobility and the peasants.
Denominations of Protestantism
Reformation Leaders
- Martin Luther
- John Calvin
- Desiderius Erasmus
- Dutch priest
- Wanted people to pursue true Christian faith
- Criticized reformers because he thought that they were trying to divide the Church
- also criticized Church officials for neglecting Christian values
- John Wycliffe
- Philosopher & priest from England
- Publicly called for reform
- Questioned pope’s right to levy taxes, authority to appoint clergy without approval of the king
- Translated Bible into English (which threatened Church’s power)
- William Tyndale
- English person who worked on an English translation of the New Testament
- Anglican officials prevented him from doing so & kicked him out → moves to Germany
- Beliefs about the Anglican church that it should reject Catholic beliefs & practices since it was separated from the Catholic Church
- Captured & executed
Lutheranism
- Started by Martin Luther, was the first Protestant Branch
- Bible was the only source of religious truth & authority
- Clergy don’t need to interpret the bible for people
- Justification by faith
- People need faith in God, a good relationship w/ God, and God’s grace to earn salvation
- Justify = to be right with God, have no sins & good relationship
Calvinism
- Started by John Calvin, a French reformer who fled to Switzerland
- Theory of predestination - god had already chosen a special group of believers for salvation
- Emphasized being devoted to God, & leading a disciplined life
- No gambling, fortune telling, dancing, singing w/ music, paintings
- Followers also governed the Church through a body of leaders & ministers called a presbytery (where we get Presbyterian)
- Had to be a devoted follower & a man
Anabaptism
- Started by dissatisfied followers of Zwingli
- Lived by an even stricter moral code than Calvinists
- Believed that everyone and all other religious groups were sinners (like Nichiren Buddhism)
- Harassed and sometimes executed by Catholics & Protestants
- True Christians should leave from the state & form their own religious communities
Anglicanism
- Aka Church of England started by King Henry VIII
- Had to get parliament to pass the “Act of Supremacy” to see the Church of England as its own body
- King Henry VIII was the head of it
- Archbishop of Canterbury is the highest Church official in the sect
- Also believed in justification by faith
- Based beliefs on the Bible
- Bible & services were in English, Hence called the Church of England
- Was a mix of Catholic & Lutheran beliefs
Catholic Counter Reformation
Who, What, When, Where, How, Why?
- Pope Paul III started the Catholic counter reformation because of the frequent uprisings and revolts due to the Protestant community.
- The Council of Trent was formed and took many meetings to decide on how to rid the church of abuse and uphold and keep original Catholic traditions.
- Salvation was to be earned through faith and good works
- The pope is the best interpretation of the bible
- Still practiced the 7 Sacred Sacraments and rituals
- Clergy will accompany exploration to convert new lands to Christianity
- The Inquisition, sort of a church court, was brought back to trial not only heretics but Protestants and people who were defying church order.
- The CCR also banned Reformation texts and executed heretics.
- Art produced by the CCR was made to glorify God
- Used Gold and silver altars to show off God’s and Heaven’s riches.
- Statues glorifying God and Jesus
New Religious Orders
- Encouraged to be formed in order to purify the Church of corruption
- Society of Jesus
- Leader was Ignatuius of Loyala, people were Jesuits
- Helped to remove corruption luxurious lifestyles
European Explorers & Ancient American Civilizations
Mesoamerica
- Means “Middle America”
- Southern Mexico & Central America (no South America)
- Includes Yucatan Peninsula which stretches into the Caribbean Sea
- Divides the Caribbean Sea & Gulf of Mexico
- Elevation = height of land (above sea level)
The Olmec Civilization
Where they lived
- Lasted from 1200-400 BC in Southern Mexico
- Two major population centers: La Venta & San Lorenzo
- Made huge stone heads that were moved with sleds and rafts
- Lived in fertile environment
- Good soil for farming
- Steady supply of food and water
- Land covered with jungle (swampy, damp like rainforest)
- Difficult to clear and traverse land; rains caused floods
Way of Life
- Grew crops like squash, beans, avocados, peppers, maize
- Ate game from rivers and jungle
- Used slash-and-burn technique to farm
- Clear the land by cutting down trees → burn trees & ashes fertilize soil → use soil for farming
- Developed calendar for growing seasons
- Competed with neighbor tribes for materials, trade routes
- Jade was valuable
- Competition for resources believed to have killed Olmec
- Divided into two classes: elite (upper class), commoners (lower class)
- Elite graves had jade and precious metals to show wealth, status
- Rulers = priest-kings; ruled both government and religion
- Religion had 15 gods (most important was Jaguar-man)
- Olmec did rituals and sacrificed animals, humans to honor gods and get good weather
- Often considered the “Mother culture of Mesoamerica”
- Mother culture = way of life that influences other cultures
The Maya Civilization
Geography
- Located in present-day Southern Mexico, Belize, Guatemala, and Yucatan Peninsula
- Settlements were in rainy, fertile, regions → started farming villages
- Had to adapt to the highlands
Mayan Life
- Built palaces and pyramids for ceremonies
- Pyramids surrounded by trade plazas
- Cities built around religious centers
- 3 main cities were Palenque, Chichen Itza, and Tikal
- Also built temples which represented the Mayan Calendar
- Steps represented the number of days in a Mayan year
- Sun and moon shadows off the temple helped them to find the perfect times to plant and harvest crops
- Played a ball game in which two warring kingdoms would compete
- Losing kingdom’s captain would be decapitated
- Reached around 3 million people at its height
- With increase of population → demand of food grew
- Caused them to develop new farming techniques to farm on hillsides
- Built moats & canals for irrigation & spread fertile soil
- Main crops were maize, beans, avocados, melons, and squash
- Traded for jade, feathers, and cacao beans
- Religion was based on gods who controlled elements of nature
- Worshiped rulers as well because they believed they could influence gods, sacrificed foods, animals, and humans
- Also believe that they could move through the world of humans and gods
- Sacrifices like feeding the gods, they put human hearts on the statue of the rain god
- Most famous ruler was Lord Pacal and he ruled Palenque
- On his tomb it depicted him falling down the World Tree
- 3 regions of the Mayan Universe were :
- Upper World
- Celestial monster, ancestors, gods, live there
- Middle World
- Underworld
Achievements
- Mayan civ. from 1500s BC to early 1500s AD but height was 250 AD - 900 AD
- Had no connection to Europe but achieved :
- Number system based on 20
- A symbol for 0
- Astronomical charts
- Writing system of hieroglyphs
- Detailed codices
- Record books about ceremonies, astronomical observations and calendars used to determine times for planting and harvesting crops, hunting, and performing religious ceremonies
- Also created amazing architecture and art (were artisans and weavers)
- Used jade, gold, and shells in weaving and art
The Fall of the Maya
- Different theories about how they fell
- Environment Theory
- Land of the Maya could not produce enough food for the growing population because it was overused & soil became less fertile → people either starved or moved to find new land
- Invasion Theory
- Neighboring tribes attacked smaller Mayan cities and weakened the Maya to gain access to resources & trade routes
- Revolution Theory
- Maya’s later rulers abused their power → Mayans started a rebellion that weakened them
- Abandonment Theory
- All of the above happened → Mayans abandon their civilization and move to new parts of Mexico and C. America
- However people of Mayan descent still live today
The Aztec Civilization
Origins of the Aztecs
- Where previously hunter/gatherers who had traveled and migrated to find a land where they would see an eagle on top of a prickly pear cactus eating a snake according to their god.
- The land was called Tenochtitlan, aka. “Place of the Prickly Pear Cactus”.
- They settled on an island in Lake Texcoco that was mostly made of swamp and didn’t have many resources, but they adapted by:
- Using reeds and mud to make huts.
- Caught fish & birds
- Farmed using Chinampas or “Floating Gardens” (narrow strips of land surrounded by canals that could be tended to on boat.
- Grew corn, squash, chili peppers, beans, & tomatoes.
- Aztecs built causeways (raised roads) that connected the empire.
- More powerful tribes forced Aztecs to serve as soldiers for them as they were weaker, but this eventually led the Aztecs to become skilled warriors.
- Aztecs formed the “Triple Alliance” an alliance between two other strong tribes, which helped the Aztecs to become more powerful as an empire.
- The strongest rulers were Ahuitzotl & Moctezuma
- The Aztec lasted between 1325 - 1521 AD and its peak population was 25 million people.
Everyday Life
- The Aztecs lived in large settlements called calpullis.
- Commoners made up the majority of the population & farming was their main job.
- Paid tribute/tax to the gov. in forms of crops, handmade items, or work/service in state projects.
- The serfs were underneath the commoners because they didn’t have the right to own land.
- At the very bottom of the Aztec social ladder: Slaves.
- Slaves were either captives of war, people who committed crimes, or people who didn;t repay a debt.
- At the very top of the Aztec social ladder: Nobles
- Served as gov. officials, priests, & warriors.
- Lived off of the tribute paid by the lower classes.
- The tribes that the Aztec conquered were allowed to keep their religion, language, & customs, but were forced to pay large tribute.
- Because of the overwhelming amount of tribute many tribes resented the Aztec rulers.
- Merchants traveled afar to bring back exotic goods and trade them in cities
- The marketplace was an important center in Aztec cities.
- The Aztecs believed that the world was alive with spirits that still lived in nature
- Thought that if people didn’t follow by rules of spirits the world would be destroyed
- The gods required prayer, thanksgiving, rituals, and sacrifices.
- Aztecs built elaborate palaces and temples, beautiful jewelry, and pottery. Archaeologists have found codices/records that told of daily life as an Aztec.
Religion & Its Effects
- Everyday life in the Aztec empire revolved around religion and the two most important gods were Huitzilopochtli (the god of sun and war) and Tlaloc (the god of rain)
- Quetzalcoatl was another major god who was the creator of the world and all living things to the Aztecs.
- Human sacrifice was common, historians think it might have been done to frighten enemies and if an Aztec was sacrificed he was promised to become a divine being.
- As the empire grew in size the Aztecs needed more land to grow crops as well as tribute to support the government more
- Therefore the Aztecs needed a well-trained army and so they became known for their skilled cruel and ruthless warriors
- This made the Aztecs the most resented/hated Empire in the Americas.
The Incan Empire
Rise to Power
- Competed with other tribes for control of the Cuzco Valley because of its fertile land, rivers, and high mountains (geographical barrier)
- Covered most of Ecuador, large areas of Peru and Bolivia, and parts of Argentina and Chile by 1525 AD
- Had no writing system so had to :
- Pass down history orally
- Memorize messages word by word through and send people to deliver them
- Called their empire Tahuantinsuyu (Land of the Four Quarters) and at its height the population was 13 mil.
A Conquering of Tribes & Controlling of Land
- Had a specific plan- first sent a scout to check military strength, the land, and the cities → then came up with a plan after hearing of the report
- Sent ambassadors to persuade the tribes to join them, but if refused then they attacked
- Stationed troops throughout their empire to stop uprisings
- Also made their religion the official one
- Forced all tribes to learn Quechua (the native Incan language) which promoted unity
- Ruler was the lord of all things
- Two classes - nobility and commoners
- Commoners worked the land as tribute to the government.
- Not allowed to travel or decide who they could marry without the government’s approval
- Nobles = govt. officials
- Government organized public projects like highways and 10,000 miles of roads throughout the empire
Farming
- Farmland divided for three parts of society - one for the government officials, religious leaders, and commoners
- Maize, beans, and squash grown in the low valleys, while llamas and alpacas raised for wool & meat in the mountains
- Growing of crops was based on the altitude of the land & called a vertical economy
- Grew a surplus of food through terrace farming on hills & mountains
- Also built canal systems for irrigation (like other civilizations)
- Markets didn’t exist since government controlled food & who got what
Religion
- Prayed to both gods & ancestors (both controlled fate)
- Inti = Sun god & most important
- Temples were built for him in all major cities & he was portrayed as a golden disk with human face
- Animal & food sacrifices most common, but sacrificed humans in crisis (floods, drought)
- Priests played major role in daily life since they predicted the future, offered prayers, and helped make important decisions
European Explorers
How did most of the explorers treat Natives?
- Gave them diseases like measles and smallpox
- Tortured & killed them for info
- Stole their gold, silver, and other valuable resources by force
- Held leaders for ransom and keeps them as puppets
- Enslaved them and forced them to work on gold mines or farms, also used the encomienda system which was like plantations that people worked on
- Forcibly baptized or converted them; if they refused they were killed or tortured
- Exception is Francis Xavier (was actually sort of nice to the natives)
Explorers & Their Achievements
- Vasco de Gama (Portuguese)
- From Portugal
- Sailed around South Africa and reached India
- Burned & Stole cargo
- Prince Henry the Navigator (Portuguese)
- Set up school for mapmakers, navigators, shipbuilders (allowed for development of caravels)
- Sponsored voyages of exploration
- Christopher Columbus (Italian by birth, sailed for Spanish)
- First European to find West Indies (Caribbean) and Americas
- Enslaved natives like Taino, Arawak
- John Cabot (English)
- Claimed parts of coastal Canada, USA for England
- Never actually settled N. America or saw natives
- But claimed their land for Spain
- Vasco Nunez de Balboa (Spanish)
- First European to see Pacific Ocean by crossing Panama (told route by natives)
- Ferdinand Magellan (Portuguese by birth, sailed for Spanish)
- Traveled across Pacific Ocean and proved it was big
- Found Strait of Magellan
- Magellan’s crew circumnavigated globe (R.I.P magellan you will be missed)
- Bartolomeu Dias (Portuguese)
- First to round the southern tip of Africa and sail up a small part of East Africa before returning back
- Hernan Cortes (Spanish)
- Conquered Aztecs (many of them died from diseases like measles & smallpox)
- Forced Christianity on them, held Moctezuma for ransom, and enslaved Aztecs to the encomienda system
- Francisco Pizzaro (Spanish)
- Conquered Incan empire & found gold, silver, and jewels
- Spread Spanish culture throughout S. America
- Treated Incans the same way as Magellan, held leaders for ransom and as puppets, overworked Incans
- Giovanni de Verrazzano (French)
- Searched for the NW Passage but failed to find it
- Instead discovered the New York Harbor
- Jacques Cartier (French)
- Explored St. Lawrence River in Canada and set up Quebec
- Failed to find the NW passage
- Amerigo Vespucci (Italian)
- One of the first people to explore and map the coasts of the Americas
- Made an account of his exploration called “New World”
- Americas named after him
- Juan Rodriguez Cabrillo (Spanish)
- First Spanish explorer to sail along the Pacific Coast
- Founded the settlement of California
- Traded & was friendly with the natives at first, but eventually fought them
- Francis Xavier (Spanish)
- Helped Ignatius of Loyola set up the Society of Jesus
- Jesuit who traveled around Asia (India, Japan) to spread Christianity
- Wanted to make religious institutions devoted to god & rid corruption
- Was nice to natives, educated them & tried to convert them without force
European Countries & Exploration
What countries participated in the Age of Exploration? What was trade between them like?
Portugal
- Government strongly supported sea exploration
- Prince Henry creates navigation school which makes new technological advances
- Dias makes it around the southern tip of Africa & Vasco continues route to India
- Gave Portugal & other European countries a direct sea route to India
- Portugal takes control of the spice trade from Muslim merchants
Spain vs. Portugal
- Christopher Columbus finds West Indies
- Leads to European colonization of the Americas & increased tension between Spain & Portugal
- Pope creates Line of Demarcation to keep the peace
- Lands to the east of the line belong to Portugal
- Lands to the west of the line belong to Spain
- Way to remember = Portugal is to the east of Spain & Spain is to the west of Portugal (country & direction mentioned in same part of the sentence)
- Later moved to the west to give Portugal more land (they only had a little bit of S. America
- Treaty of Tordesillas
- Signed by Spain & Portugal and agreed to honor the Line of Demarcation
- Ferdinand Magellan claims Philippines for Spain (R.I.P broski)
- Spain wants to establish its own trade empire & end Portuguese control over Asian trade
Other European Countries vs. Portugal
- Dutch Republic (Netherlands) forms Dutch East India Company (East Indies = Indonesia)
- Established and directed trade in Asia
- Had power to mint coins, make treaties, and create armies
- Chartered company (like HBC in Canada) meaning that it is granted rights by a royal charter for purpose of trade, colonization, trade, or exploration
- Great naval power
- Allied w/ England to break Portugal’s control of trade but then betrayed them & drove them out of the region
- Took over Malacca & Spice Islands from Portugal, set up headquarters in Java, and controlled Cape of Good Hope in Southern Africa
- England (English East India Company)
- Developed trade and control in India
- Had colonies in the West Indies & North America (British colonization)
- Wins against the Spanish Armada which weakens Spain but they are still rich
- France (East India Company [India])
- East India Company not successful
- Quebec more successful in Canada
Systems of Trade
- Columbian Exchange - movement of living things between the hemispheres (between Americas and Europe) such as potatoes & quinine (malaria cure) sent to Europe while horses sent to Americas
- Was important because it created international trade patterns controlled by Europeans → sent new goods to different parts of the world
- Triangular Trade - a three way trade system between Europe, Africa, and the Americas that brought African slaves to the Americas which lasted 300 years in which 10 million slaves were shipped to the Americas
- Created wealth for europeans but some Americans
- Moved many Africans to the Americas which created a long lasting impact on trade & the movement of wealth internationally
- Spread of diseases among Native Americans caused many of them to die (around 20 million) which helped the Europeans conquer Native American empires/tribes
- Colonization of America also led to slave trade because crops grown were labor-intensive so they needed more workers → importation of slaves
- Native Americans ran away or died from disease so African slaves more desirable
- Colonies provided home/mother country with gold and silver = more powerful
- also provided raw materials for industries and were ready markets for home country’s manufactured goods
- Some mother countries would prevent colonies from creating certain goods and force them to buy goods from the home country
Why did they explore?
+ Knowledge
- to increase their intelligence stat……
- The more they explored the more they knew about the rest of the world (exotic goods, natives in different countries, how large bodies of land/water were) & could add more to the world map
More Trade Goods
- Many exotic goods in other countries (spices, silk, gems, cotton, fabric dyes)
- High demand for these goods → more explorers could bring back = more riches
- Also wanted to avoid middlemen (they increased prices) and tried to find direct trade routes to Asia
Preventing Trade Monopolies
- Monopoly = complete control over something (like the game)
- European centers of trade like Venice had dominance over trade → other countries also seeked monopolies over trade
Gold (D. Roger)
- Mercantilism policy = a nation’s power depends on its wealth
- Gold instantly increased the wealth of a country & was used to pay off debts → people wanted to search for gold & silver
- Found deposits of gold/silver
- Countries wanted to have a positive balance of trade (more exports than imports
- Imports = foreign goods sent to your country to buy
- Exports = goods sent to another country to sell (make $$$ and power cause of mercantilism)
Spreading Christianity
- Missionaries often traveled with explorers to convert natives
- Sometimes used force (punishment, enslavement, torture, death) or sometimes educated them
Fame
- Explorers wanted to become famous for exploring new lands/trade routes
- Also wanted to bring power & fame to their country by claiming land for their country
- Bartolomeu Dias = Example of a explorer
- Said that he explored “to serve God and His Majesty, to give light to those who were in darkness, and to grow rich as all men desire to do”
- Three Gs - Gold, God, Glory
Technological Advancements for Long Distance Voyaging
- Caravel (square and triangular sails)
- Astrolabe (Muslim) allowed for night navigation
- Magnetic Compass (Chinese)
The Bad Part
- Spoiled food
- Limited freshwater
- Scurvy (lack of vitamin C)
- Rats & water in ships
- last but not least… Death
The Spanish Invade The American Empires
Empires Weakened
- Aztec and Inca were both in the middle of a civil war when Spanish came
- Conquered tribes rebelled in the Aztecs and was too widespread → won few battles
- Moctezuma demands more tribute from conquered tribes → angry tribes
- Two sons of the former Inca ruler fighting for the throne
- Battle between north and south, when one son won the empire was greatly weakened
- Allows for the Spanish to easily conquer the Incas and Aztecs
Hernan Cortes & the Aztec
- Arrived in the year 1519 and was believed by the Aztecs & Moctezuma to be a god because of his pale skin → gave them gold and silver
- Cortes took Moctezuma hostage and demands more gold & silver
- Some natives betrayed their empire & helped them translate Spanish to Mayan to Nahuatl (ancient Aztec language)
- Aztec attempt a rebellion and drive the Spanish out of the Capital but Moctezuma dies & Spanish returned with help of resentful conquered tribes
- Blockaded Tenochtitlan so supplies could not get out or in & epidemic of measles breaks out which kills thousands of Aztecs
- Aztecs surrender & people who survived flee to countryside or become slaves
Francisco Pizzaro & the Inca
- Convinced the Inca that they only wanted to admire the empire
- Pizzaro tries to convert the Inca ruler (Atahualpa) to Christianity & for him to surrender peacefully
- Didn’t work so Spanish attacked and took Atahualpa prisoner and demanded gold & silver
- Killed him after he gave them the gold & silver
- Incan army of 200,000 soldiers was sent to take back the capital city of Cuzco
- Most supplies has been used up in the civil war → attack didn’t last long and had to retreat into the Andes
- Incas fully conquered by 1572 (40 years after Pizzaro arrived)
The Aftermath
- The Spanish were successful in defeating the Aztec and Inca because…
- Smallpox & measles killed many natives or weakened them
- Took advantage of rebellions and resentful conquered tribes to help them learn the territory & add more manpower
- Weapons were more advanced (guns, crossbows, swords, irons spears, cannons, and horses)
- Spanish fought more fiercely because they thought the Aztec & Inca were pagans (held different beliefs) and had to be destroyed
- Different ways of fighting; Aztec & Inca were all about taking captive while Spanish fought to kill
- Nearly 90% of the Aztec & Inca populations destroyed
- Both empires responded differently
- Aztecs: When Tenochtitlan was captured the whole empire gave up since the capital was the most important city
- Conquered tribes were resentful and didn’t feel any allegiance to defend the empire
- Inca: Resisted the Spanish longer because the Inca rulers took better care of the conquered tribes (protection, shelter, food) = spread Inca culture, religion, and language so that tribes felt more like a part of the empire














